Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0430–0469) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: RA-ILD is significant determinants of morbidity and mortality. This study aims to evaluate the demographic and serological characteristics of RA-ILD patients and investigate the relationship with smoking, phenotypic features and lung involvement using HRCT, treatments administered, and parameters affecting mortality.
Methods: We evaluated 65 patients with RA-ILD who showed interstitial changes on HRCT imaging. We collected data on demographics, clinical findings, laboratory results, pulmonary function tests, HRCT images, and treatments from the hospital information system patient records. We analyzed the relationships between disease progression, mortality, and factors such as age, gender, smoking history, serological test results, disease duration, HRCT findings, DAS28-ESR, pulmonary function tests, and treatments.
Results: The study included 65 patients, with a mean age of 67.14 ± 9.52 years. 60% were female and 40% were male. Of the total, 26.2% had died, with 58.8% of these deaths attributed to ILD. Patients who had lung involvement exceeding 20% on HRCT had a significantly higher mortality rate. Serological evaluations showed high positivity rates for RF at 60% and ACPA at 71.4%. The mean duration between diagnoses of RA and ILD was 7.82 ± 10.16 years. The most common HRCT pattern observed was UIP, present in 46.2% of patients, while 32.3% had lung involvement exceeding 20% on HRCT. At the time of ILD diagnosis, 33.3% of patients were in remission, which increased to 71.9% at the final follow-up. The proportion of patients exhibiting high disease activity decreased from 3.5% initially to none at the last evaluation. Additionally, FVC and diffusing capacity of the lungs for DLCO values declined over time, with the final mean DLCO value recorded at 56.69 ± 21.68. In terms of treatment, 90.8% of patients received MTX, 75.4% received HCQ, and 56.9% received RTX.
Conclusion: Our study findings indicating that RA-ILD is more common in older patients, males, seropositive individuals, and with a smoking history. RA-ILD mortality is higher than non-ILD. Among ILD phenotypes, UIP is the most frequently observed pattern, with higher lung involvement percentages in this group. As lung involvement increases, pulmonary function declines, and mortality rises. Consistent with previous studies, no correlation was found between seropositivity, DAS28 score, and ILD phenotype. However, although numerically significant, the finding that patients with high-titer seropositivity may have more extensive lung disease was not statistically significant. In deceased patients, pulmonary function test results were lower, disease activity was higher, and the interval between RA and ILD diagnoses was shorter. Patients with high disease activity at RA diagnosis had lower FVC values at ILD diagnosis, while those in remission had higher FVC values. Patients with UIP and NSIP patterns exhibited greater declines in pulmonary function, with UIP associated with higher mortality. Unlike similar studies, no significant decline in FVC and DLCO values was observed with increased smoking history. Furthermore, in contrast to previous research, no statistically significant relationship was found between TNFi agents and mortality.
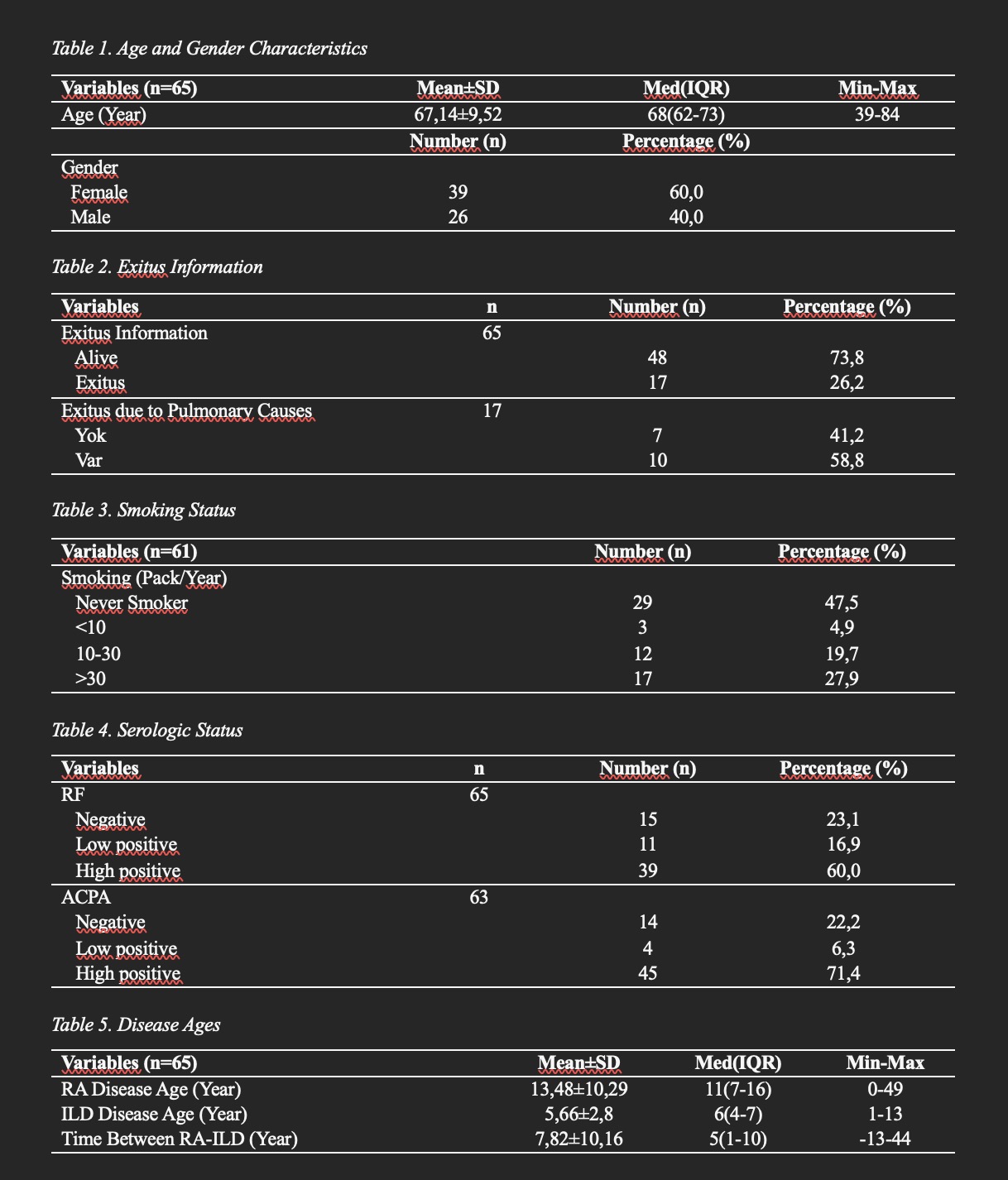 Table 1. Age and Gender Characteristics
Table 1. Age and Gender Characteristics
.jpg) Table 2. FVC and DLCO values at diagnosis and last follow-up According to ACPA positivity
Table 2. FVC and DLCO values at diagnosis and last follow-up According to ACPA positivity
.jpg) Table 3. HRCT Pattern and Involvement Rate According to RF Positivity
Table 3. HRCT Pattern and Involvement Rate According to RF Positivity
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
ŞAhiner f, Nokay M, erbasan f, Yazisiz V, terzioglu E. Retrospective evaluation of the clinical impact of democgraphic , serological , clinical , radiological parameters and treatment modalities in patients with RA-ILD [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/retrospective-evaluation-of-the-clinical-impact-of-democgraphic-serological-clinical-radiological-parameters-and-treatment-modalities-in-patients-with-ra-ild/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/retrospective-evaluation-of-the-clinical-impact-of-democgraphic-serological-clinical-radiological-parameters-and-treatment-modalities-in-patients-with-ra-ild/
