Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Vaccination against SARS-CoV2 has been the primary global strategy to prevent severe forms of this respiratory infection. However, multiple studies have shown that patients undergoing treatment with biological therapies, especially those targeting B lymphocytes, have a poorer response to vaccination. It should be taken into consideration that a lower IgG titer is associated with higher mortality from Covid-19. Objective: To describe the vaccine response rate in patients treated with rituximab (RTX), ocrelizumab (OCR), abatacept (ABT), belimumab (BEL), and compare the response between rheumatic and neurological patients.
Methods: Descriptive study. Rheumatic and neurological patients undergoing treatment with RTX, OCR, ABT, and BEL between January 2020 and July 2022 at the Germans Trias i Pujol Hospital were included. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels against the SARS-CoV2 spike protein were quantified, considering >260 BAU/mL as a positive response to vaccination. Variables such as age, vaccination schedule, recent infection, corticosteroid therapy, or synthetic DMARDs were analyzed. Additionally, clinical-demographic variables and risk factors for severe SARS-CoV2 infection were described.
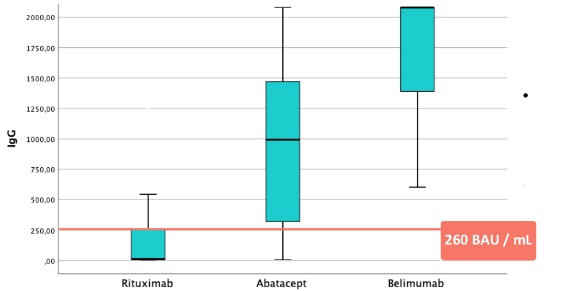
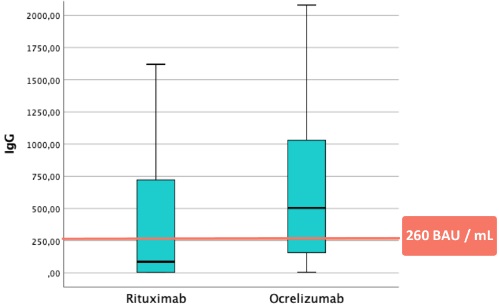
Results: The study included 122 rheumatic patients, of whom 59 received RTX, 45 ABT, and 18 BEL, as well as 17 neurological patients undergoing treatment with OCR and 7 with RTX. The mean age was 51 years, and 72% were women. The most frequent rheumatic diagnoses were rheumatoid arthritis (55), systemic lupus erythematosus (31), small vessel vasculitis (8), among others. All neurological patients had demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis. Concomitant DMARD therapy was received by 48% of the patients studied. 92% of the patients were fully vaccinated (3 or more doses), and 8% had experienced the infection in the previous 3 months. Corticosteroid therapy was received by 49% of the patients, with 92% receiving low-dose corticosteroids. 39% were on DMARDs, with hydroxychloroquine (27%) and methotrexate (19%) being the most common. In rheumatic patients, serology was negative in 40 patients treated with RTX (67%), and 8 with ABT (17%). No patient treated with BEL had negative serology. The median IgG level was 30 BAU/mL in patients undergoing treatment with RTX, 993 BAU/mL with ABT, and 1797 BAU/mL with BEL (p < 0.001) (Fig 1). Regarding negative serology, there were no differences in terms of age (RTX p=0.28, ABT p=0.71), corticosteroid use (RTX p=0.67, ABT p=0.25), or DMARDs (RTX p=0.06, ABT p=0.21). In neurological patients, the median IgG level with OCR was 504 BAU/mL, and with RTX it was 361 BAU/mL, compared to 30 BAU/mL in rheumatic patients with RTX (p 0.005) (Fig 2).
Conclusion: In our cohort, not all patients undergoing biological treatment exhibit the same vaccine response to SARS-CoV2. Patients receiving RTX show the lowest response, followed by ABT. However, all patients treated with BEL had positive serology. Neurological patients treated with B lymphocyte-targeted therapies showed a greater vaccine response than rheumatic patients. No serological differences were observed depending on the use or non-use of DMARDs, age, or low-dose corticosteroid therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Calomarde Gomez C, Ugena García R, Valera J, Mena M, Esteve M, Casas I, Dominguez-Benitez j, Carabias-Ane l, Nuño-Ruiz i, ramo-Tello C, Santesmases J, Mateo Soria L, Martinez Morillo M. Response to Sars-Cov2 Vaccination in Rheumatic and Neurological Patients Treated with Different Immunosuppressive Therapies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-sars-cov2-vaccination-in-rheumatic-and-neurological-patients-treated-with-different-immunosuppressive-therapies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-sars-cov2-vaccination-in-rheumatic-and-neurological-patients-treated-with-different-immunosuppressive-therapies/