Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Avacopan, an oral C5aR antagonist, is approved for the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) as a steroid-sparing alternative. While clinical trials demonstrated a positive benefit/risk ratio, post-marketing surveillance remains essential to assess its real-world safety. Based on its pharmacological activity and on case reports from the literature, we sought to evaluate infectious and hepatic adverse events (AEs) associated with avacopan.
Methods: We used VigiBase, the WHO global pharmacovigilance database, up to April 30, 2025. We analyzed and described individual case safety reports related to infectious and hepatic AEs. Disproportionality analyses were performed using reporting odds ratios (RORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). A signal was considered significant if the lower CI limit exceeded 1.
Results: Of 32.3 million individual case safety reports, 2,775 involved avacopan (median age 62 years, 40.4% female), with 88.3% from North America (Tables 1 and 2). Infectious AEs occurred in 438 cases (15.8%). The median time to onset of infection was 28 days (IQR 7-78). Most cases were considered serious (262, 59.8%), including 130 (29.7%) with hospitalization or prolonged hospitalization, and 41 (9.4%) were fatal. Most frequent reported infections were respiratory tract infections (47%), with COVID-19 (21.9%) and pneumonia (26.9%), urinary tract infections (10.3%) and ENT infections (9.8%). Invasive fungal, CMV and Pneumocystis jiroveci infections were reported in 1.1%, 0.9% and 0.5%, respectively. Hepatic events occurred in 77 cases (2.8%), mainly cytolytic hepatitis (24.1%), with a median time to onset of 47 days (IQR 40-63), and 3 were fatal. No vanishing bile duct syndrome was reported. Disproportionality analysis revealed a significant overreporting of infections (ROR 2.50 [2.25-2.76]) or sepsis (ROR 2.37 [1.69-3.30]) compared to all treatments in VigiBase, but not compared to immunosuppressants (ROR 0.78 [0.70-0.86] and ROR 1,02 [0,73-1,42], respectively), with even a significant underreporting of infections with avacopan (Table 3).
Conclusion: This study based on VigiBase characterizes the profile of infectious AEs reported with avacopan, which does not appear to differ from the known profile of infections in AAV patients. Avacopan was not associated with an increased risk of reporting of infections compared to immunosuppressants. These data, while reassuring, are preliminary and highlight the need for continued post-marketing surveillance to confirm the long-term safety profile of avacopan.
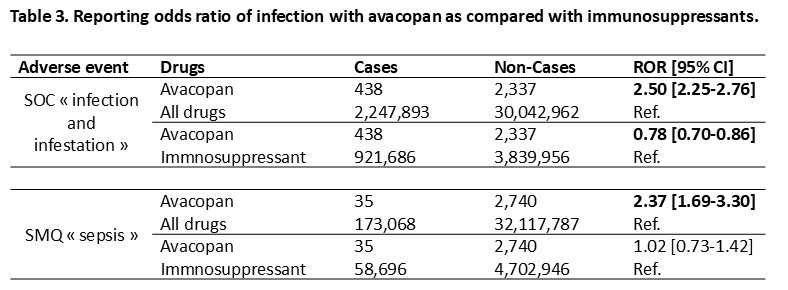 Note: Data are presented as N (%) or median [IQR].
Note: Data are presented as N (%) or median [IQR].
Abbreviations: AE Adverse event; a Patients could enter different categories.
.jpg) Note: Data are presented as N (%).
Note: Data are presented as N (%).
Abbreviations: a Patients could enter different categories.
.jpg) Footnote: “Cases” were safety reports including an infectious adverse reaction identified using the System Organ Class (SOC) “Infections and infestations”, and Standardised MedDRA Queries (SMQ) “Sepsis” (MedDRA, https://www.meddra.org/). Comparators were all drugs and immunosuppressants drugs (ATC code L04).
Footnote: “Cases” were safety reports including an infectious adverse reaction identified using the System Organ Class (SOC) “Infections and infestations”, and Standardised MedDRA Queries (SMQ) “Sepsis” (MedDRA, https://www.meddra.org/). Comparators were all drugs and immunosuppressants drugs (ATC code L04).
ROR (95% CI) were calculated as adbc ( adbc. e ±1.961a+1b+1c+1d), where a is the number of cases reported with avacopan, b is the number of non-cases (i.e., all other adverse drug reactions reports) reported with avacopan, c is the number of cases reported with all other drugs and d is the number of non-cases reported with all other drugs. Threshold for signal detection is defined as a ROR lower boundary 95% confidence interval ≥1 and a number of cases ≥3. Significant associations (adverse event-drug combination) are presented in bold.
Abbreviations: Ref., reference; ROR, reporting odds ratio; SMQ, Standardised MedDRA Queries; SOC, System Organ Class,
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mettler C, Chouchana L, Terrier B. Reporting of infectious and hepatic adverse events with avacopan: insights from the World Health Organization pharmacovigilance database (VigiBase) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reporting-of-infectious-and-hepatic-adverse-events-with-avacopan-insights-from-the-world-health-organization-pharmacovigilance-database-vigibase/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reporting-of-infectious-and-hepatic-adverse-events-with-avacopan-insights-from-the-world-health-organization-pharmacovigilance-database-vigibase/
