Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment I: Nephritis
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Renal Activity In Lupus (RAIL) Urinary Biomarkers Predict Treatment Response
Background/Purpose: We have previously demonstrated the strong predictive value of the Renal Activity In Lupus (RAIL) algorithm, using 6 urinary biomarkers (UBMs), in children (RAIL) and adult (A-RAIL) populations. The purpose of the present study was to prospectively study these six UBMs in relation to the response to therapy for lupus nephritis.
Methods: Patients with a diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) with new biopsy proven class III/IV lupus nephritis were enrolled. In addition to routine lab work, including anti-dsDNA antibody levels, complement levels, and urinalysis, the patientsÕ serial urine samples were collected during the 12 months of treatment with immunosuppressive medications. The six RAIL biomarkers, namely neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL), ceruloplasmin (CP), kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM 1), monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP 1), adiponectin (ADIPO) and hemopexin (HPX), were measured longitudinally using standardized ELISA-based assays during the patientsÕ course. Patients were treated with standard induction regimen using cyclophosphamide versus mycophenolate mofetil, and categorized as responders or non-responders, based on the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) lupus nephritis response criteria. Longitudinal patterns of RAIL biomarkers were assessed and compared between visits (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months) and groups (Responders versus Non-responders) using mixed effect models.
Results: A total of seventy-two patients were enrolled in this longitudinal prospective study, with 32 responders and 40 non-responders. About 80 percent in each group were females, and non-Caucasian race was predominant (13 out of 32 responders; 19 out of 40 non-responders, respectively). At 6 month follow up since induction therapy, all 6 UBMs showed significantly lower levels among responders when compared to non-responders (Figure 1). The differences were also significant for all except NGAL at 3 month follow up. At 12 months of treatment, the responders and non-responders did not continue this trend and differences in biomarkers became largely non significant, except NGAL and HPX, which showed significant differences.
Conclusion: The RAIL UBMs demonstrate strong value in predicting response to therapy, can be used as a reliable surrogate in predicting treatment response, and will be highly valuable in making therapeutic changes and clinical decisions. 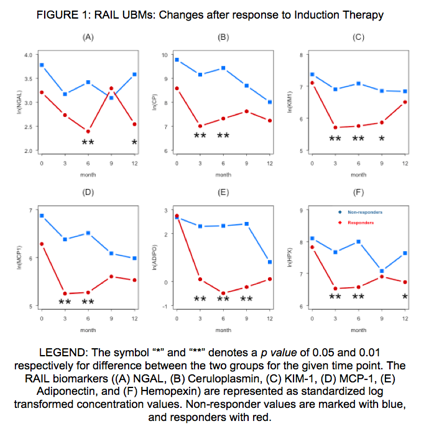
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gulati G, Bennett M, Abulaban K, Ma Q, Klein-Gitelman MS, Rouster-Stevens KA, Haffner C, Wiley K, Ardoin SP, Ying J, Devarajan P, Brunner HI. Renal Activity in Lupus (RAIL) Urinary Biomarkers Predict Treatment Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/renal-activity-in-lupus-rail-urinary-biomarkers-predict-treatment-response/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/renal-activity-in-lupus-rail-urinary-biomarkers-predict-treatment-response/
