Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Inflammatory rheumatic disease (IRD) related fatigue is pervasive and disabling, even in otherwise stable disease. Although cognitive-behavioural approaches (CBAs) and personalised exercise programmes (PEP) are considered effective treatments, rheumatology services encounter significant implementation barriers: 1) existing interventions have not been standardised and tested across the range of IRDs managed by rheumatology 2) the requisite specialist expertise does not commonly exist within rheumatology multi-disciplinary teams (MDT) 3) regular face to face sessions are often undesirable for patients, especially during a pandemic.
This is the first study to test remotely delivered CBA and PEP, by the rheumatology MDT, across IRDs.
Methods: A multicentre, three-arm randomised controlled trial of usual care (UC) alongside telephone delivered CBA or PEP were tested against UC alone. UC typically comprised a fatigue self-management education booklet. Patients with any stable (unaltered immunomodulatory therapy for ≥3 months), physician diagnosed IRD were considered eligible if they reported significant (≥6 on numeric rating 0-10 scale, NRS) and persisting (≥3 months) fatigue. CBA and PEP was delivered by members of the rheumatology MDT, who received specialist training and supervision. Patients received up to 7 sessions across 14 weeks with a booster session at 6 months. Primary outcomes were fatigue severity (Chalder Fatigue Scale, CFS) and impact (Fatigue Severity Scale, FSS) at 12 months. Secondary outcomes included depression (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale), pain (NRS), sleep disturbance (Jenkins) and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPA-I), also at 12 months. Generalized linear mixed models were used to compare the effectiveness of active therapies versus UC following an Intention-To-Treat approach. Results are expressed as mean difference (md) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI).
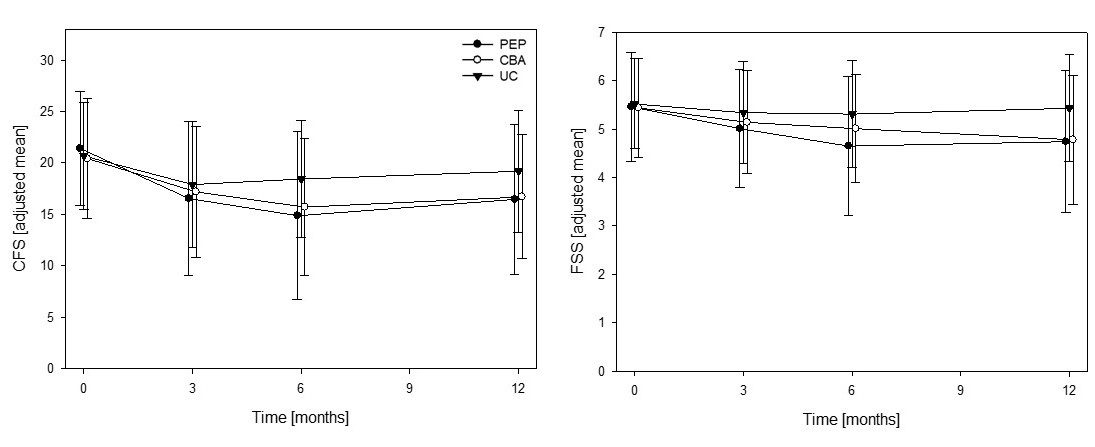
Results: 368 IRD patients (55% rheumatoid arthritis, 21% connective tissue disease, 19% spondyloarthritis, 5% other IRD) were randomised. Baseline characteristics were similarly distributed across the trial arms (table 1). 73% and 85% completed PEP and CBA respectively and primary outcome data was available for 77% of all patients. PEP and CBA significantly improved fatigue severity (CFS md -2.9, 95% CI [-4.6, -1.2], p=0.001 and md -2.5, 95% CI [-4.01, -0.8], p=0.003, respectively) and fatigue impact (FSS md -0.6, 95% CI [-0.9, -0.3], p< 0.001 and md -0.6, 95% CI [-0.8, -0.3], p< 0.001, respectively) compared to UC alone at 12 months (figure 1). Both PEP and CBA also improved sleep (Jenkins md -1.3, 95% CI [-2.56, -0.1] and -1.8, 95% CI [-3.0, -0.6], respectively), while PEP further improved depression (HADS md -1.0, 95% CI [-1.7, -0.2]) and overall work impairment (WPAI md -14.1, 95% CI [-26.7, -1.4]) (table 2).
Conclusion: Telephone delivered CBA and PEP provided statistically and clinically significant reductions in fatigue severity and impact for a wide range of stable IRD patients. The benefit was maintained for 6 months following treatment completion and was successfully delivered by members of the rheumatology MDT after specialist training.
†Ordinal data: N n(%)
Data are shown as adjusted means (sd). All models adjusted for their baseline outcome measure, HADS depression subscale >10 at baseline as fixed effects fixed effect with Centre clustering and individuals nested within Centre’s as random effects. PEP, personalised exercise programme; CBA, cognitive-behavioural approach; UC, usual care; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale;
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bachmair E, Martin Remmes K, Aucott L, Dures E, Emsley R, Gray S, Kidd E, Kumar V, Lovell K, MacLennan G, McNamee P, Norrie J, Paul L, Packham J, Ralston S, Siebert S, Wearden A, Macfarlane G, Basu N. Remotely Delivered Cognitive Behavioural and Personalised Exercise Interventions Reduce Fatigue Severity and Impact in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: Results from a Multi-centre Randomised Controlled Parallel Group Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/remotely-delivered-cognitive-behavioural-and-personalised-exercise-interventions-reduce-fatigue-severity-and-impact-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-results-from-a-multi-centre-randomised-controlle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/remotely-delivered-cognitive-behavioural-and-personalised-exercise-interventions-reduce-fatigue-severity-and-impact-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-results-from-a-multi-centre-randomised-controlle/