Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of rare, debilitating systemic diseases characterized by proximal muscle weakness, which limit activities of daily living and lower health-related quality of life. Patient’s assessment of physical functional status is a core outcome measure in IIM contributing to treatment decisions and the FDA has strongly endorsed development and validation of patient-reported outcomes as critical measures in rheumatic diseases. Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) is a validated, patient-reported outcome measure developed by the NIH, but it has not been studied in adult IIM. Currently, the most commonly used PRO in IIM is Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ-DI), which has several limitations. PROMIS-physical function-20 (PF-20) offers several superior features over HAQ related to clarity of questions, improved items, computer adaptive options and allowing comparison across different disease states. In this study, we investigated reliability, validity and responsiveness of PROMIS PF-20 in patients with IIM compared to HAQ-DI by employing a longitudinal prospective study design.
Methods: Patients with IIM [dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), necrotizing myopathy (NM) or anti-synthetase syndrome] completed PROMIS PF-20 as well as 6 myositis core set measures [manual muscle testing (MMT), physician global disease activity (MD-GDA), patient global disease activity (PT-GDA), extra-muscular global disease activity (EM-GDA), HAQ-DI and creatine kinase (CK)], SF-36 and 3 functional measures [six-minute walk (6MWD), timed up-and-go (TUG) and sit-to-stand tests (STS)] at baseline, 3 and 6 months. PROMIS PF-20 consists of 20 items. Each item is scored on a 5-point rating scale, with higher scores indicating better functioning (0-100). HAQ-DI consists of 20 items. Each item is scored on a 4-point scale with higher scores indicating worse functioning (0-3). Physician-reported change and total improvement score (TIS) using 2016 ACR/EULAR myositis response criteria were obtained at each visit as measures of change.
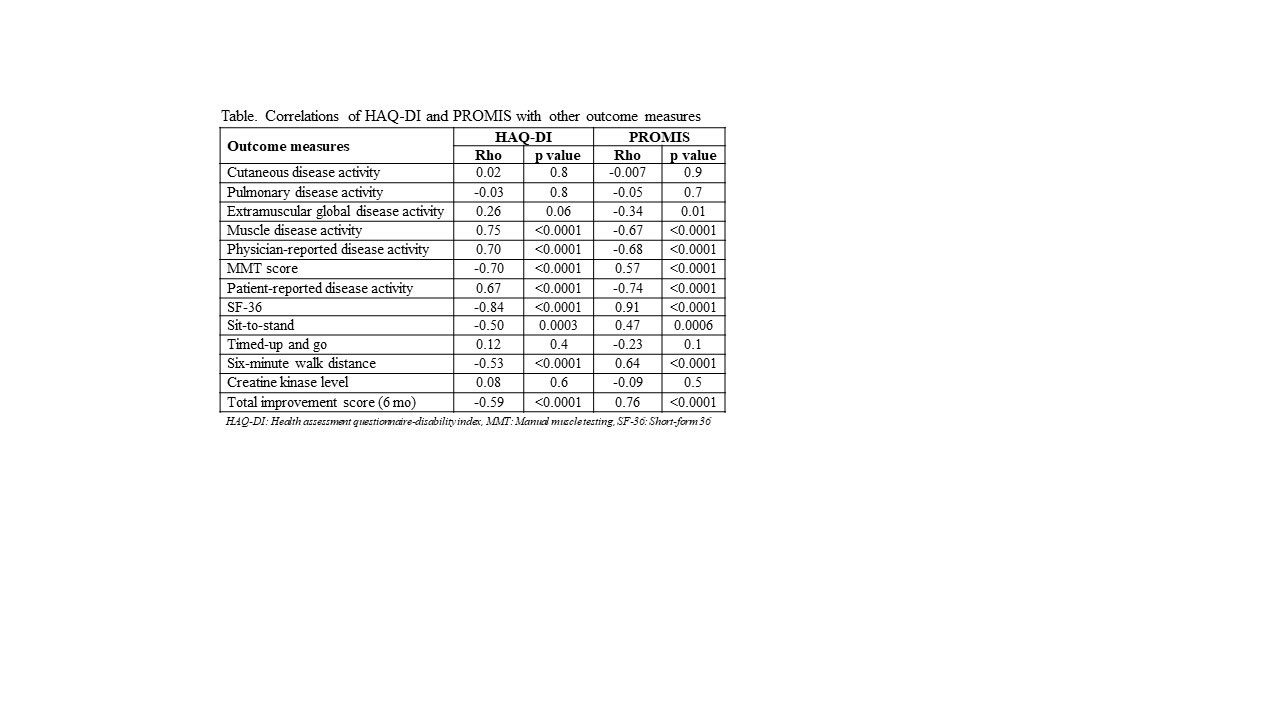
Results: Fifty patients [mean age, 53.6 (±14.6); 60% females] were studied; 11 PM, 28 DM, 7 NM and 4 with anti-synthetase syndrome. PROMIS PF-20 showed strong test-retest reliability when repeated in 1 month in stable patients (Rho:0.9, p< .0001). PROMIS PF-20 at baseline correlated strongly with MD-GDA, PT-GDA, MMT, HAQ-DI, SF-36, and 6MWD and moderately with STS and weakly with EM-GDA (Figure). There was no correlation with cutaneous and pulmonary disease activity, TUG, and CK levels. Longitudinal change in PROMIS PF-20 strongly correlated with TIS (Rho:-0.8, p< .0001) at 6 months and showed significant differences between physician-reported change demonstrating excellent responsiveness (p< .0001). HAQ and PROMIS-20 showed similar correlations with other outcome measures, however changes in PROMIS-20 over 6 months had stronger correlations with TIS which may indicate better responsiveness (Table).
Conclusion: PROMIS PF-20 demonstrates good test-retest reliability, construct validity and responsiveness in a large cohort of patients with IIM and could replace the HAQ-DI as a core-set measure in myositis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saygin D, Oddis C, Neiman N, Koontz D, Moghadam-Kia S, Aggarwal R. Reliability, Validity and Responsiveness of PROMIS PF-20 in Patients with Inflammatory Myopathy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-validity-and-responsiveness-of-promis-pf-20-in-patients-with-inflammatory-myopathy/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-validity-and-responsiveness-of-promis-pf-20-in-patients-with-inflammatory-myopathy/