Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with AS often experience impaired work productivity.1 In pts with AS receiving tofacitinib (oral Janus kinase inhibitor), improvements were observed in work productivity, activity impairment, and other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) 2,3; however, the relationships between these have not yet been quantified. This post hoc analysis examined these relationships in pts with AS.
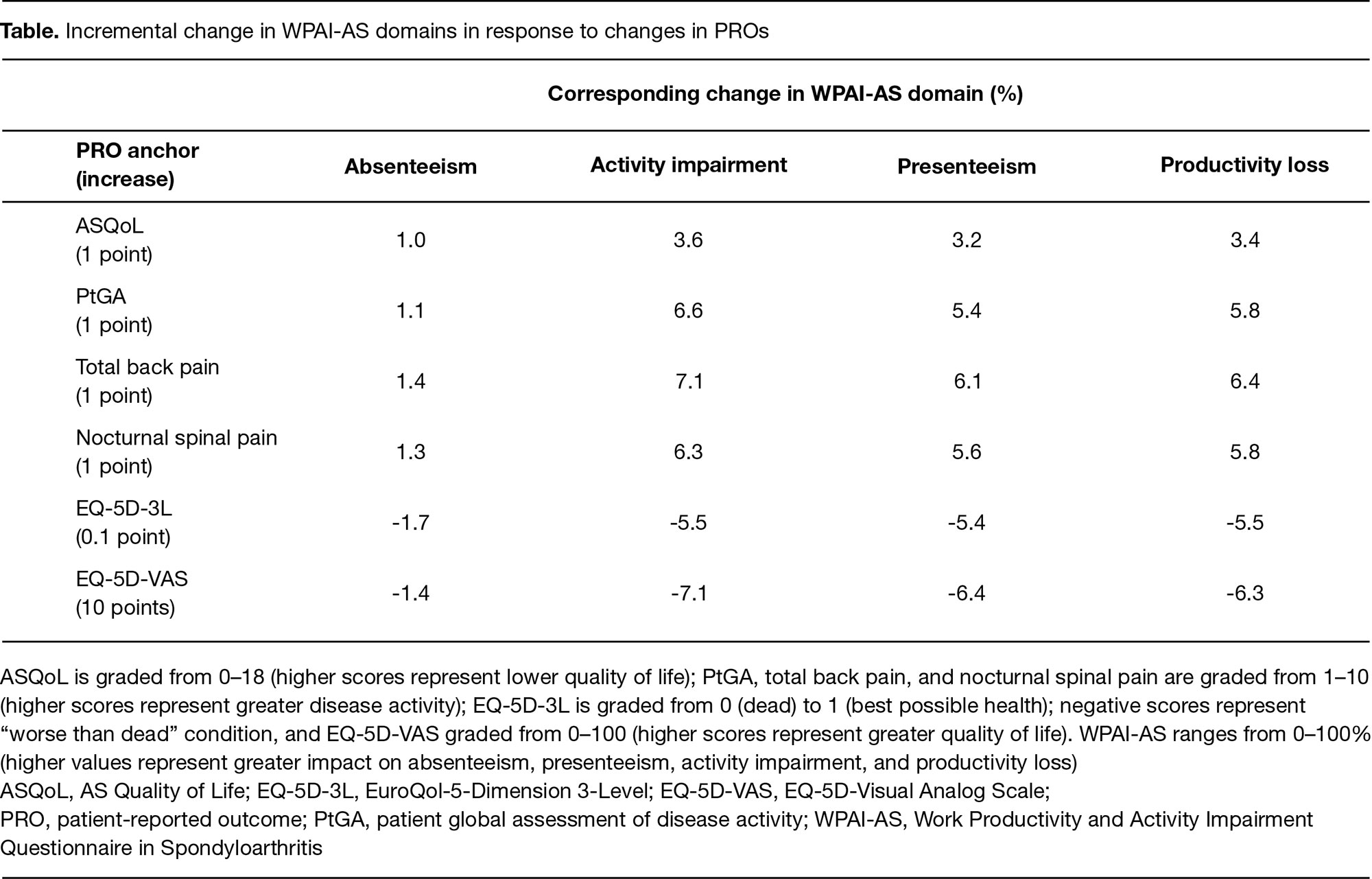
Methods: Data were pooled from two placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind studies in pts with active AS receiving tofacitinib 2, 5, or 10 mg twice daily or PBO (Phase [P]2: NCT017866683; P3: NCT035026162). In the trials, work performance was evaluated by the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire in Spondyloarthritis (WPAI-AS). A repeated measures model assessed relationships between select PROs (AS Quality of Life [ASQoL], Pt Global Assessment of Disease [PtGA], pt assessment of total back pain and nocturnal spinal pain, and EuroQol-5-Dimension 3-Level [EQ-5D-3L] and EQ-5D-Visual Analog Scale [EQ-5D-VAS]) as predictors (anchors), and WPAI-AS domains (absenteeism, presenteeism, activity impairment, and productivity loss) as outcomes at baseline and Week (W)12/W16 (P3 study only), using the anchors as continuous variables; imposing a linear relationship between anchor and outcome. Available data from all treatment groups and time points were pooled. Incremental change analysis quantified the change of the WPAI-AS domains associated with 1 point (ASQoL, PtGA, total back pain, nocturnal spinal pain), 0.1 point (EQ-5D-3L), or 10 point (EQ-5D-VAS) change in PROs. Sensitivity analyses were performed using the anchors as categorical variables (no functional relationship imposed).
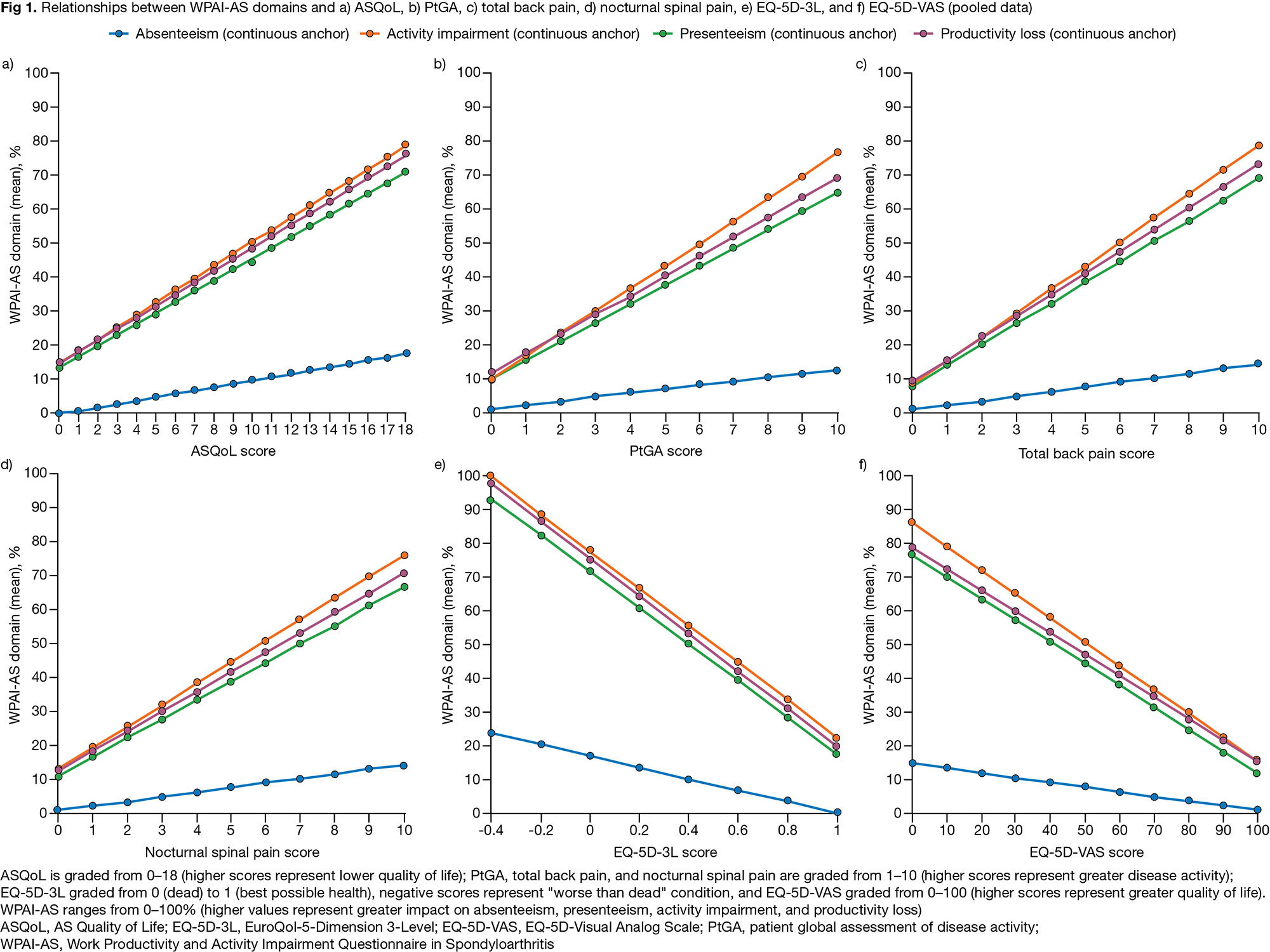
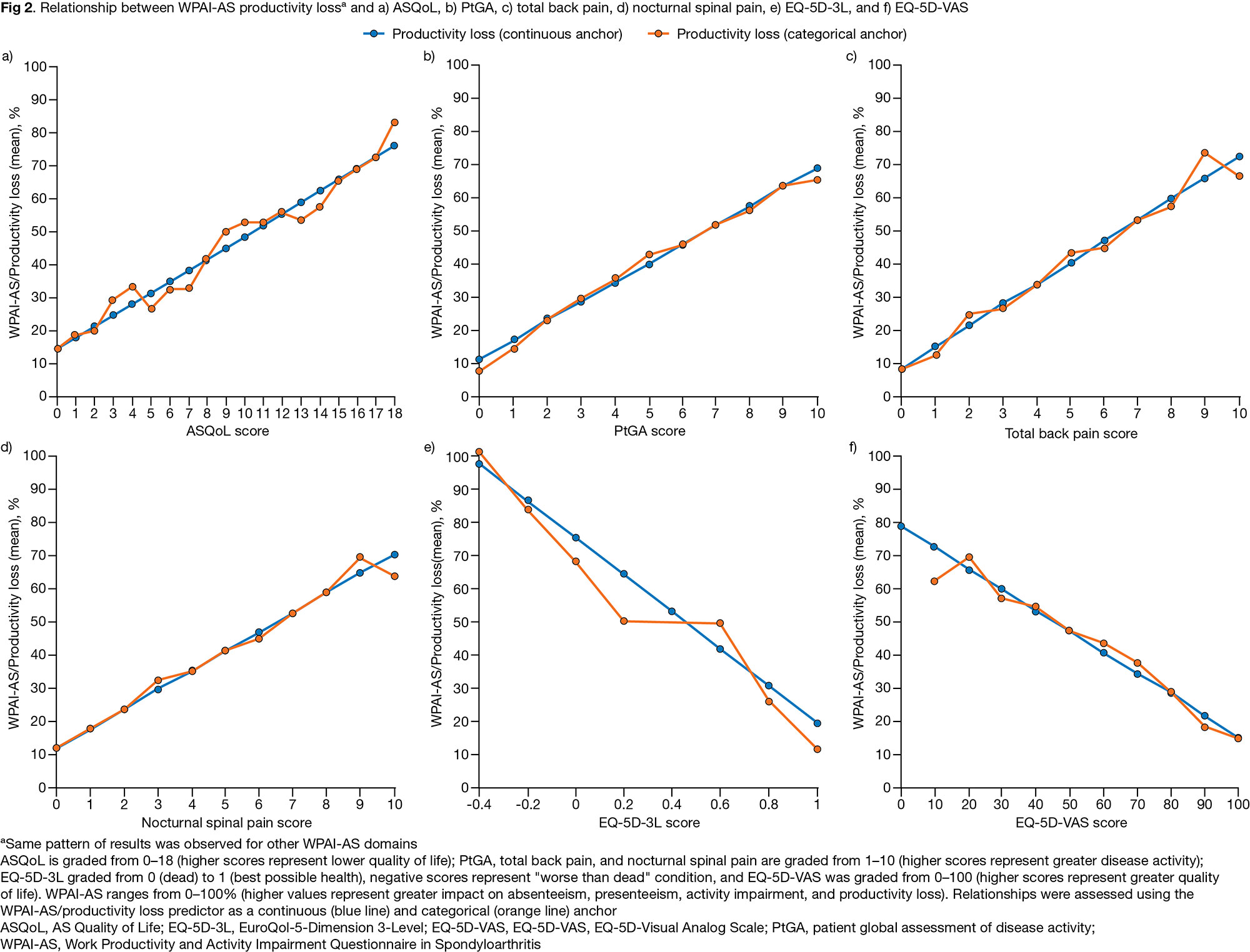
Results: Data from 330–475 pts were available, depending on the analysis. Approximately linear relationships were observed between PROs and WPAI-AS domains (Fig 1). Worst PRO scores were associated with a decline in pts’ work capacity (measured by presenteeism, productivity loss, and activity impairment [ > 65%]); best PRO scores were associated with improvements in WPAI-AS domains (8–23%) (Fig 1). Relationships between PROs and absenteeism were the weakest owing to absenteeism being low (Fig 1). Incremental worsening in PROs resulted in increased absenteeism, activity impairment, presenteeism, and productivity loss; incremental improvement in EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-VAS resulted in decreases in the WPAI-AS domain scores (Table). Sensitivity analysis confirmed the results of the models (Fig 2; same pattern observed for all WPAI-AS domains).
Conclusion: Evidence for linear relationships between PROs and WPAI-AS domains was observed; these were weakest for absenteeism. Interventions that control disease activity and pain are therefore likely to improve work productivity and reduce activity impairment in pts with AS.
1. Nikiphorou & Ramiro. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2020; 22: 55
2. Deodhar et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80: 1004–13
3. van der Heijde et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2017; 76: 1340–7
Study sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support was provided by C Zauchenberger, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Magrey M, WEI J, Yndestad A, Bushmakin A, Cappelleri J, Dina O, Deodhar A. Relationships Between Work Productivity, Activity Impairment, and Select Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Post Hoc Analysis of Two Placebo-Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationships-between-work-productivity-activity-impairment-and-select-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-placebo-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationships-between-work-productivity-activity-impairment-and-select-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-placebo-controlled-trials/