Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: The dynamics of monosodium urate (MSU) crystal changes across a range of serum urate concentrations in people with gout are unknown. The aim of this study was to systematically examine the relationship between serum urate and changes in dual energy computed tomography (DECT) urate volume in people with gout and stable serum urate concentrations.
Methods: Individual participant data were analysed from three studies of people with gout. The time periods for the analysis were selected to identify study participants with serial DECT scans of both feet over a 12-month epoch of stable urate-lowering therapy and serum urate concentrations. Data from 251 study participants were analysed using a mixed-models analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) approach according to mean serum urate cut-points and mean serum urate bands. Study and first DECT urate volume were included in the models.
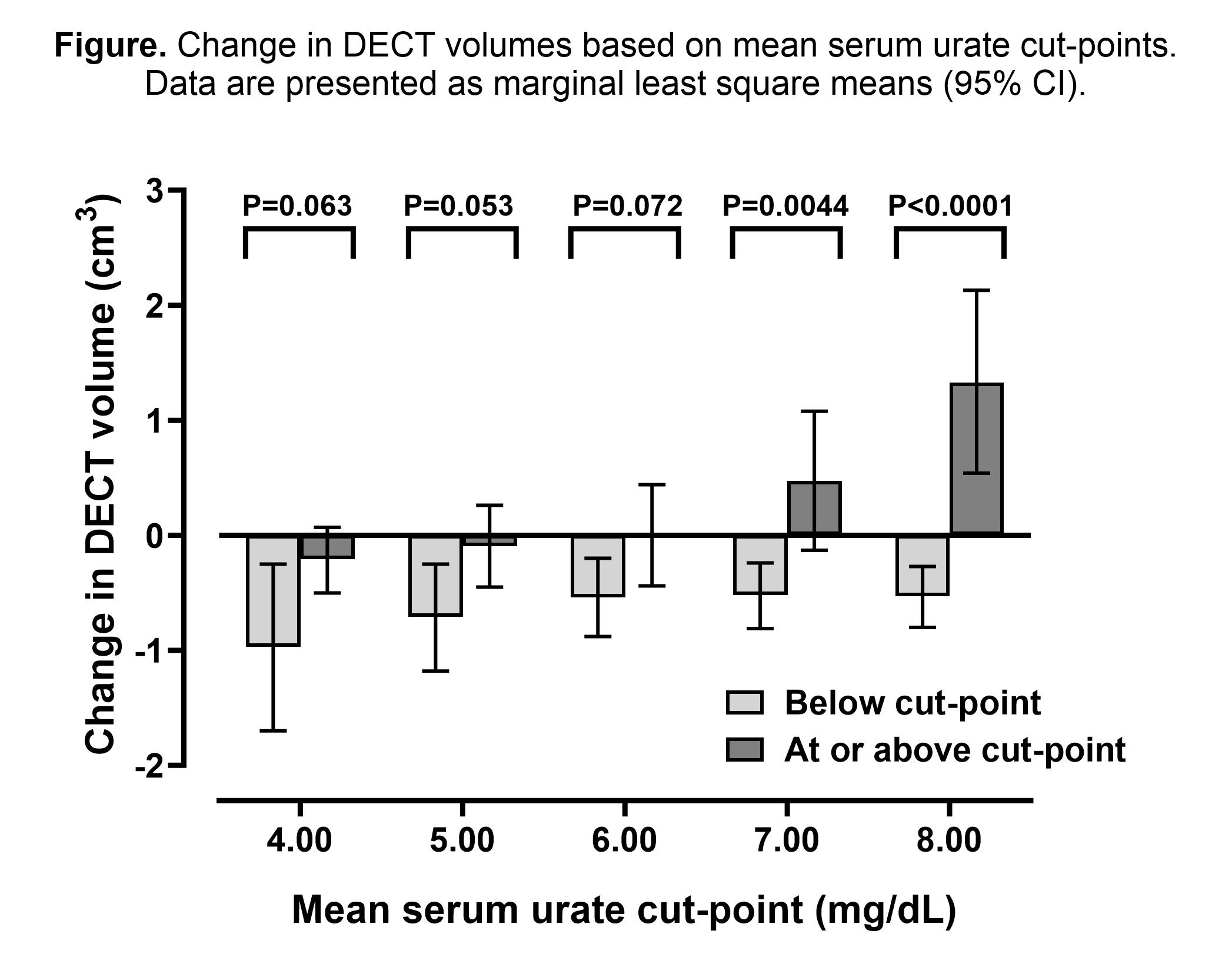
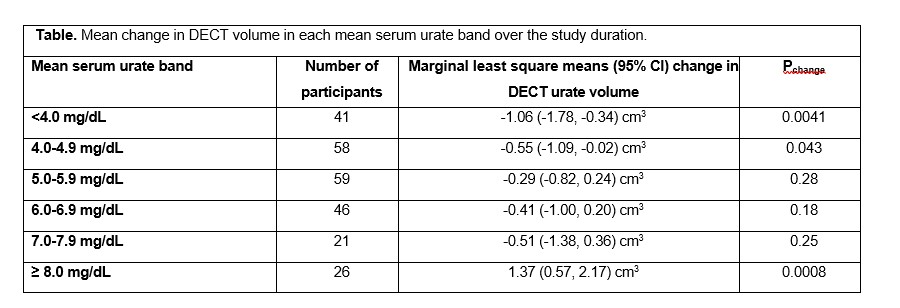
Results: For all mean serum urate cut-points assessed (4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0 and 8.0 mg/dL), reductions in DECT urate volumes were observed below the cut-point (Figure). Significantly increased DECT urate volumes were observed at or above the 8.0mg/dL mean serum urate cut-point. Differences in the change in DECT volume were observed for the 7.0 mg/dL cut-point (P=0.0044) and the 8.0 mg/dL cut-point (P< 0.0001). Significantly reduced DECT urate volumes were observed for the mean serum urate bands < 4.0 mg/dL and 4.0-4.9 mg/dL, and increased DECT urate volume was observed for the mean serum urate band ≥ 8.0 mg/dL (Table). For the mean serum urate bands 5.0-5.9, 6.0-6.9, 7.0-7.9 mg/dL, significant changes in DECT urate volumes were not observed.
Conclusion: The study findings support the concept that different serum urate targets may be appropriate at different stages of gout treatment. Serum urate bands below 5.0 mg/dL lead to MSU crystal dissolution over one year. Once MSU crystal dissolution is achieved, a higher target may be sufficient to prevent crystal formation; this study indicates that the higher target may be < 7.0 mg/dL. The study also provides empirical support for the EULAR recommendation of early use of urate-lowering therapy for patients with serum urate > 8.0 mg/dL, noting the increased MSU crystal volume at or above this level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kelly B, Gamble G, Horne A, Doyle A, Drake J, Aati O, Son C, Kalluru R, Latto K, Stamp L, Dalbeth N. Relationship Between Serum Urate and Changes in Dual Energy Computed Tomography MSU Crystal Volume over One Year in People with Gout: An Individual Participant Data Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-serum-urate-and-changes-in-dual-energy-computed-tomography-msu-crystal-volume-over-one-year-in-people-with-gout-an-individual-participant-data-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-serum-urate-and-changes-in-dual-energy-computed-tomography-msu-crystal-volume-over-one-year-in-people-with-gout-an-individual-participant-data-analysis/