Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Bugs & Drugs (0980–0983)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-2:15PM
Background/Purpose: Paraoxonase-1 (PON1) is a high-density lipoprotein-associated enzyme with paraoxonase, lactonase, and arylesterase activities.1 PON1 gene polymorphisms at the Q192R allele (rs662) have been associated with a reduced risk of cancers, although larger samples are needed to confirm any prognostic role.1,2 This post hoc analysis investigates the relationship between PON1 genotype/activity and risk of malignancies in the tofacitinib RA clinical program.
Methods: Data were pooled from patients (pts) enrolled in 9 Phase 2/3 studies of tofacitinib in RA (completed by March 31, 2015). Enzyme activities in pt plasma samples were measured at individual study baseline (BL), and at follow‑up visits, using 3 substrates: paraoxon (paraoxonase activity), dihydrocoumarin (lactonase activity), and phenylacetate (arylesterase activity). The effect of the PON1 Q192R genotype (QQ, QR, or RR) on BL paraoxonase/lactonase/arylesterase activity was assessed using linear regression for each study, with age and sex as covariates; a fixed‑effects meta-analysis assessed effects across studies. The risk of malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), and NMSC events by enzyme activity, was determined using Cox proportional hazards regression, stratified by clinical studies. Univariate regression against BL enzyme activity and other risk factors, as well as both minimally and fully adjusted multivariable regressions against time-varying enzyme activity, are presented.
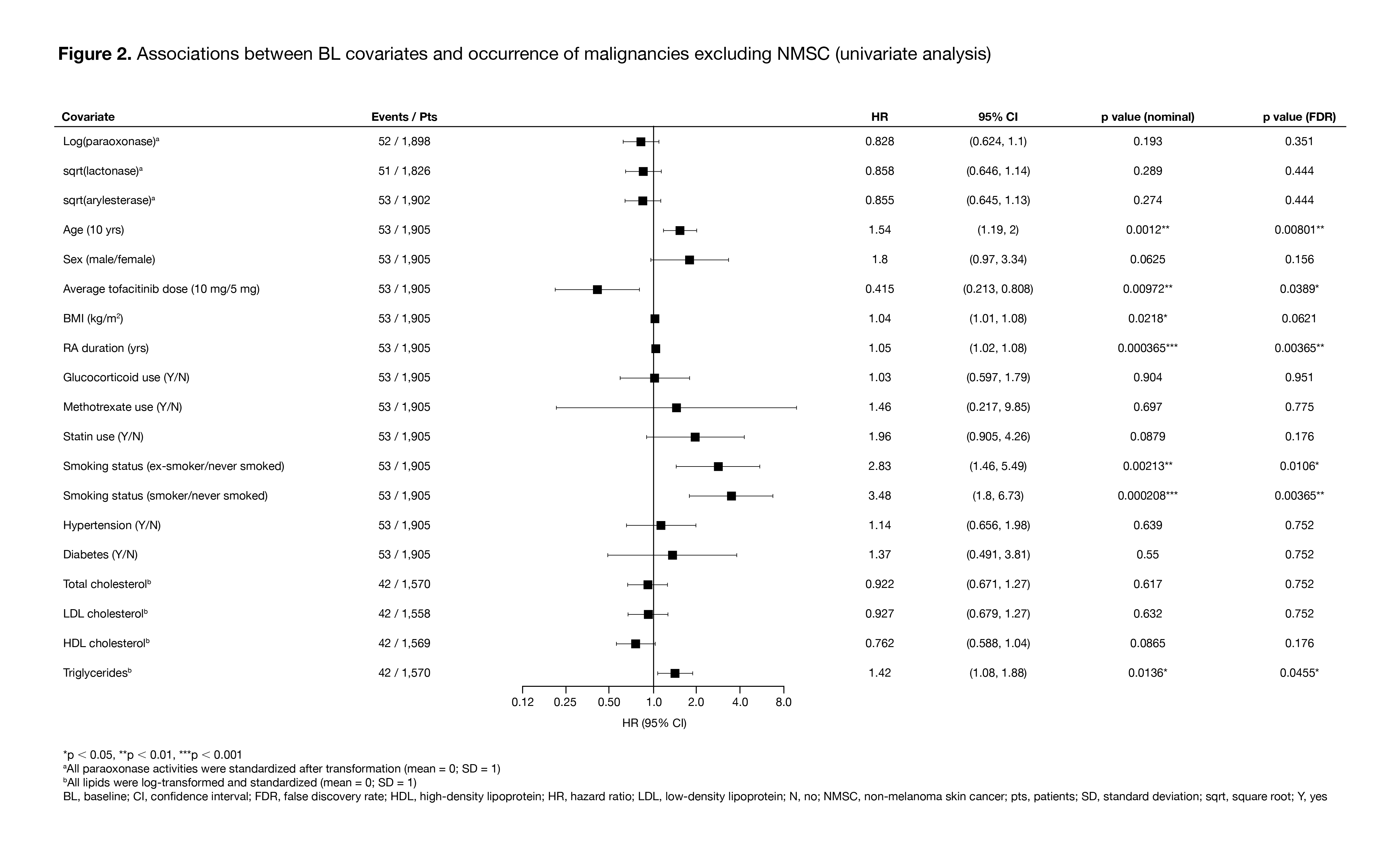
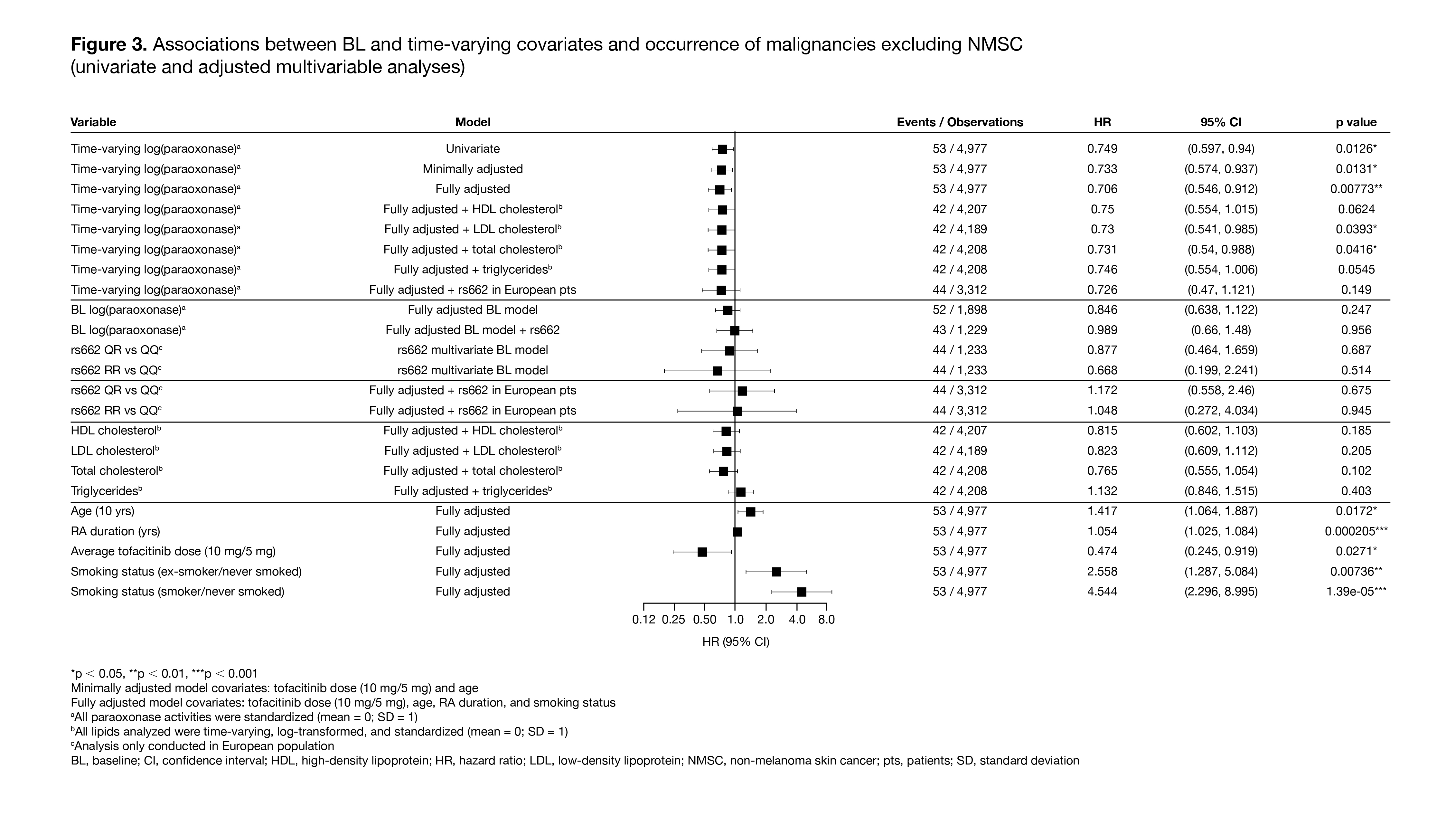
Results: The analysis included 1,969 pts with RA who received ≥ 1 dose of tofacitinib and had ≥ 1 PON1 activity measure available at BL; 53 pts had ≥ 1 malignancy event excluding NMSC, and 56 pts had ≥ 1 NMSC event. Compared with the QQ genotype, the RR genotype had a highly significant positive association with BL paraoxonase activity, and a highly significant negative association with BL lactonase and arylesterase activity (Figure 1). In the univariate analysis, age, RA duration, and smoking status (‘ex-smoker/never smoked’) were identified as risk factors for both malignancies excluding NMSC (Figure 2) and NMSC (data not shown). Time-varying models found a highly significant association of increased paraoxonase activity over time with lower risk of future malignancies excluding NMSC (Figure 3), but not with NMSC events (data not shown), even after controlling for risk factors including RA duration, age, and smoking status. No such trend was observed for lactonase and arylesterase for malignancies excluding NMSC or for NMSC events (data not shown).
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis, higher paraoxonase activity over time was associated with a significantly reduced risk of future malignancies excluding NMSC in pts with RA receiving tofacitinib, after controlling for risk factors such as RA duration, age, and smoking. Based on these findings, further investigation of PON1 as a novel functional lipid biomarker to assess malignancy risk in pts with RA is warranted.
1. Mackness M & Mackness B. Gene 2015; 567: 12-21
2. Pan X et al. Biomed Res Int 2019: 2019: 5897505.
Acknowledgments:Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by K Irving and E Finn, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Charles-Schoeman C, Hyde C, Guan S, Parikh N, Wang J, Shahbazian A, Stockert L, Andrews J. Relationship Between Paraoxonase-1 Genotype, Activity, and Malignancies in Patients with RA Receiving Tofacitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-paraoxonase-1-genotype-activity-and-malignancies-in-patients-with-ra-receiving-tofacitinib/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-paraoxonase-1-genotype-activity-and-malignancies-in-patients-with-ra-receiving-tofacitinib/