Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Urinary CD163 is a macrophage marker which correlates with histological activity index and response to treatment in lupus nephritis (LN), as evidenced by urine proteomic analyses in at least two independent cohorts. We investigated whether this finding could be confirmed in the BLISS-LN trial.
Methods: A total of 54 BLISS-LN (Furie et al., NEJM 2020) participants with biopsy-proven LN were included in this study. LN response status was determined at Week 52 based on proteinuria < 500 mg/mg, serum creatinine no greater than 1.25 times the Week 0 value, and prednisone dosage of no greater than 10 mg per day. Note that this response definition was specific to this series and differed from the BLISS-LN endpoints, which were not available. Urine samples were collected at Week 0 (time of randomization), Week 24, and Week 52, and 1,000 urinary proteins including CD163 were quantified using antibody microarrays (Raybiotech Kiloplex) at each time point and normalized using urine creatinine. The abundance of each urinary protein was compared in complete responders (n = 31) versus non-responders (n = 22) at each time point using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons with a false discovery rate (FDR) of 5%. One participant was excluded from analysis due to missing the clinical information required to determine response status.
Results: By Week 52, CD163 was the urine protein with the most significant difference in abundance between complete responders (median 1.8 pg/mg, IQR 0.8-2.6 pg/mg) versus non-responders (median 8.3 pg/mg, IQR 4.0-48.4 pg/mg) with a p value of 0.0004 after adjustment for multiple comparisons (Figure 1). This divergence in CD163 abundance was also observed at Week 24 though at a lower degree of significance between complete (median 3.5 pg/mg, IQR 1.1-10.4 pg/mg) and non-responders (median 17.4 pg/mg, IQR 6.2-36.1 pg/mg; adjusted p value = 0.07). CD163 versus time is shown in Figure 2, demonstrating a longitudinal reduction in both groups, but with a more robust reduction in CD163 in complete responders. All of the above findings were similarly found within both the belimumab and standard of care treatment subgroups (not shown).
Conclusion: Longitudinal reduction in urinary CD163 abundance was strongly associated with complete response (per the definition used in Methods) in the BLISS-LN trial. These results are consistent with our previous findings in the Accelerating Medicines Partnership SLE project and also those of Mejia-Vilet et al. (J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020), and support the potential use of specific urinary biomarkers such as CD163 as noninvasive measures of lupus nephritis response.
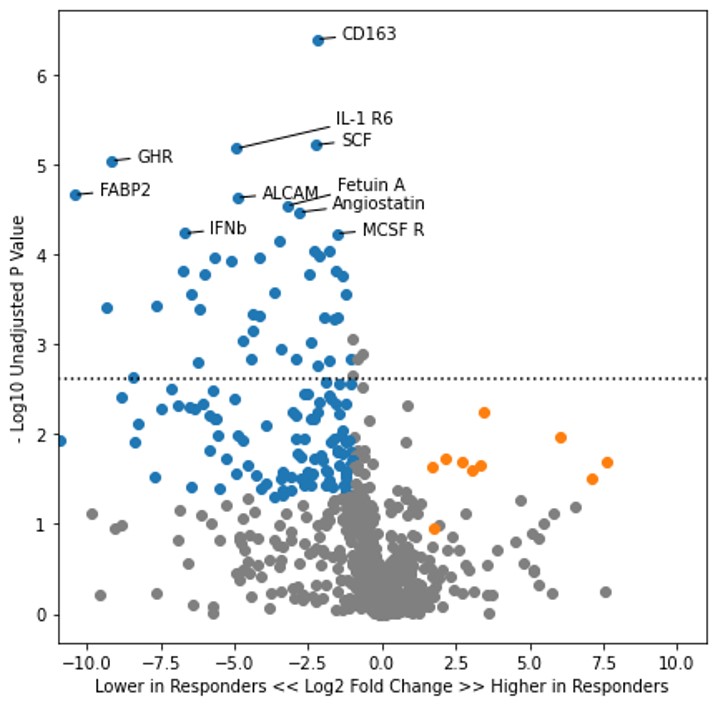 Figure 1. Volcano plot of urinary proteins at Week 52 in the complete responders versus non-responders. Points in blue represent proteins which were lower in the complete response group with an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. Points in orange represent proteins which were higher in the complete response group with an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. The dashed line is the p value threshold for a false discovery rate of 5%.
Figure 1. Volcano plot of urinary proteins at Week 52 in the complete responders versus non-responders. Points in blue represent proteins which were lower in the complete response group with an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. Points in orange represent proteins which were higher in the complete response group with an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. The dashed line is the p value threshold for a false discovery rate of 5%.
 Figure 2. Abundance of CD163 over time in complete responders and non-responders. Each symbol represents one participant’s CD163 value at the given time, and the lines represent the median CD163 value per response group at each time point.
Figure 2. Abundance of CD163 over time in complete responders and non-responders. Each symbol represents one participant’s CD163 value at the given time, and the lines represent the median CD163 value per response group at each time point.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weeding E, Fava A, Mohan C, Goldman D, Petri M. Reduction in Urinary CD163 Is Associated with Treatment Response in the Belimumab Lupus Nephritis Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-in-urinary-cd163-is-associated-with-treatment-response-in-the-belimumab-lupus-nephritis-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-in-urinary-cd163-is-associated-with-treatment-response-in-the-belimumab-lupus-nephritis-trial/
