Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most frequent organ manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), affecting morbidity and mortality in SLE. LN is usually treated with initial therapy (immunosuppressants/immunomodulators added to intravenous pulse and/or oral glucocorticoids [GCs]), and maintenance therapy (optimal reduction of GCs in stable LN). Though GCs improve LN prognosis, prolonged use especially at high dose is associated with comorbidities. Thus, a GC dose reduction target (prednisolone equivalent) of ≤ 5 mg/day is recommended. However, real-world data on GC dose reduction in LN patients are scarce. We investigated the actual prescription status of oral GCs after initial therapy and characterized the patients with reduced GCs.
Methods: This retrospective, non-interventional study (UMIN000053093) used data from the JMDC payer database extracted between May 2016 and March 2023. Included patients had ≥ 2 LN diagnoses; follow-up for ≥ 90 days pre-index and ≥ 540 days post-index (to assess the baseline characteristics and impact of long-term GC prescription pattern, respectively); oral GC prescription dose ≥ 20 mg/day intravenous pulse methylprednisolone therapy; and ≥ 2 urinalysis, anti-DNA antibody and complement tests within 360 days post-index. Index date (Day 0) was the date of first GC prescription in the month of LN diagnosis. Patients with and without dose reduction achievement of GC ≤ 5 mg/day at Day 540 were included in ‘achieved’ and ‘non-achieved’ groups, respectively. Descriptive statistical analyses were performed.
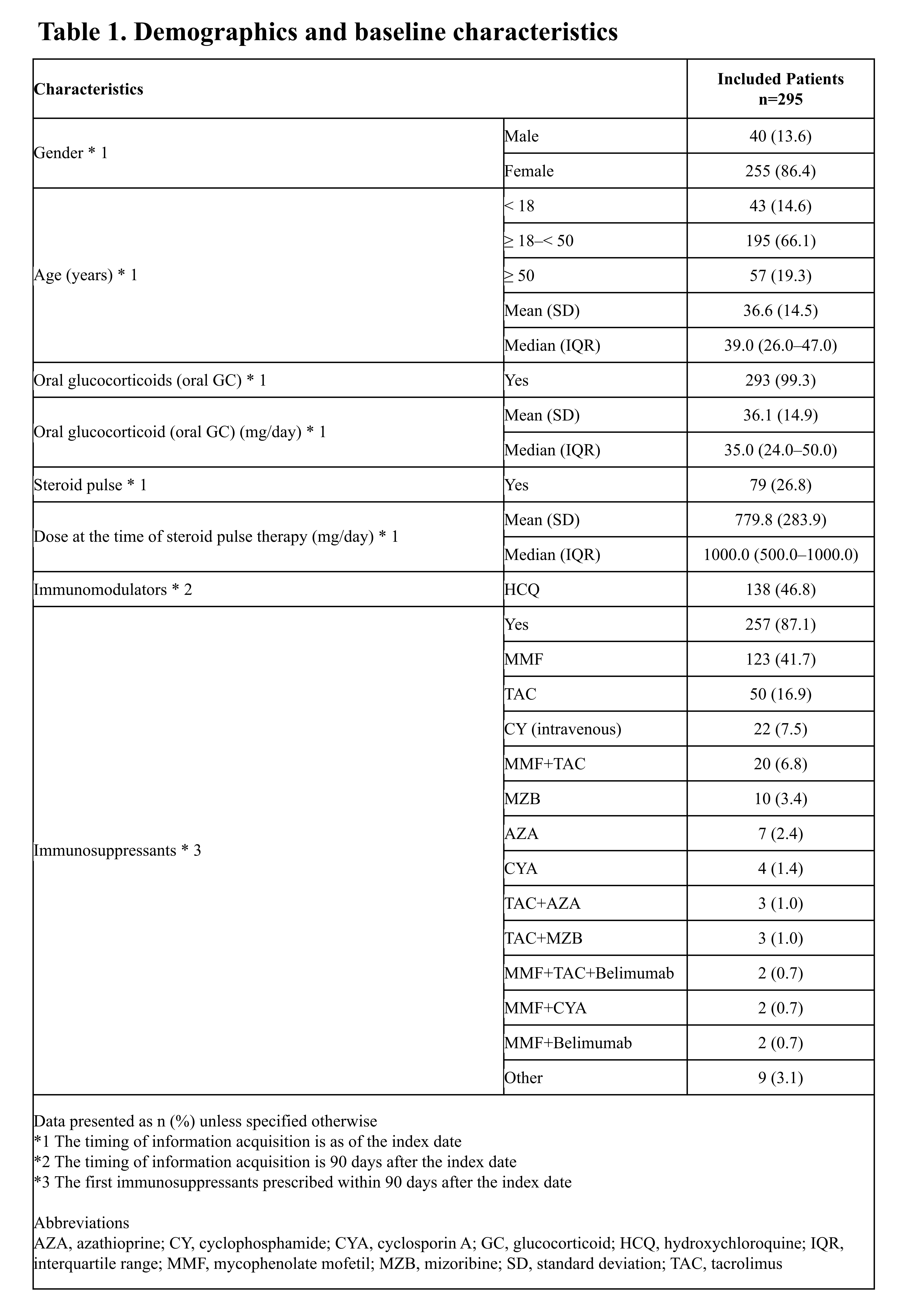
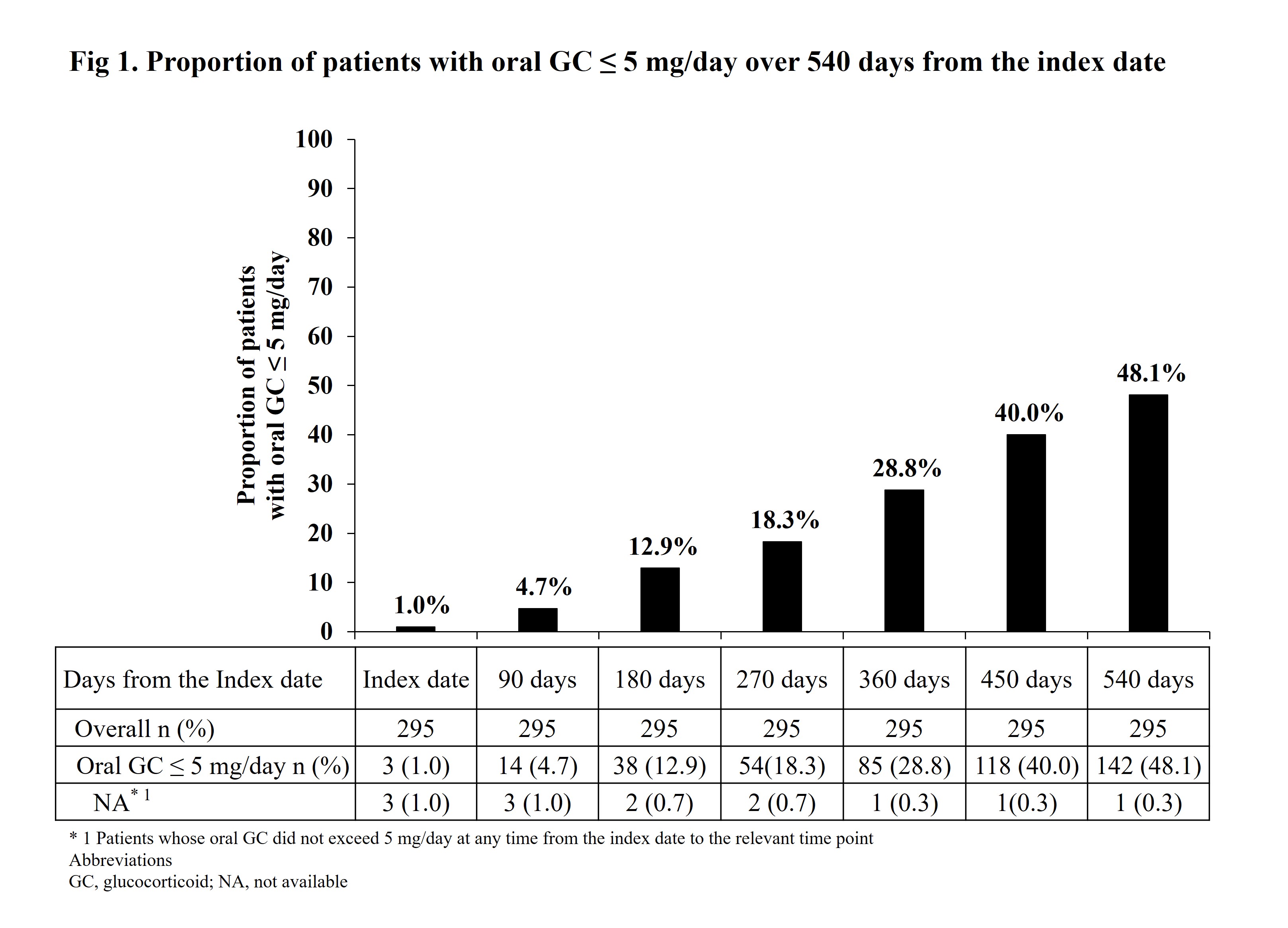
Results: Baseline characteristics of the overall population (n=295) are shown in Table 1. The median oral GC dose was 35.0 mg/day. At baseline, 26.8% patients had received steroid pulse before initiation of oral GC therapy. The 2 most prescribed concomitant immunosuppressants, within 90 days post-index, were mycophenolate mofetil only (MMF, 41.7%) and tacrolimus only (TAC, 16.9%). Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), an immunomodulator, was prescribed concomitantly to 46.8% patients at baseline. Proportion of patients receiving oral GC ≤ 5 mg/day increased from 1.0% at index to 48.1% at Day 540 post-index (Fig 1). The median GC prescription dose 540 days post-index was 6.0 mg/day. From 180 to 540 days post-index, flares per pre-defined algorithms occurred in 24.7% (15.9% moderate; 10.8% severe) patients.
In achieved (n=142; 90.1% females) and non-achieved (n=153; 83.0% females) groups, the median ages were 38 and 39 years and the median GC doses at baseline were 37.5 and 35.0 mg/day, respectively. The baseline concomitant immunosuppressants and immunomodulator were calculated (MMF only: 51.4% and 32.7%; TAC only: 15.5% and 18.3%; HCQ: 53.5% and 40.5% in achieved and non-achieved groups, respectively). Correspondingly, the flare rates were 23.9% and 25.5%, with severe flares in 6.3% and 15.0% patients. The proportion of patients with GC dose of ≤ 7.5 mg/day and ≤ 10 mg/day on Day 180 was higher in achieved than non-achieved groups (both p ≤ 0.0001).
Conclusion: These real-world administrative data from Japan showed the actual status of oral GC prescription after initial therapy of LN. Of note, the proportion of GC dose of ≤ 7.5 mg/day even in achieved group was only 31.0% on Day 180.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Atsumi T, Hanaoka H, Nishijima N, Murakami K, Nio M, Urakawa T, Fujimura T, Hayashi H. Real-world Glucocorticoid Prescription Patterns in Patients with Lupus Nephritis: A Retrospective Study Using a Healthcare Insurance Claims Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-glucocorticoid-prescription-patterns-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-a-retrospective-study-using-a-healthcare-insurance-claims-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-glucocorticoid-prescription-patterns-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-a-retrospective-study-using-a-healthcare-insurance-claims-database/