Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) inhibitors, including tocilizumab and sarilumab, are approved treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, comparative safety data on cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in real-world settings remain limited. We conducted a multi-cohort analysis to evaluate the safety profiles of IL-6 inhibitors compared to non-IL6 regimens, including sensitivity analyses by follow-up duration and sex.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network, including adult RA patients treated with tocilizumab, sarilumab, or no IL-6 inhibitors. Patients were grouped into three matched cohorts: Non-IL6, Tocilizumab-only, and Sarilumab-only. Propensity score matching (1:1) was conducted using demographics, comorbidities, medications, and laboratory variables. Outcomes included all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, heart failure (HF), and venous thromboembolism (VTE) over a 5-year follow-up. Sensitivity analyses included a truncated 3-year window and sex-stratified comparisons.
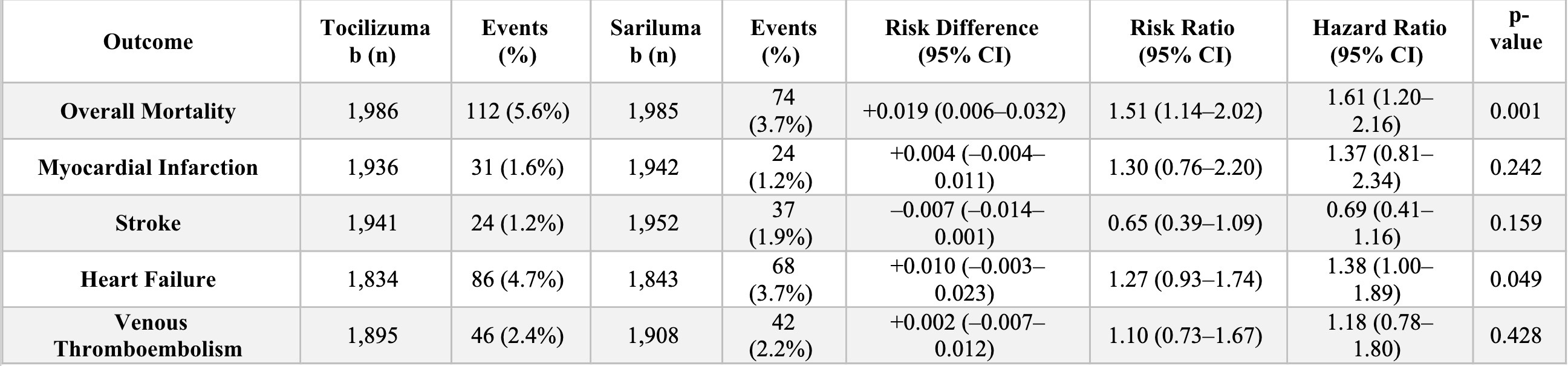
Results: Matched cohorts included 17,958 patients per group (non-IL6 vs Tocilizumab), 1,855 per group (non-IL6 vs Sarilumab), and 1,992 per group (Tocilizumab vs Sarilumab). Tocilizumab was associated with higher mortality than Sarilumab (5.6% vs 3.7%; risk difference [RD]: 1.9%; hazard ratio [HR]: 1.61; 95% CI: 1.20–2.16; p = 0.001), and higher mortality than non-IL6 (6.4% vs 5.5%; RD: –1.0%; p < 0.001). Mortality did not significantly differ between Sarilumab and Non-IL6. MI, stroke, HF, and VTE risks were comparable across all groups, with findings consistent in the 3-year analysis. In sex-stratified analyses, mortality was significantly higher in males treated with Tocilizumab versus Sarilumab (8.3% vs 4.8%; RD: 3.5%; p = 0.049; HR: 1.86; 95% CI: 1.04–3.32), while the difference in females was not significant.
Conclusion: In this large real-world RA cohort, sarilumab was associated with lower all-cause mortality than tocilizumab, particularly among male patients. Cardiovascular outcomes were similar across treatments. These findings support the need for individualized IL-6 inhibitor selection, with consideration of treatment duration and patient sex.
 Forest Plot of Hazard Ratios for Adverse Outcomes: Tocilizumab vs Non-IL6, Tocilizumab vs Sarilumab, and Non-IL6 vs Sarilumab
Forest Plot of Hazard Ratios for Adverse Outcomes: Tocilizumab vs Non-IL6, Tocilizumab vs Sarilumab, and Non-IL6 vs Sarilumab
.jpg) Clinical Outcomes: Risk Differences, Hazard Ratios, and Odds Ratios for Adverse Events Across Matched Cohorts
Clinical Outcomes: Risk Differences, Hazard Ratios, and Odds Ratios for Adverse Events Across Matched Cohorts
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sharkas S, Abughazaleh S, Jahandideh D. Real-World Comparative Safety of Tocilizumab and Sarilumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multi-Center Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-comparative-safety-of-tocilizumab-and-sarilumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multi-center-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-comparative-safety-of-tocilizumab-and-sarilumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multi-center-observational-study/
