Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Achieving remission is the treatment target for patients (pts.) with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).Remission rates over longer periods in a real-life setting have not been studied so far. To evaluate the remission rates in a cohort of axSpA pts. treated in a tertiary care center using retrospective and prospective data.
Methods: Adult pts. with a diagnosis of axSpA were eligible for inclusion when ≥ 2 consecutive ASDAS assessments were documented in the hospital information system in the past. At the next clinical visit, patients and disease characteristics as well as standard assessments using validated outcome parameters for disease activity (ASDAS, BASDAI) and physical function (BASFI) were then prospectively documented. Values of BASDAI, ASDAS and BASFI were taken retrospectively from the hospital information system. ASDAS was calculated either by ASDAS-CRP or alternative-ASDAS the latter one, when patient global assessment was unavailable.1Remission was defined as an ASDAS < 1.3 and sustained remission was defined by ASDAS < 1.3 for at least 6 consecutive months. Multivariable logistic regression was used to estimate ORs, 95% CIs and p-values of achieving remission.
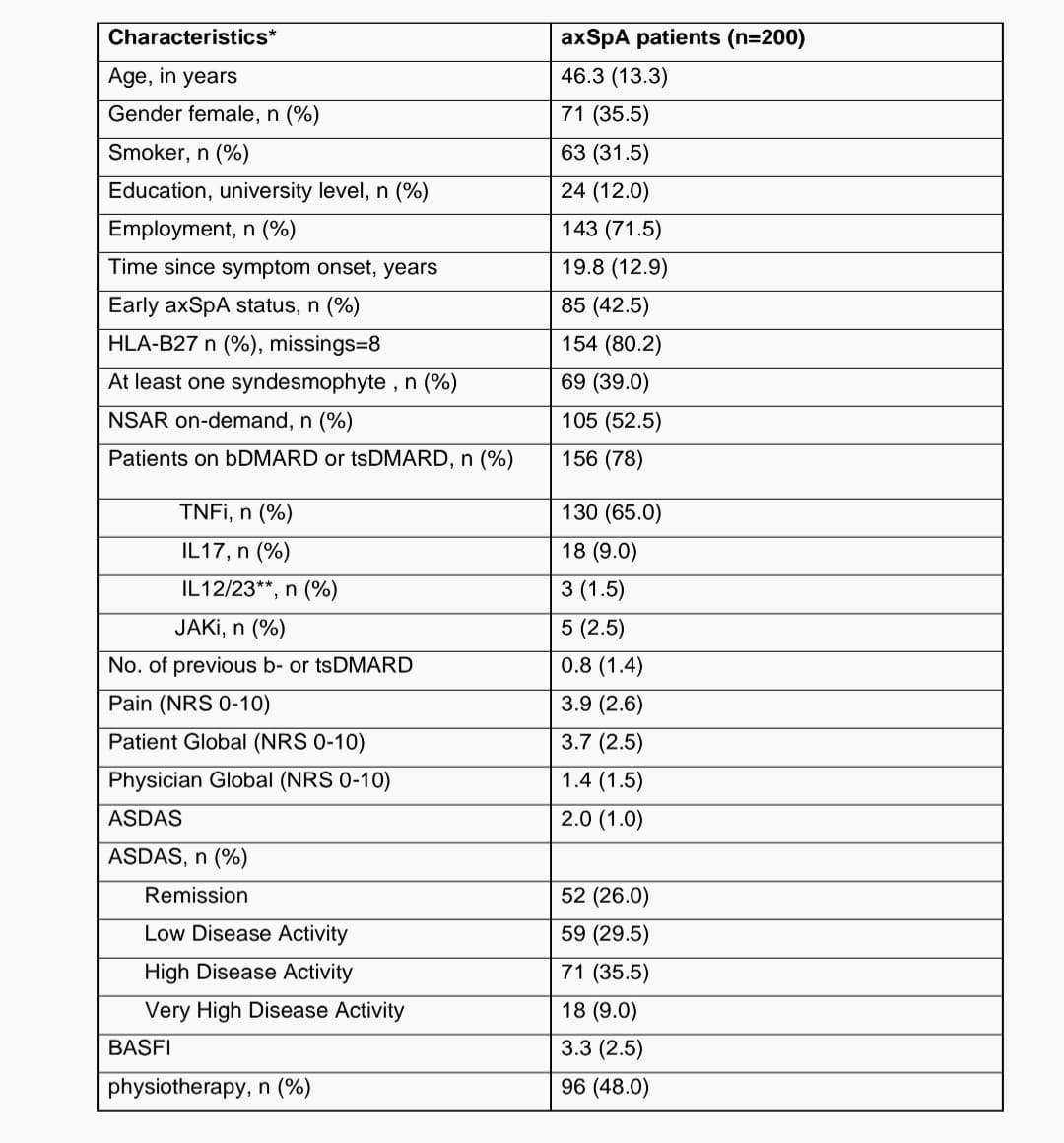
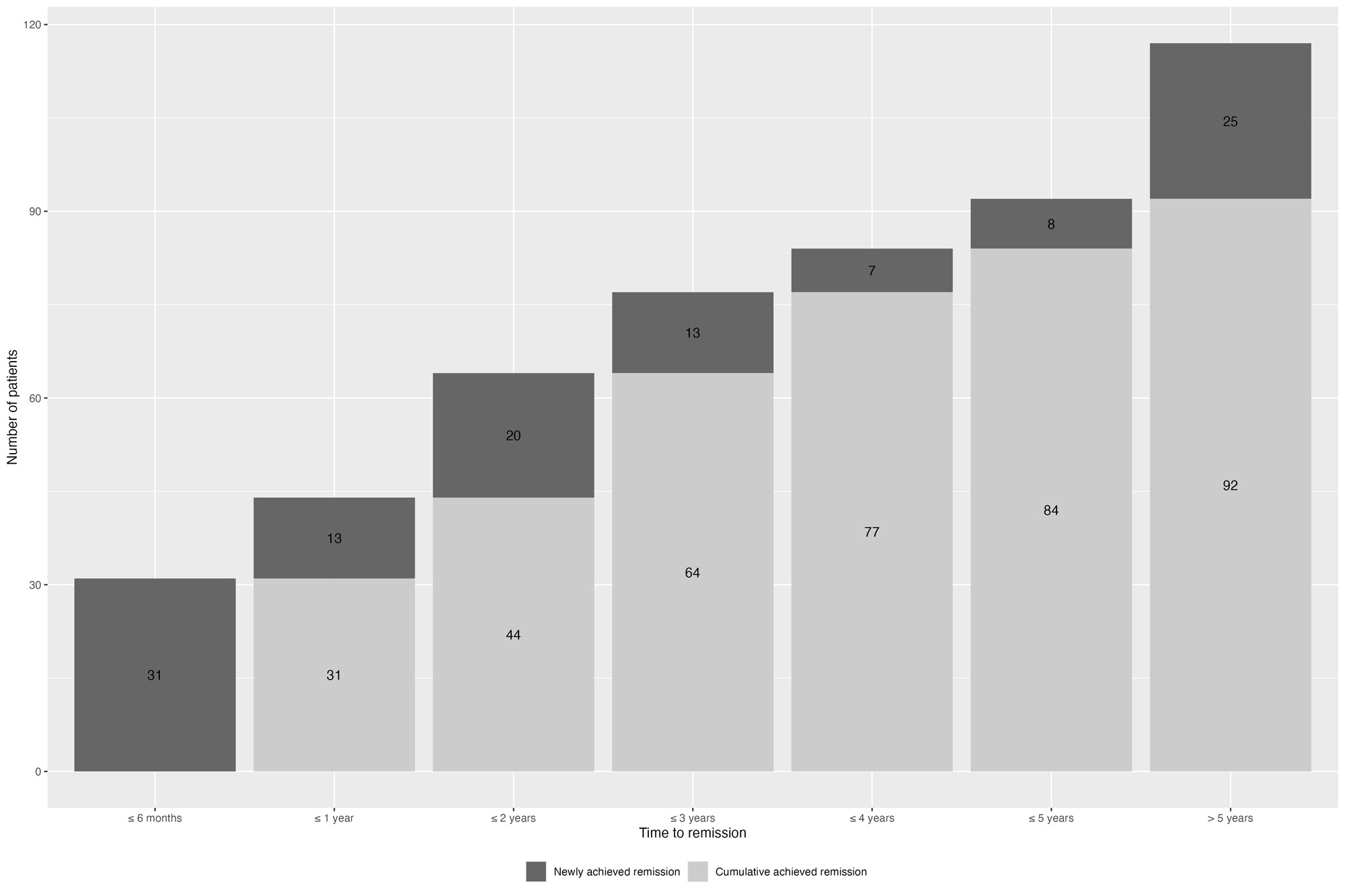
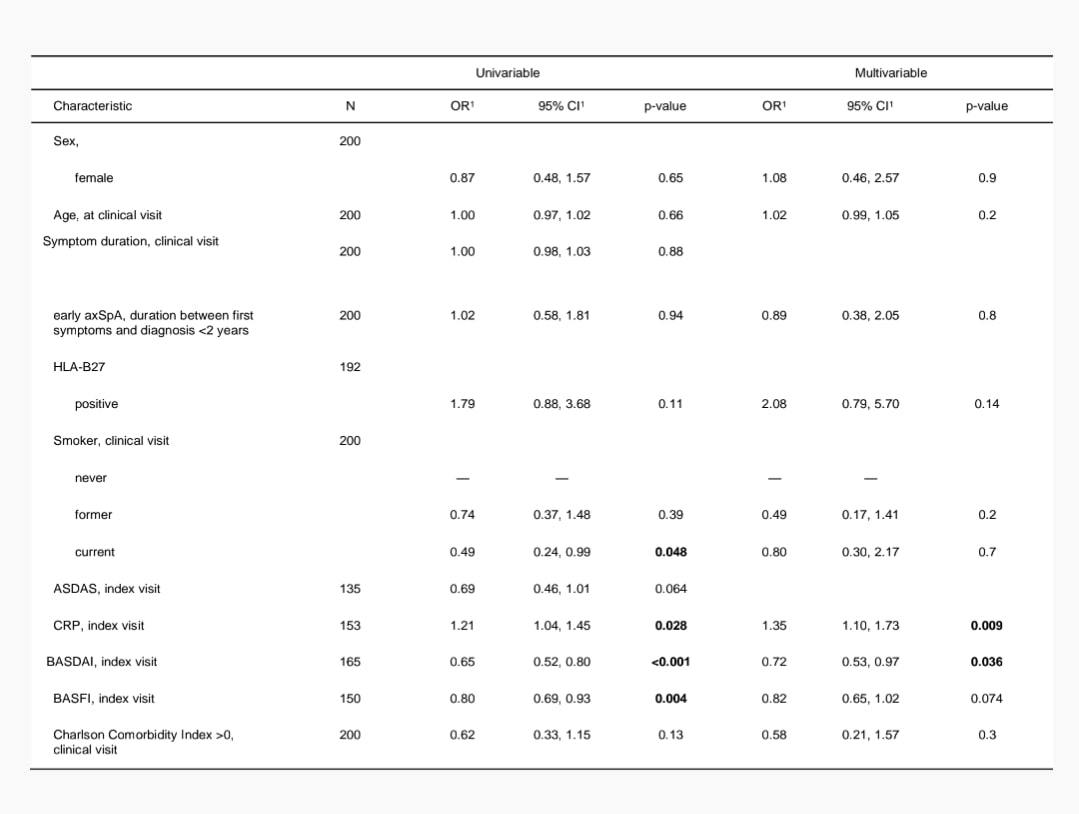
Results: A total of 200 pts. were consecutively examined at their clinical visit between March and September 2022. Retrospective chart data were available over a period of 82.6 (58.6) months. Mean ASDAS at the clinical visit was 2.0 (1.0) and 52 pts. (26.0%) were in ASDAS remission. 74 (37.0%) pts. showed limitations in physical functioning (BASFI >4) (table 1). 117 pts. (58.5%) achieved ASDAS remission at least once. On average, remission was reached 37.7 (44.5) months after the index visit. 44 pts. achieved remission within the first year (37.6%), 20 in the second (17.1%), 13 in the third (11.1%) and 40 patients (34.2%) after 3 years (figure 1). 9 (7.7%) pts. achieved their first ASDAS remission at the clinical visit. During the observation period pts. achieved remission for 9.9 (16.8) months or 21.6% (29.9%) of the time, while 51 pts. (43.6%) achieved sustained remission for at least 6 consecutive months, 31 pts. (26.5%) achieved sustained remission for at least 12 consecutive months. 83 pts. (41.5%) never achieved ASDAS remission. In a multivariable model, high CRP (OR=1.35, 95% CI 1.10 to 1.73) and low BASDAI (OR=0.72, 95% CI 0.53 to 0.97) at index visit were associated with higher odds of achieving remission at least once (both p< 0.05). Pts. with low BASFI at index visit also tended to have higher odds of achieving remission, however this was not significant (OR=0.82, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.02, p=0.074). Age nor gender was significantly associated with achieving remission (OR=1.02, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.05, p=0.2), (OR=1.08, 95% CI0.46 to 2.57, p=0.9, respectively).
Conclusion: Achievement of remission is an attainable goal for patients with axSpA. High CRP and low BASDAI at index visit were shown to be predictors of ASDAS remission. The majority of patients achieved remission within the first two years after the initial visit. However, also after the fifth year of follow up a quarter of patients achieved ASDAS remission for the first time.
*values are mean (SD)
**all of these pts. suffered from severe psoriasis vulgaris, which could not be successfully treated by other bDMARDs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Neinert F, Redeker I, Tsiami S, Kiefer D, Guminski B, Baraliakos X, Braun J, Kiltz U. Rates of Remission in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Treated in Tertiary Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rates-of-remission-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-treated-in-tertiary-care/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rates-of-remission-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-treated-in-tertiary-care/