Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite more effective therapeutic strategies in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), there is still a significant risk of morbidity and mortality, mainly due to infection, and cardiovascular disease. Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) is a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis associated with cardiovascular risk factors and is predictive of major cardiovascular events (MACE). We hypothesized that patients with AAV might benefit from statin treatment in primary prevention to reduce subclinical markers of atherosclerosis and the incidence of major cardiovascular events.
Methods: This phase 3, multicentre, randomized, controlled, double-blind, superiority study compared rosuvastatin with placebo in reducing the progression of subclinical markers of atherosclerosis. Patients with AAV in remission after a first flare or relapse were randomized 1:1 to receive the experimental strategy based on the use of rosuvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo for 24 months. The primary endpoint was the mean change in mean cIMT (distal wall of primary carotid arteries) at 24 months.
Results: A total of 111 participants underwent randomization (55% male, mean age 54.8 (13.3) years, 63.1% GPA, 28.8% EGPA, 8.1% MPA), with 54 participants assigned to receive rosuvastatin and 57 to placebo.
The primary endpoint was not met. The mean change in cIMT at month 24 was not different between the two study groups (difference -0.002 [-0.034 ; 0.030], p=0.89) (Figure 1). The annualized rate of change in mean cIMT was 0.0110 (0.0617) mm/year in the rosuvastatin group and 0.0189 (0.0556) mm/year in the placebo group (difference -0.0062 [-0.0318 ; 0.0193], p=0.61). Similar results were found for the mean change in the number of plaques in the carotid and femoral arteries and abdominal aorta (difference 0.01 [-0.39 ; 0.42], p=0.94).
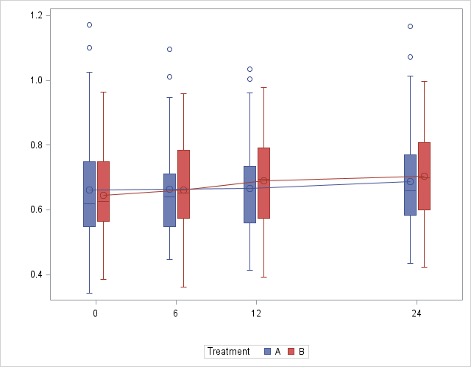
Mean LDL-cholesterol levels were significantly different between the two study groups at all time points evaluated (P< 0.001, P< 0.001, and P< 0.001 for reductions between the rosuvastatin and the placebo groups at months 6, 12 and 24, respectively) (Figure 2). Also, high-sensitivity CRP levels were significantly different between the two study groups at month 24 (difference -3.16 [-5.58 ; 0.74], p=0.011 for reductions between the rosuvastatin and the placebo groups).
There was only one MACE in the rosuvastatin group. Vasculitis relapse-free survival did not differ between the two groups (HR 1.59, 95%IC = [0.81 ; 3.09], p=0.18).
Eleven and seventeen patients discontinued intervention in the rosuvastatin and the placebo groups, respectively. The incidence of serious adverse events was similar in the two groups: 27.8% in the rosuvastatin group and 22.8% in the placebo group.
Conclusion: Among patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, 24 months of rosuvastatin reduced LDL-cholesterol but did not reduce the progression of subclinical markers of atherosclerosis (Funded by the French Ministry of Health; STATVAS ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02117453).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Terrier B, Pugnet G, Sirieix M, Quemeneur T, Puéchal X, Maurier F, Néel A, BENHAMOU Y, Bonnotte B, Schmidt J, Michon A, Baudet A, Charles P, Cohen F, De Moreuil C, Dernis E, Belenotti P, Ruivard M, Aumaitre O, Fain O, Seror R, Durel C, Jourde-Chiche N, Lazaro E, Chironi G, Armengol G, Bellien J, Ravaud P, Baron G, Guillevin L. Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Trial on the Impact of Rosuvastatin on Sublinical Markers of Atherosclerosis in Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/randomized-controlled-double-blind-trial-on-the-impact-of-rosuvastatin-on-sublinical-markers-of-atherosclerosis-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/randomized-controlled-double-blind-trial-on-the-impact-of-rosuvastatin-on-sublinical-markers-of-atherosclerosis-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis/