Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's – Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Objectives: The aim of this study is to evaluate the usefulness of photoacoustic imaging (PAI) for quantitative analysis of the peripheral vascular bed in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc).
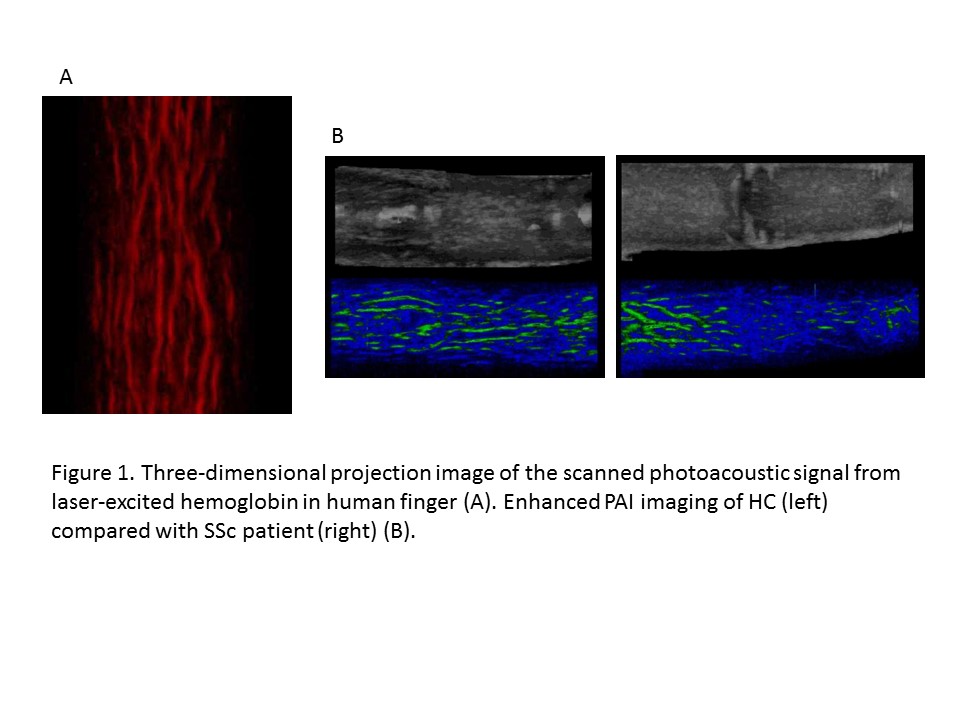
Background/Purpose: PAI is a technique that uses the photoacoustic effect of living tissues. Pulsed short-length light waves excite the living tissue to produce strong ultrasonic waves in accordance with the absorbance of substances in the tissue. These ultrasonic waves can be detected with ultrasound probes, and reconstructed as an ultrasound image. Detecting the ultrasonic wave which is produced by 750 nm wavelength pulsed laser-excited hemoglobin enables small blood vessels of low flow velocities to be visualized without using contrast agents. The quantitative evaluation of digital vascular bed volume in patients with SSc may enable us to diagnose SSc earlier, and to determine the progression and severity of the disease.
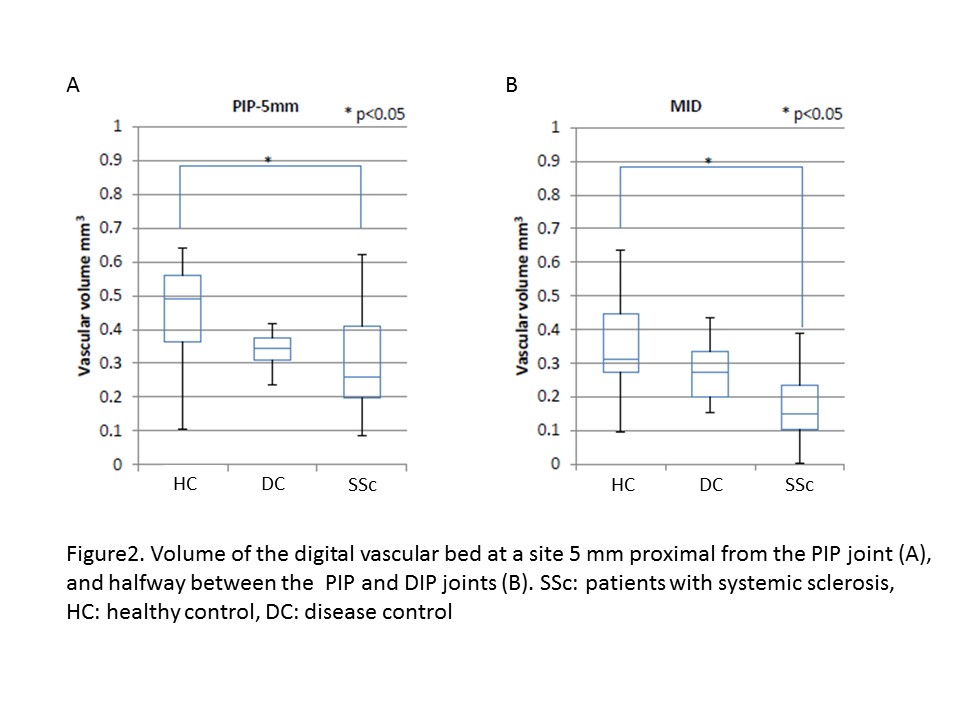
Patients and Methods: Nine patients with SSc, two patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) complicating Raynaud’s phenomenon as disease control (DC), and three healthy adult volunteers as healthy control (HC) were enrolled in the study. The volume of the vascular bed was measured in the proximal and distal sites of fingers 2–5 bilaterally using PAI.
Results: The volume of the digital vascular bed in 37 sites of SSc patients, 21 sites of HC, and 14 sites of DC could be obtained. All SSc patients showed a severely decreased digital vascular bed volume in both proximal and distal sites of all measured fingers, and the vascular bed volumes were significantly lower compared with HC. DC showed a tendency of decreased digital vascular bed, but not significantly compared with HC.
Conclusion: PAI is a useful device for determining digital vasculopathy by quantitative analysis of vascular bed volume. More data with clinical signs, and comparison with other modalities such as color Doppler sonography, will provide the information to determine the prognosis of peripheral ischemic damage, and the effectiveness of treatments to improve peripheral circulation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kusanagi Y, Suzuki R, Murakoshi D, Hirota K, Irisawa K, Wada T, Okawa S, Ishihara M, Kimura F, Itoh K. Quantitative Analyze of Peripheral Vascular Bed in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis By Using Photoacoustic Imaging Technology: A Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-analyze-of-peripheral-vascular-bed-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-by-using-photoacoustic-imaging-technology-a-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-analyze-of-peripheral-vascular-bed-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-by-using-photoacoustic-imaging-technology-a-pilot-study/