Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatology patients prescribed teratogenic medications often are not prescribed effective contraception. Efforts to improve this important quality indicator are limited by inadequate and poorly standardized contraception documentation. We demonstrated a sustained increase in contraception documentation for all reproductive-aged women seen in a rheumatology fellows’ clinic from 11% to 54% over 24 weeks with a multi-cycle quality improvement (QI) intervention targeting nursing staff (Siegel C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 [suppl 9]). The current QI initiative aimed to increase contraception screening and documentation for reproductive-aged women prescribed a teratogenic medication seen across four adult rheumatology units.
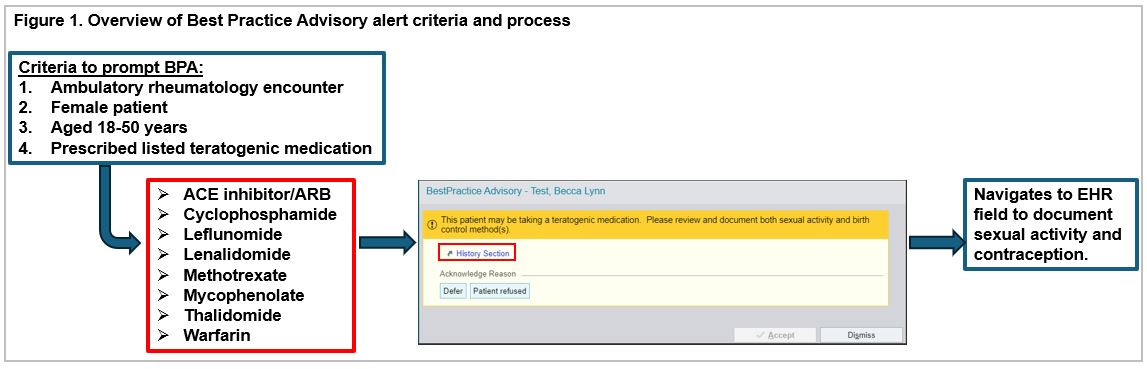
Methods: We developed and implemented a Best Practice Advisory (BPA) pop-up alert in the Electronic Health Record (EHR), set to trigger when a clinician opens an ambulatory encounter for 18-50-year-old female patients prescribed a teratogenic medication, and educated key stakeholders [Figure 1]. Nursing leadership sent a staff reminder and interim progress update. We led an interactive session to solicit feedback from nursing staff regarding contraception documentation barriers.
The primary outcome measure was the percentage of eligible encounters with contraception information documented in the structured EHR field. Process measures included sexual activity status and contraception documentation stratified by unit location. We assessed all measures biweekly and the aggregate frequency of documentation by unit over 24 weeks.
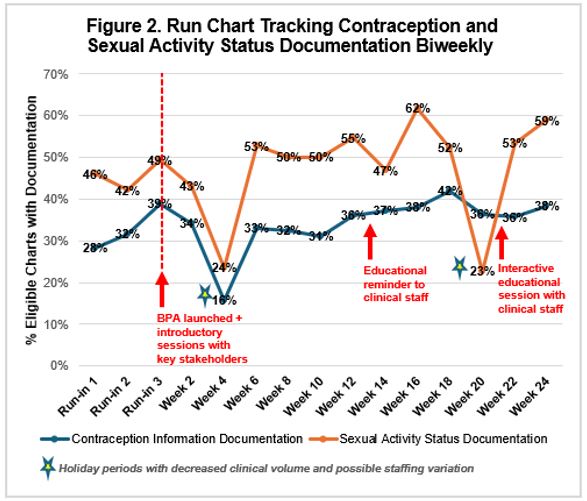
Results: The contraception documentation rate for female rheumatology patients aged 18-50 prescribed a teratogenic medication was unchanged from 39% to 38% over 24 weeks. After BPA implementation, contraception documentation remained at 31-36% through week 12 (with a 16% nadir during winter holidays). Contraception documentation peaked at 42% by week 20 following the staff reminder. The median sexual activity documentation rate was 51% (range: 23%-62) [Figure 2].
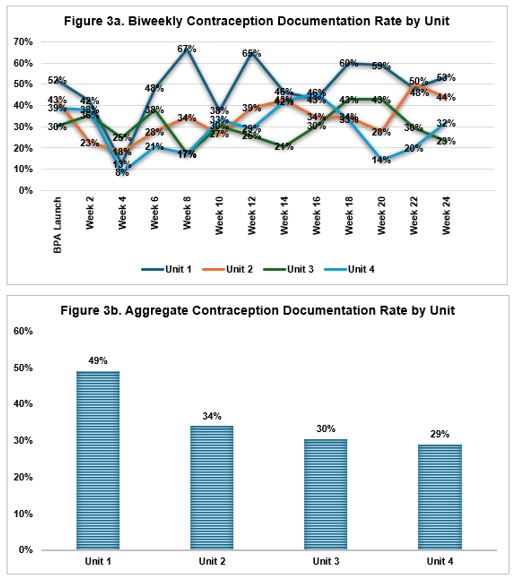
Contraception documentation rates were highest in Unit 1, the site of our pilot QI initiative including a site-specific nursing champion, reaching a 67% peak, but without a trend over 24 weeks [Figure 3a]. Of all eligible encounters, 49% in Unit 1 had contraception information documented versus 29-34% in Units 2-4 [Figure 3b]. Barriers elicited from staff included misaligned timing of the BPA during the rooming workflow and discomfort with screening questions.
Conclusion: We developed an EHR-based BPA to prompt contraception documentation for reproductive-aged women prescribed teratogenic medications in an academic rheumatology center. Despite this system-wide intervention, contraception documentation did not significantly increase over 24 weeks and existing unit-based discrepancies persisted. Next steps will include BPA optimization based on stakeholder feedback and engaging unit-based champions to tailor interventions. Increasing standardized contraception status documentation among at-risk rheumatology patients will facilitate targeted counseling and streamlined gynecology referrals in the future.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Siegel C, Mikhaylov A, Wu E, Jannat-Khah D, Abramson E, Sammaritano L, Pan N. Quality Improvement Initiative to Increase Contraception Screening and Documentation for Reproductive-Aged Women Prescribed Teratogenic Medications in an Academic Rheumatology Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-improvement-initiative-to-increase-contraception-screening-and-documentation-for-reproductive-aged-women-prescribed-teratogenic-medications-in-an-academic-rheumatology-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-improvement-initiative-to-increase-contraception-screening-and-documentation-for-reproductive-aged-women-prescribed-teratogenic-medications-in-an-academic-rheumatology-center/