Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) administration in autoimmune diseases (AID) is associated with severe infectious events (SIE). Frequency of SIE and immune reconstitution (B cells, T cells, and immunoglobulins) after RTX have not yet been fully assessed in a prospective study in patients with various AID.
We aimed to explore the impact of RTX on immune system in patients with AID including kinetic evolution of biological parameters, and to estimate the rates of hypogammaglobulinemia (HG), severe infectious events (SIE) and immunoglobulins replacement therapy (IgRT).
Methods: Patients treated by RTX for AID were included in a prospective study (200 patients planned between May 2019 and May 2022, clinical trial number: NCT03778840). Clinical and biological parameters were recorded at baseline and then every 3 months for one year (M3, M6, M9 and M12). The influence of baseline characteristics on immune reconstitution was assessed using mixed models.
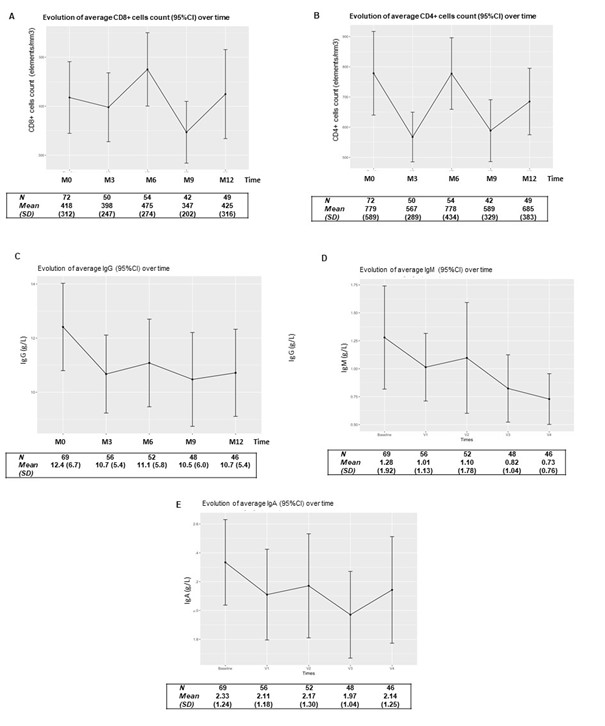
Results: The expected number of inclusions was not met because of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, which limited RTX prescription and patients’ recruitment. Seventy-two patients were eventually included. There were mostly women (45/72, 62%) presenting with autoimmune cytopenia, connective tissue diseases, organ-specific AID, systemic vasculitis, acquired hemophilia, or other AID. We observed 10 SIE in 9 patients. Three patients received IgIV for immunomodulatory indication (2g/kg), including 2 during the first 3 months of follow-up. All patients experienced deep B cells depletion and decreased neutrophils count which were both influenced underlying disease in the mixed models. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells count varied over time, with a more profound depletion at M3 and M9 (Figure 1A and B). Mixed model revealed that the use of immunosuppressants (IS) prior to RTX was associated with a more pronounced decrease in CD8+ T cells (p-value: 0.022) and concomitant use of IS at baseline was associated with a more pronounced decrease in CD4+ T cells (p-value: 0.003). We observed a progressive depletion of IgG, IgM, and IgA over time between baseline and M9 (Figure 1C, D and E). HG occurred in 9 patients at M3, 6 at M6, 9 at M9, and 5 at M12. The mixed model revealed that underlying diseases influenced IgG and IgA evolution (p-value 0.004 and 0.007 respecticley). Concomitant use of glucocorticosteroids (GC) ≥ 10 mg/day was associated with a more pronounced decrease in IgG rate in the first 6 months (p-value: 0.036). Concomitant use of IS influenced IgM evolution over time (p-value: 0.013). History of GC ≥ 10 mg/day was associated with a more pronounced decrease of IgA rate during follow-up (p-value: 0.023) and IS use prior to RTX injection influenced the evolution of IgA rate over time (p-value: 0.037).
Conclusion: Our study provides several insights into immune reconstitution in patients treated with RTX for AID. B cell depletion and decreased neutrophils count appeared to be directly linked to RTX administration and underlying disease. IgG levels trajectories were influenced by GC and underlying disease. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells count trajectories appeared to be influenced by previous IS use.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chepy A, Genin M, Terriou L, Chenivesse C, Staumont-Sallé D, Zéphir H, philippe P, Lefevre G, Stabler S, HACHULLA E, Launay D, Sobanski V. Prospective Study of Severe Infectious Events and Immune Reconstitution After Rituximab in Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prospective-study-of-severe-infectious-events-and-immune-reconstitution-after-rituximab-in-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prospective-study-of-severe-infectious-events-and-immune-reconstitution-after-rituximab-in-autoimmune-diseases/