Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We have previously shown that PROMIS-29 physical (pain, fatigue) and emotional (depression, anxiety) symptom clusters can be used to identify 4 distinct early RA patient sub-groups, and that patient sub-groups with higher emotional symptoms experienced greater physical and emotional symptom burden despite all receiving conventional RA treatment with MTX over 6-months follow up. Here, we examine whether these 4 identified patient subgroups also follow distinct trajectories of disease activity over the first 6 months of MTX therapy.
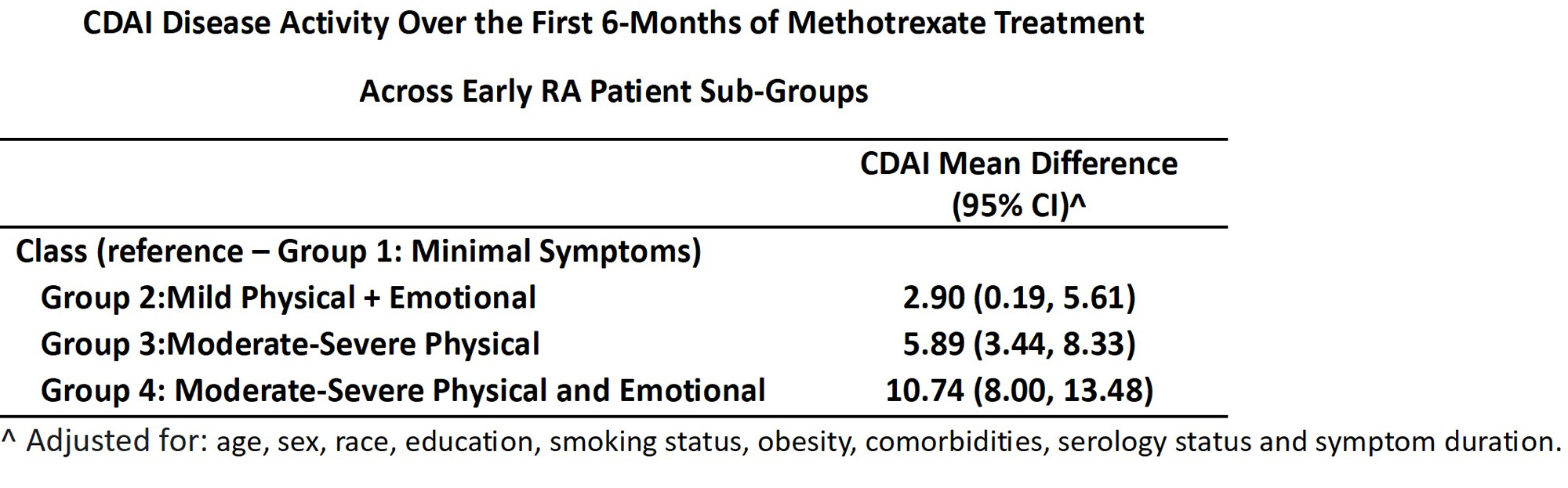
Methods: Data were from adults with newly diagnosed early RA (symptoms < 1 year) enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) study who were initiating treatment with MTX for the first time and had complete clinical and PRO measures at baseline, 3- and 6-month follow up. PROMIS-29 anxiety, depression, fatigue, and pain scores were used to classify patients into 4 patient sub-groups using latent transition analysis: Group 1: Minimal Sx; Group 2: Mild Physical + emotional Sx; Group 3: Moderate-Severe Physical Sx; and Group 4: Moderate-Severe Physical + emotional Sx. Linear mixed effects regression was used to estimate trajectories of CDAI disease activity over the first 6 months of MTX treatment across groups adjusting for age, sex, race, education, smoking status, obesity, comorbidities, serology status and symptom duration.
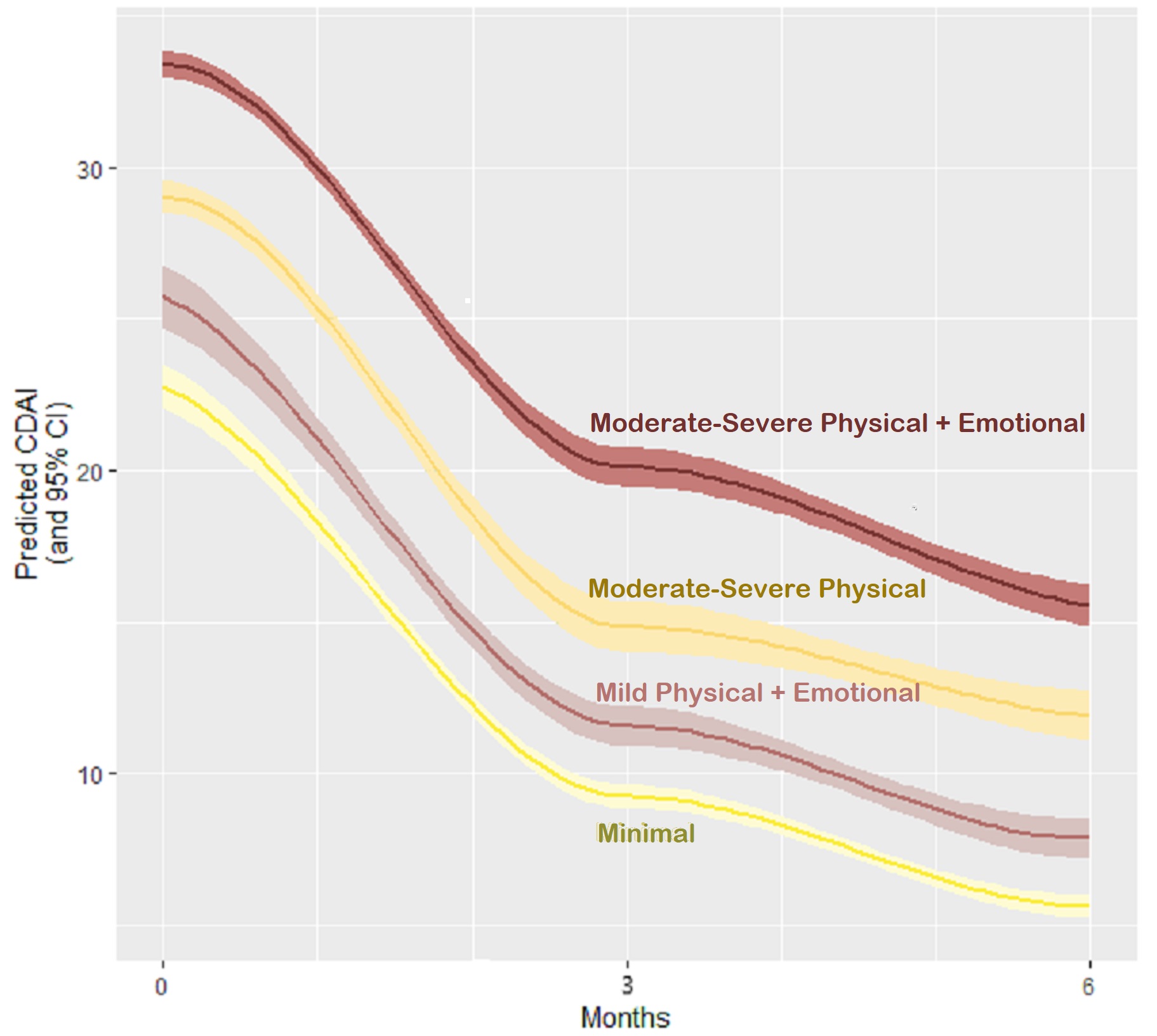
Results: The sample included 310 early RA patients initiating MTX treatment for the first time. Participants had a mean age of 56, CDAI of 29.3, and symptom duration of 5 months; 67% were women and 78%were White. At baseline, average disease activity was high across all 4 patient groups though mean CDAI scores were highest for patients in Group 3 (Moderate-Severe Physical Sx) (mean (sd) CDAI: 29.2 (12.7)) and Group 4 (Moderate-Severe Physical + emotional Sx) (mean (sd) CDAI: 32 (14.0). Disease activity improved for all groups over 6-months of treatment with MTX though not to the same degree across groups. Compared with patients in Group 1 (Minimal Sx), mean CDAI was nearly 3 points higher for participants in Group 2 (Mild Physical + emotional Sx) was nearly6-points higher for Group 3 (Moderate-Severe Physical Sx) and nearly 11 points higher for Group 4 (Moderate-Severe Physical + emotional sx) (FIGURE).
Conclusion: We found that despite being treated with the same conventional RA MTX treatment, early RA patients displayed varying levels of physical (pain, fatigue) and emotional symptoms [anxiety, depression] and that these symptom clusters could be used to identify distinct patient sub-groups with substantial differences in disease activity over 6-months of follow up. Results suggest that both the presence and intensity of physical symptoms plus the levels of anxiety and depression may indicate more complex subtypes of RA with a less favorable prognosis. Evaluating both physical and emotional symptoms at the time of diagnosis may help providers better tailor RA treatment by potentially combining medications and supportive interventions that reduce overall symptom burden and improve treatment outcomes and QOL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bartlett S, Bingham C, Schieir O, Valois M, Boire G, Bessette L, Pope J, Tin D, Thorne C, Hazlewood G, Hitchon C, Keystone E, Bykerk V. PROMIS Symptom Clusters Predict Disease Activity in the First 6 Months in Newly Diagnosed RA Patients Starting MTX Therapy: Data from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/promis-symptom-clusters-predict-disease-activity-in-the-first-6-months-in-newly-diagnosed-ra-patients-starting-mtx-therapy-data-from-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/promis-symptom-clusters-predict-disease-activity-in-the-first-6-months-in-newly-diagnosed-ra-patients-starting-mtx-therapy-data-from-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort/