Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0283–0307) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lipid oxidation products produced by artery wall cells under oxidative stress not only regulate immune responses, but their accumulation in HDL are shown to hinder the protective properties of HDL. Our prior work demonstrated that IIM patients had impaired HDL antioxidant function and decreased activity of HDL-associated antioxidant enzyme paraoxonase-1 (PON1), and both correlated with higher disease activity. We hypothesize that higher circulating levels of certain lipid oxidation products that function as proinflammatory bioactive lipid mediators (BLM) will inhibit HDL function and perpetuate vascular damage to enhance IIM disease burden.
Methods: A panel of proinflammatory BLM were assessed from plasma samples of our myositis cohort using liquid chromatography, tandem mass spectroscopy. PON1 activity by paraoxonase, arylesterase, lactonase assays and HDL antioxidant function (HDL inflammatory index, HII) were measured as in prior studies. HDL associated Apolipoprotein A-I(HDL-ApoAI) was measured by sandwich ELISA to assess the major apolipoprotein component of HDL, which normally prevents vessel inflammation. Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM) were assessed by ELISA as markers of endothelial dysfunction.
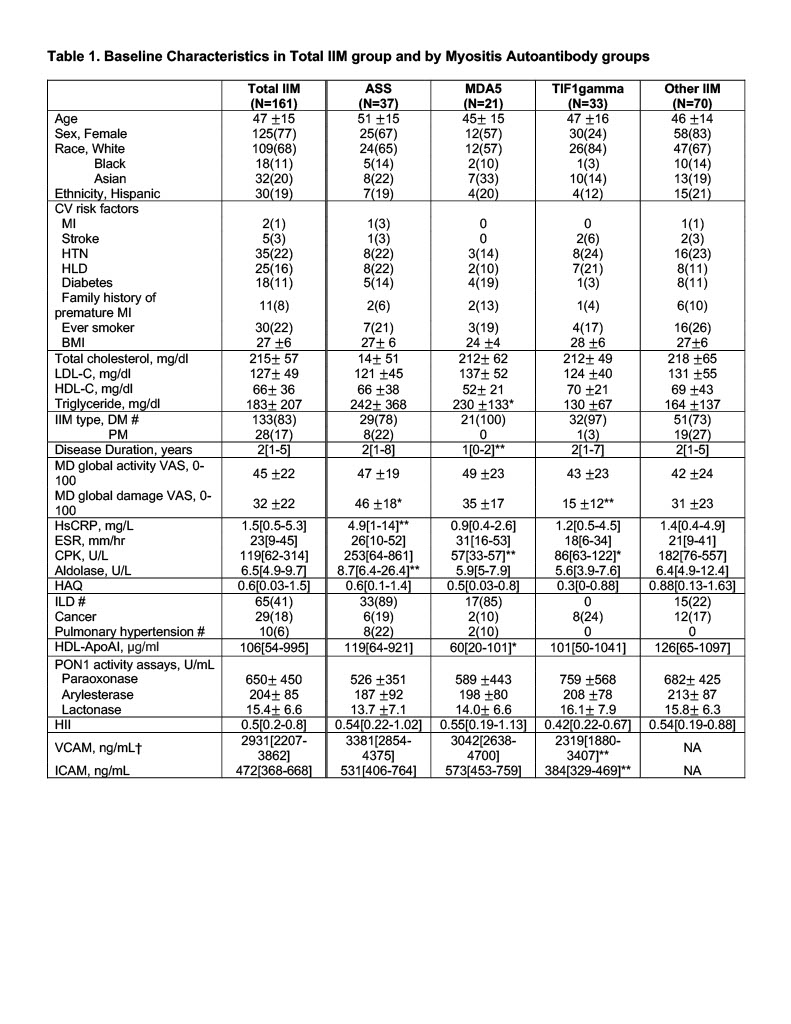
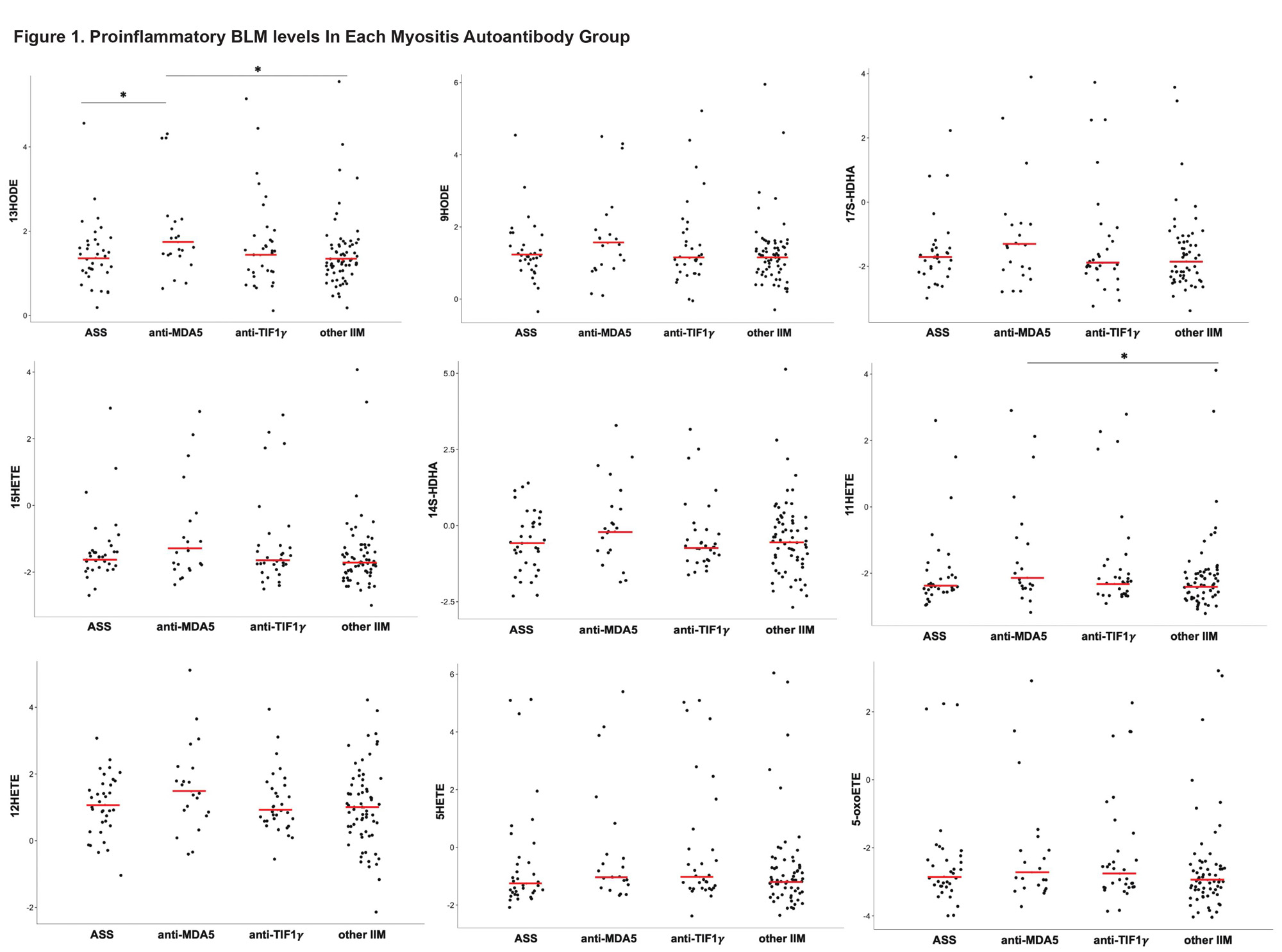
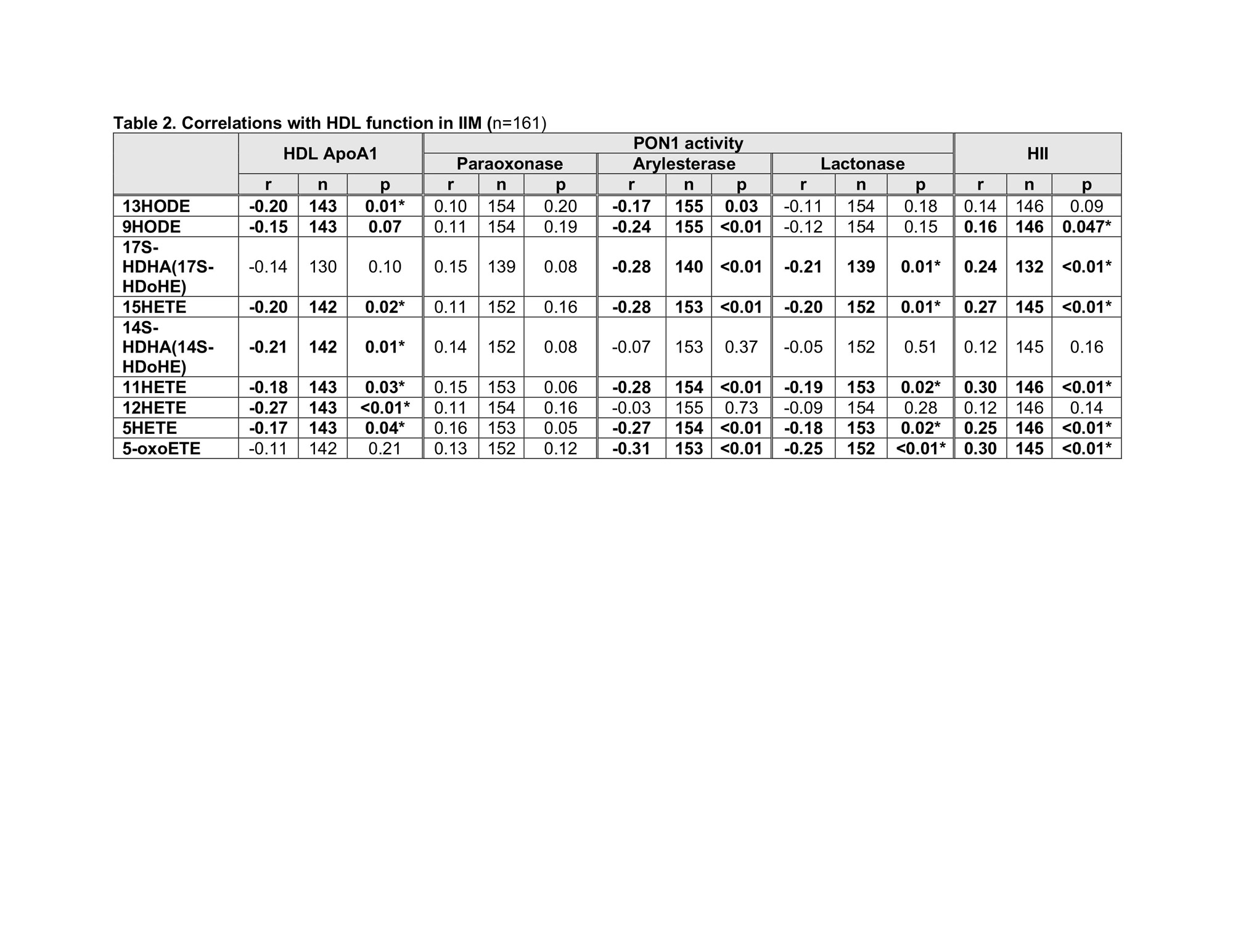
Results: A total of 161 IIM samples were analyzed (Table 1). When grouped by myositis autoantibodies, the anti-MDA5 group had the highest level of all 9 BLM tested with 13HODE and 11HETE showing statistically significant differences (Figure 1). HDL-ApoAI was lowest in anti-MDA5 and PON1 activity was numerically lower in patients with anti-MDA5 or antisynthetase antibodies (ASS) compared to patients with other myositis antibodies (Table 1). Correlations between BLM and biomarkers of HDL function (HDL-ApoAI, PON1, HII; Table 2) demonstrated that 5HETE, 11HETE, 15HETE correlated with lower HDL-ApoAI and PON1 activity and worse HDL antioxidant function (higher HII). 13HODE, 14S-HDHA, 12HETE also correlated with lower HDL-ApoAI, and 13HODE, 9HODE, 17S-HDHA, and 5-oxoETE correlated with lower PON1 and worse HII. 12HETE also correlated with higher levels of ICAM-1 (r=0.28, p=0.02). Associations between BLMs and measures of myositis disease burden (MD global VAS, CPK, aldolase, hsCRP, ESR) showed 12HETE to have a modest positive correlation with MD global activity score (r=0.16, p=0.047) but otherwise no significant associations were noted. Patients with a history of cancer had numerically higher levels of all BLMs compared to those without cancer, most notably of 17S-HDHA, 15HETE and 5-oxoETE (data not shown). Other clinical characteristics including ILD, arthritis, Raynauds, calcinosis, amyopathic disease and mechanics hands were not associated with the assessed BLMs in our study.
Conclusion: Higher levels of circulating proinflammatory BLM are associated with worse HDL antioxidant function and lower levels of PON1 activity and HDL-ApoA1 in IIM patients. Patients with anti-MDA5 antibodies had the highest level of proinflammatory BLM. Further work is needed to study the relationship between BLM and abnormal HDL function and the mechanism of how they may contribute to IIM disease burden.
Values are in Mean± SD, Median[IQR] or n(%)
*p<0.05 compared to other IIM group and **p<0.05 compared to all other MSA groups, using student’s t-test for values in Mean ±SD, Wilcoxon for values in Median[IQR]
#p<0.05 by chi-square for values reported in n(%)
†VCAM and ICAM were only done in 69 patients from ASS, MDA5, TIF1 gamma group, none from other IIM group
*p<0.05 by Wilcoxon test of each pair
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bae S, Shahbazian A, Wang J, Sulaiman D, Meriwether D, Reddy s, Charles-Schoeman C. Proinflammatory Bioactive Lipid Mediators (BLM) Are Associated with Worse Anti-Oxidant Function of High Density Lipoproteins (HDL) in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proinflammatory-bioactive-lipid-mediators-blm-are-associated-with-worse-anti-oxidant-function-of-high-density-lipoproteins-hdl-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-iim/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proinflammatory-bioactive-lipid-mediators-blm-are-associated-with-worse-anti-oxidant-function-of-high-density-lipoproteins-hdl-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-iim/