Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Compared to the general population, adults living with autoimmune disease are at nearly twice the risk of vaccine-preventable infections, making this a high priority vaccination group. The objective of this study was to prioritize topics for future patient-centered research to reduce vaccine hesitancy and increase uptake of vaccines for conditions such as pneumococcal pneumonia, influenza, zoster, human papillomavirus, and SARS-CoV-2 among adults living with autoimmune conditions, as informed by a range of stakeholders in the autoimmune health community.
Methods: We convened a steering committee (SC) of clinicians and patients with representation from rheumatic diseases (PsA, RA, vasculitis), inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis. Through literature review and iterative discussions, SC members identified 33 vaccine uptake/hesitancy research topics in four domains. A larger multistakeholder group including patients and patient advocates (Patients/Advocates); clinicians and researchers (Clinicians/Researchers); policy makers, regulators, and vaccine manufacturers (Other Stakeholders) was convened to conduct a modified online Delphi process with two rounds currently completed. In each round, group members rated each topic on a 9-point scale (1-3 = not important, 4-6 = important but not critical, 7-9 = critical) and could propose additional topics for inclusion in the next round. When completing round 2 (R2), participants were able to view their ratings from the previous round and view aggregate ratings from their respective stakeholder group before confirming or changing how they rated each topic. Frequency analysis and comparisons across the three stakeholder groups (Patients/Clinicians/Other) was conducted.
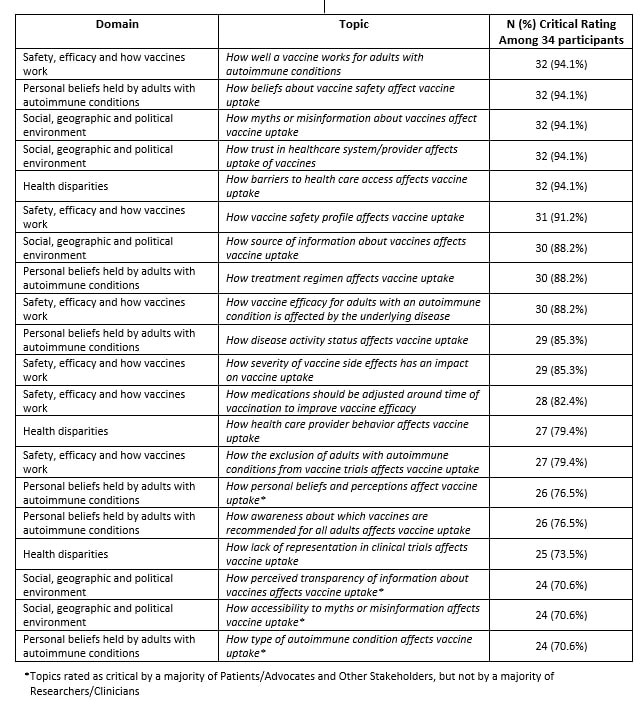
Results: A total of 34 stakeholders participated in both R1 and R2 of the Delphi to rate the 33 R1 and 34 R2 topics. Overall, six topics, representing at least one topic from each domain, were rated as critical by > 90% of stakeholders, including topics related to vaccine effectiveness in autoimmune disease, beliefs about safety, myths and misinformation, trust in the healthcare system, barriers to access, and vaccine safety profiles (Table 1). The Patient/Patient Advocate group unanimously rated three topics as critical: How myths or misinformation about vaccines affect vaccine uptake, How source of information about vaccines affects vaccine uptake, and How perceived transparency of information about vaccines affect vaccine uptake. The Researchers/Clinicians group unanimously rated How well a vaccine works for adults with autoimmune conditions as critical.
Conclusion: Topics identified as critical across stakeholder groups can inform future research efforts to decrease vaccine hesitancy and improve uptake of relevant vaccines for adults with autoimmune conditions, a high-priority group for vaccinations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Venkatachalam S, Nowell W, Banerjee S, Gavigan K, Stradford L, Gordon J, Emerich L, Sullivan H, Blazer A, Banbury B, Dronadula V, Weaver K, Degrassi A, Merkel P, McBurney R, Kappelman M, Curtis J, George M. Priority Research Topics for Vaccine Uptake Among Adults with Autoimmune Conditions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/priority-research-topics-for-vaccine-uptake-among-adults-with-autoimmune-conditions/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/priority-research-topics-for-vaccine-uptake-among-adults-with-autoimmune-conditions/