Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The management of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) comorbidities includes the metabolic syndrome (2). The latter includes steatotic liver disease (SLD) (3), which is present in approximately 40% of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) cases and approximately 30% in the global population of the United States but data is lacking in axSpA. The CT liver minus spleen ratio enables to determine the presence of macrovesicular steatosis of 30% or greater of the liver (1). The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence of liver steatosis in axSpA using CT scan.
Methods: This is a retrospective monocentric study including patients with axSpA meeting the ASAS 2009 criteria who underwent an abdominal CT-scan (Somatom 64 definition AS+, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany), without injection for any reasons. We obtained liver and spleen densities in Hounsfield units (HU) and used the CT liver minus spleen (L-S) attenuation ratios < - 10 to assess steatosis. To obtain the indices, hepatic attenuation and splenic attenuation were measured through the averaging of the Hounsfield units of different regions of interest (ROIs) in each parenchyma of the liver. Each ROI (1.5*1.5) was placed on 4 different sites (for the liver, 2 on the right lobe and 1 on the left lobe and one on the spleen). For each patient, we searched for the phenotype of the disease. Non-inclusion criteria were the existence of tumour lesion of the spleen and the liver and a history of hemochromatosis.
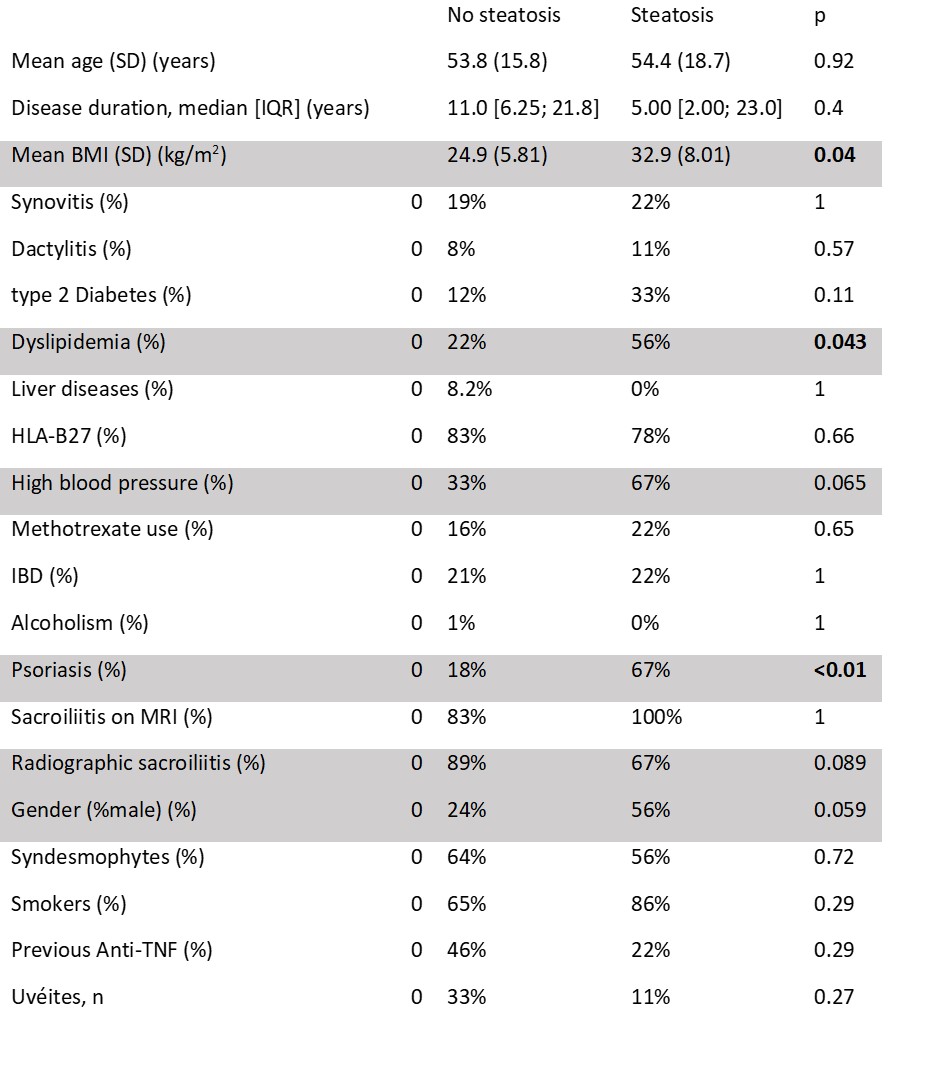
Results: We included 108 patients with axSpA with a mean age of 54.0 (16) years old and 15,3 (12.8) years of disease duration, 82% HLA B27+, 31% of uveitis, 22% of psoriasis, 21% of IBD, 87% with radiographic sacroiliitis, 66% with syndesmophyte, 72% of male, a mean BMI of 25,6 kg/m2 , 14% of type 2 diabetes and 68% were smoker. In total, 8,4% of patients had a liver-minus-spleen ratio < -10. The factors associated with the presence of liver steatosis (table) were the BMI (32.9 (8.0) VS 24.9 (5,8) kg/m2; p= 0.04), a dyslipidemia (56% VS 22%; p=0.04), the female gender (56% VS 24%; p=0.059), the presence of skin psoriasis (67% VS 18%; p< 0.01) and a trend towards an association between the absence of radiodographic sacroiliitis and hepatic steatosis (67% VS 89%; p=0.08). The peripheral involvement, the notion of dactylitis, NSAIDs use and cs / bDMARDs use were not associated with the presence of liver steatosis.
Conclusion: Our study showed a low prevalence of liver steatosis in axSpA despite a high prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Female with higher BMI and psoriasis were more likely to develop liver steatosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Da silva L, Fakih o, chouk m, weil-verhoeven d, WENDLING D, PRATI C, VERHOEVEN F. Prevalence of Liver Steatosis in Axial Spondyloarthritis : A Retrospective Study Using Computed Tomography Liver Minus Spleen Attenuation Ratio [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-liver-steatosis-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-retrospective-study-using-computed-tomography-liver-minus-spleen-attenuation-ratio/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-liver-steatosis-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-retrospective-study-using-computed-tomography-liver-minus-spleen-attenuation-ratio/