Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, mainly caused by elevated serum uric acid (sUA) levels. The American College of Rheumatology guidelines recommend lowering sUA levels to <6 mg/dL for all patients with gout. Studies reported that elevated sUA levels are also associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is suggested that urate-lowering therapy, predominantly xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOIs), can potentially slow progression of renal disease. This study aims to estimate the prevalence of CKD among US adult patients with gout, both controlled (sUA <6 mg/dL) and uncontrolled (sUA ≥6 mg/dL), stratified by XOI treatment status.
Methods: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a large, cross-sectional study conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics using a multistage, complex sampling design. This study utilized NHANES (2007–2012) by combining interviews, physical examinations, and laboratory data. Participants aged ≥20 years with valid gout status, gender, race/ethnicity, and sUA/serum creatinine were included in the study sample. Participants were assumed to have gout if they had ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that they had gout. CKD stages were defined using both estimated glomerular filtration rate (estimated by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation) and albumin-creatinine ratio. CKD stages were grouped into “normal to Stage 2 CKD,” “Stage 3a CKD,” and “Stage 3b-5 CKD”. Descriptive analyses were performed accounting for the survey’s complex sampling design to estimate the US population from the study sample.
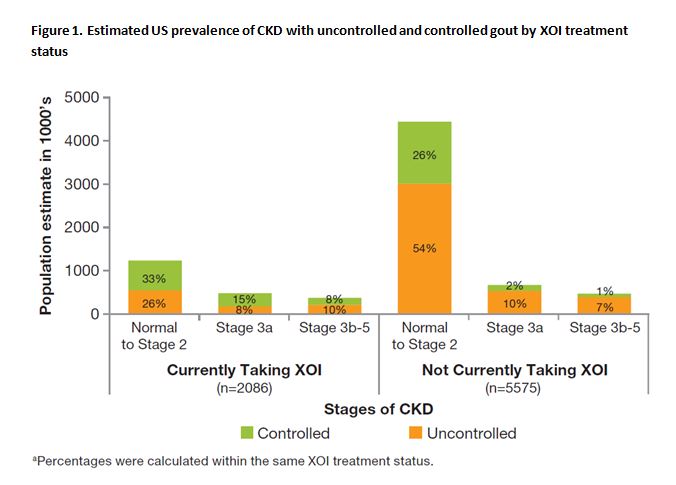
Results: Out of 15,868 participants in NHANES 2007–2012 (representing 206 M US non-institutionalized population, aged 20 years or older), 715 participants had been told by a doctor that they had gout. These participants represented an estimated total of 7.7 M with gout (US prevalence of 3.7%). Among the gout population, 5.7 M (74%) had kidney function of normal to Stage 2 CKD, 1.1 M (15%) had Stage 3a CKD, and 0.8 M (11%) had Stage 3b-5 CKD. Of the gout population, 22% with normal to Stage 2 CKD, 42% with Stage 3a CKD, and 44% with Stage 3b-5 CKD were currently taking an XOI, most of whom were taking allopurinol. The majority of gout patients were uncontrolled regardless of CKD stage (63% of those with normal to Stage 2 CKD, 62% of those with Stage 3a CKD, and 72% of those with Stage 3b-5 CKD). Among those taking an XOI, 34% were uncontrolled and had normal to Stage 3a CKD (Figure 1).
Conclusion: The majority of non-institutionalized US adults who self-report that they have been diagnosed with gout have uncontrolled gout regardless of CKD stage. Even among those patients with gout who are taking an XOI, 34% are uncontrolled and have normal to Stage 3a CKD, and therefore, may benefit from alternative treatment options indicated for their CKD stage.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lim JJ, Fu AC, Reasner DS, Taylor DCA. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease and Uncontrolled Serum Uric Acid Levels in US Adult Gout Population: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-chronic-kidney-disease-and-uncontrolled-serum-uric-acid-levels-in-us-adult-gout-population-results-from-the-national-health-and-nutrition-examination-survey-2007-2012/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-chronic-kidney-disease-and-uncontrolled-serum-uric-acid-levels-in-us-adult-gout-population-results-from-the-national-health-and-nutrition-examination-survey-2007-2012/