Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2524–2546) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis (CryoVas) is a rare immune-complex-mediated disorder, often associated with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, autoimmune diseases (ADs), or other etiologies. Despite its clinical relevance, data on the prevalence and diagnostic yield of cryoglobulin testing remain scarce. This study aims to evaluate the prevalence, clinical manifestations, outcomes, and underlying etiologies of CryoVas among patients with positive cryoglobulin tests over a 10-year period in a specialized laboratory.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective monocentric study analyzing all cryoglobulin tests performed in a specialized laboratory from 2013 to 2023. A total of 13,607 tests were performed, of which 1,593 (11.7%) yielded positive results, corresponding to 596 individual patients. Medical records were reviewed to confirm CryoVas diagnoses per classification criteria.
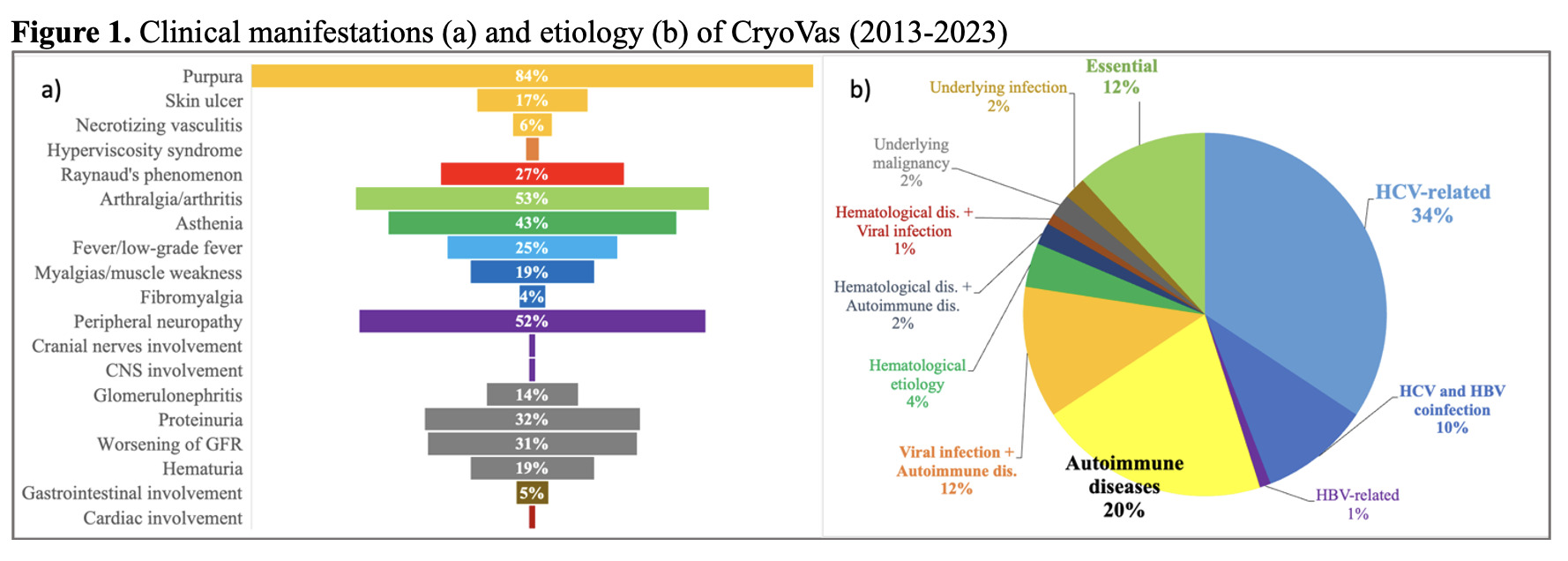
Results: Among 596 patients, 102 (17%) were diagnosed with CryoVas. Median age at onset was 65 years (IQR 56–73), with females comprising 65%. HCV-related CryoVas accounted for 34%, AD-related for 20% (mainly Sjögren’s disease, 67%), and essential CryoVas for 12%.CryoVas was diagnosed before 2013 in 40% of cases, 66% of whom had HCV/HBV. After 2017, with pan-genotypic HCV treatments, CryoVas incidence declined significantly (from 8.4 ± 1.7 to 3 ± 1.6 cases/year; p=0.001).At onset of CryoVas, median BVASv3 was 6 (IQR 2–9). Type I CryoVas more often presented with ulcers, necrotizing vasculitis (p=0.001), and hyperviscosity. Raynaud’s was more frequent in AD-related CryoVas (p=0.025). Glomerulonephritis and GI involvement were more common in essential CryoVas (p=0.011 and p=0.380, respectively). RF levels were higher in essential CryoVas (median 473 IU/L; p=0.010).Two-thirds of AD-related CryoVas patients received Rituximab (RTX), while Belimumab (BEL) was used exclusively in AD-related and essential CryoVas.Over a median 7-year follow-up (IQR 3–11), relapse occurred in 71% of AD-related CryoVas vs. 42% of others (p=0.097). Nearly one-quarter of AD-related patients were still on RTX at last follow-up. Although 94% achieved clinical remission, cryoglobulin clearance occurred in only 60%.
Conclusion: CryoVas remains a significant clinical condition, with its etiology progressively evolving in recent years.Treatment approaches varied by etiology, with RTX serving as a cornerstone for CryoVas associated with ADs, while BEL demonstrated potential in select cases.Despite advancements in treatment and high rate of complete clinical response, relapse rates remain high, particularly in autoimmune-related CryoVas. Additionally, cryoglobulin clearance was achieved in approximately 60% of patients during follow-up, reflecting a partial immunological response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Manfrè V, treppo e, Pillon M, De Martino M, Fabro C, Isola M, Fabris M, Curcio F, Quartuccio L. Prevalence, Clinical Correlations and Outcomes of Cryoglobulinemic Vasculitis: a Retrospective Monocentric Study (2013–2023) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-clinical-correlations-and-outcomes-of-cryoglobulinemic-vasculitis-a-retrospective-monocentric-study-2013-2023/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-clinical-correlations-and-outcomes-of-cryoglobulinemic-vasculitis-a-retrospective-monocentric-study-2013-2023/

.jpg)