Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1467–1516) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease with multisystem involvement. A rare but life-threatening hyper-inflammatory hematological complication of SLE is hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). This study aims to determine the prevalence of HLH among SLE patients and to compare clinical characteristics and outcomes between SLE patients with and without HLH.
Methods: In this study, we utilized data from the TriNetX global research network, which includes electronic medical records from 101 healthcare organizations. Our search in the TriNetX yielded 130,187 patients with SLE (ICD-10: M32), of which 448 patients had a diagnosis of HLH (ICD-10: D76.1) and 129,739 did not have an HLH diagnosis. Propensity score matching was performed using 59 demographic and clinical variables, yielding two well-balanced cohorts of 443 patients each. Variables studied included baseline patient demographics, clinical manifestations/comorbidities, and autoantibody profile. Outcomes analyzed included mortality, laboratory findings, and medication usage. Kaplan-Meier curve and log-rank test were used for survival analysis. Statistical significance was defined as a p-value of < 0.05.
Results: The prevalence of HLH among the general SLE population was 0.34%. Prior to propensity matching, higher rates of HLH were seen in males (26.1% vs 13.4%), African-American (35.3% vs 24.7%) and Asian populations (16.1% vs 7.5%) (all p-values < 0.001). Clinical manifestations such as glomerular disease, anti-phospholipid syndrome, seizures & epilepsy, and pericarditis (all p-values < 0.001) as well as pleurisy (p=0.008) were seen more frequently in HLH patients before propensity matching (Table 1).After matching, SLE patients with HLH were significantly more likely to have positive Ro/SSA (14.9% vs. 7.2%), RNP (11.3% vs. 4.3%) autoantibodies, low C3 complement (44.7% vs. 29.3%) and low C4 complement (30.5% vs. 20.1%) (all p values < 0.001) (Table 2).Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed that HLH is a significantly poor prognostic factor in SLE patients , with diminished survival probability compared to patients without HLH (HR: 2.62, 95% CI: 1.67-4.1, p< 0.001). During the study period, 14.7% of patients with HLH died and 6.1% of patients without HLH died (RR: 2.41, 95% CI: 1.57-3.70) (Figure 1A & 1B).
Conclusion: HLH is an uncommon but clinically significant complication of SLE, associated with hypocomplementemia, distinct autoantibody patterns, and markedly increased mortality. These findings underscore the need for heightened clinical awareness and timely intervention in SLE patients presenting with features suggestive of HLH.
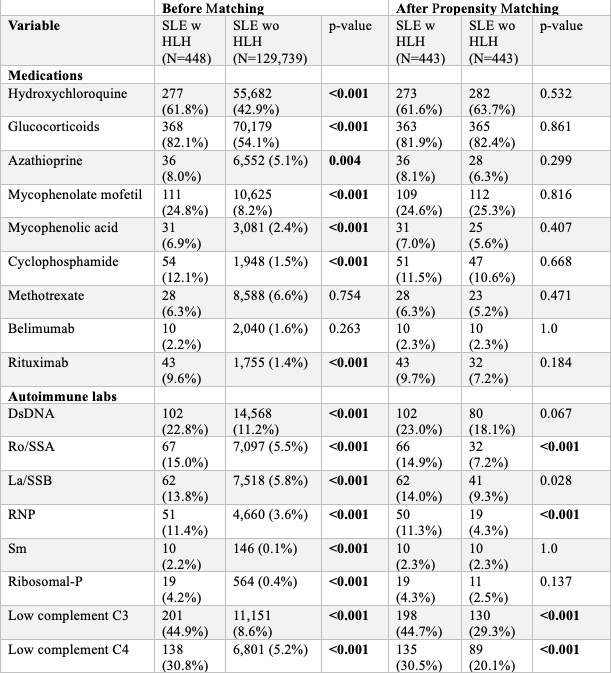 Table 1: Demographic Characteristics and Clinical Manifestations/Comorbidities of Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Before and After Propensity Matching.
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics and Clinical Manifestations/Comorbidities of Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Before and After Propensity Matching.
.jpg) Table 2: Medication Treatment and Autoantibody Profile of Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Before and After Propensity Matching.
Table 2: Medication Treatment and Autoantibody Profile of Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Before and After Propensity Matching.
.jpg) Figure 1A: Survival Probability in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Using Kaplan-Meier Survival Analysis
Figure 1A: Survival Probability in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Using Kaplan-Meier Survival Analysis
Figure 1B: Mortality Rate Data in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With and Without Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Daneshvar A, Wajsberg J, Guan C, Pfeil K, Harper E, Frumker L, Gump M, Pamuk O. Prevalence and Clinical Outcomes of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Multi-Institutional Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-and-clinical-outcomes-of-hemophagocytic-lymphohistiocytosis-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-multi-institutional-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-and-clinical-outcomes-of-hemophagocytic-lymphohistiocytosis-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-multi-institutional-cohort-study/
