Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster IV
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) have emerged as an effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), improving patients’ quality of life throughout the disease course. However, there is a significant proportion of patients who fail to respond to biologics. Identifying the predictors that may affect the response to biologics remains challenging.
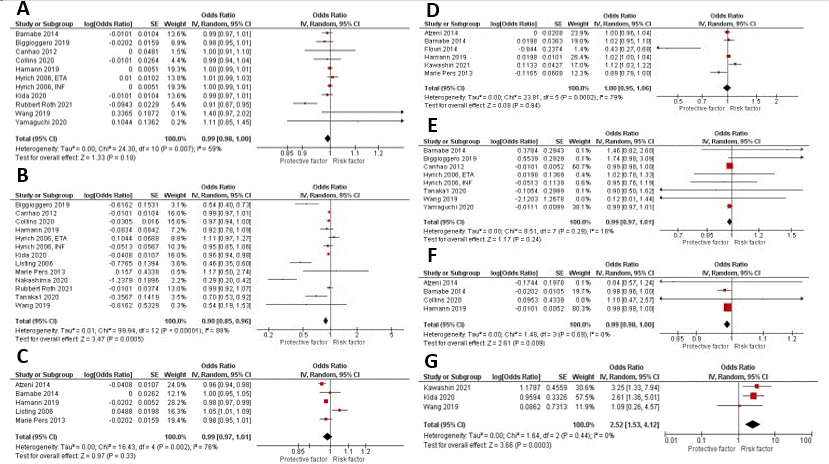
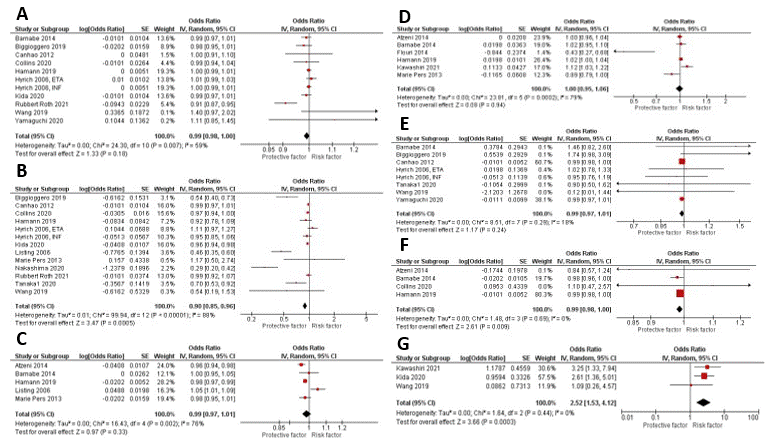
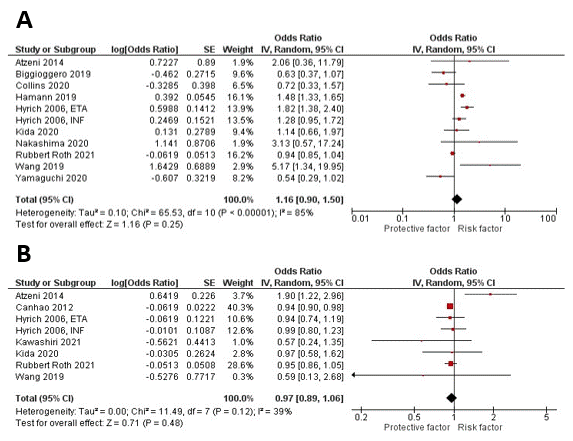
Methods: A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases was conducted through May 01, 2022. We included all studies that used a multivariate model to assess for the predictors of remission in RA patients treated with biologics. We calculated pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for risk factors reported in ≥3 studies using a random-effects model. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was performed for risk factors reported by ≥10 studies to evaluate the robustness of our results.
Results: A total of 16,934 patients with RA who were treated with biologics were included in twenty-one studies. Fifteen different risk factors were reported in a multivariate model in ≥3 studies. Meta-analysis showed that old age (OR 0.98 (0.97, 0.99), P < 0.00001), female gender (OR 0.66 (0.56, 0.77), P < 0.00001), smoking history (OR 0.86 (0.75, 0.99), P 0.04), BMI >30 kg/m2 (OR 0.95 (0.91, 0.99), P 0.02), baseline HAQ >2 (OR 0.62 (0.48, 1.27), P < 0.00001), high disease activity at the time of diagnosis (OR 0.90 (0.85, 0.96), P 0.0005), and elevated ESR (OR 0.99 (0.98, 1.00), P 0.009) were poor predictors of remission. On the other hand, positive ACPA (OR 2.52 (1.53, 4.12), P 0.0003) was associated with high remission rate. However, presence of comorbidities (OR 0.77 (0.51, 1.15), P 0.20), disease duration > 10 years (OR 0.99 (0.98, 1.00), P 0.18), high TJC (OR 0.99 (0.97, 1.01), P 0.33), high SJC (OR 1.00 (0.95, 1.06), P 0.94), positive RF (OR 0.99 (0.97, 1.01), P 0.24), prior use of steroids (OR 0.97 (0.89, 1.06), P 0.48), and prior use of MTX (OR 1.16 (0.9, 1.5), P 0.25) were not associated with significant decrease or increase in remission rate. The results remained consistent on the sensitivity analysis for increased age, female gender, prior use of MTX, increased disease duration, and disease activity.
Conclusion: Old age, female gender, obesity, smoking history, poor functional status, high disease activity, and elevated ESR at the time of diagnosis have been associated with poor response to biologics. While positive ACPA was associated with higher remission rate. These predictors should be taken into consideration before starting medications with known serious side effects like biologics. Our findings could help establish a risk stratification model for predicting the remission rate in RA patients receiving biologics.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khader Y, Beran A, Ghazaleh S, Fatima R, Acharya A, Altorok N. Predictors of Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Biologics: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-remission-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-biologics-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-remission-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-biologics-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/