Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Clinical Manifestations
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Repeat renal biopsies are considered in patients with Lupus Nephritis (LN) flares or with failure of response to treatment. The influence of repeat renal biopsies on decisions of further management in LN flares has been debated. We assessed biochemical, pathological and demographic factors and evaluated their impact on risk of repeat renal biopsies. The role of repeat biopsies in further management of LN flares was also assessed.
Methods: Of the 66 biopsy-proven LN patients identified at two institutions in New York from 2000-2019, 16 were identified to have repeat renal biopsies. LN classes were identified based on the 2003 ISN/RPS Classification and tubulointerstitial pathology was defined by use of NIH LN Activity and Chronicity Indices. A logistic regression model and Wilcoxon signed-rank test were used to analyze the data. P value < 0.05 was deemed to be statistically significant.
Results: Repeat renal biopsies showed that a majority of patients (81%) did not transition between proliferative (class III, IV) and non-proliferative (class II, V) classes of LN. Only 18% of patient’s showed a transition from non-proliferative to proliferative class and none of the patient’s transitioned from proliferative to non-proliferative class of LN. All patients with a class switch to a proliferative type of LN were seen to have an escalation in immunosuppressive therapy. Escalation of immunosuppressive therapy was seen in 77.7% of patients with LN flares having no class switch between non-proliferative and proliferative. There was a statistically significant progression of chronicity index (mean ± SD) from initial (4.2 ± 2.77) to repeat (7.2 ± 2.58) biopsy, P = 0.043.
The logistic regression model had a 96.9% correct prediction, indicating that the model is highly successful in predicting the outcome. The Chi-square probability value was < 0.0005 and McFadden Pseudo R2 value >0.5, indicating the model is a good fit. The results indicated that sex, age at SLE diagnosis, quality of first biopsy, urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) at time of biopsy or Class III LN on initial biopsy influenced either positively or negatively the probability of a repeat renal biopsy. Females are 10% less likely to have repeat biopsies than their male counterparts, P = 0.022. Patient risk of repeat biopsy increased by 0.29% with every 10 year increase of age at SLE diagnosis, P = 0.029 and reduced with increase in number of glomeruli in initial biopsy, P = 0.042. Identification of Class III LN on initial biopsy decreased risk of repeat by 96.9% when compared to Class II and V (P = 0.03); Class IV LN showed no significant correlation. Higher UPCR at time of biopsy increased the risk of repeat biopsy, P = 0.037.
Conclusion: Demographic, serological and pathological factors can be used to assess likelihood of patients requiring repeat renal biopsies in the future. A majority of patient’s did not switch between non-proliferative and proliferative classes of LN on repeat biopsy, however most of these patient’s still had an escalation of immunosuppressive therapy. This study shows that there is little relation between repeat renal biopsy findings in LN flares and its use as a tool in determining further management in LN flares
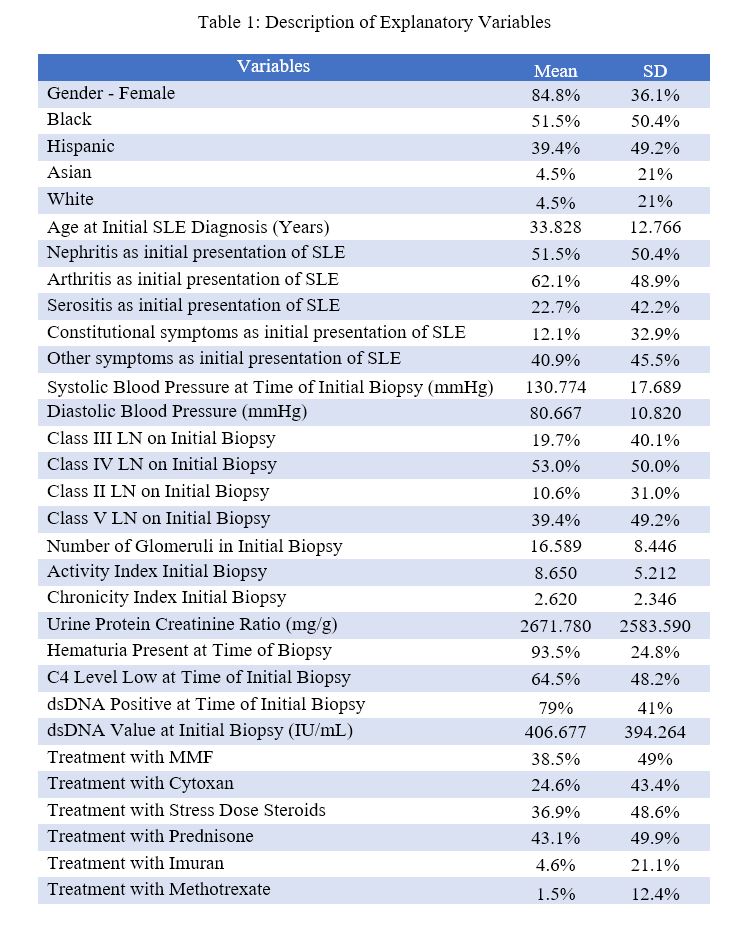 Description of Explanatory Variables
Description of Explanatory Variables
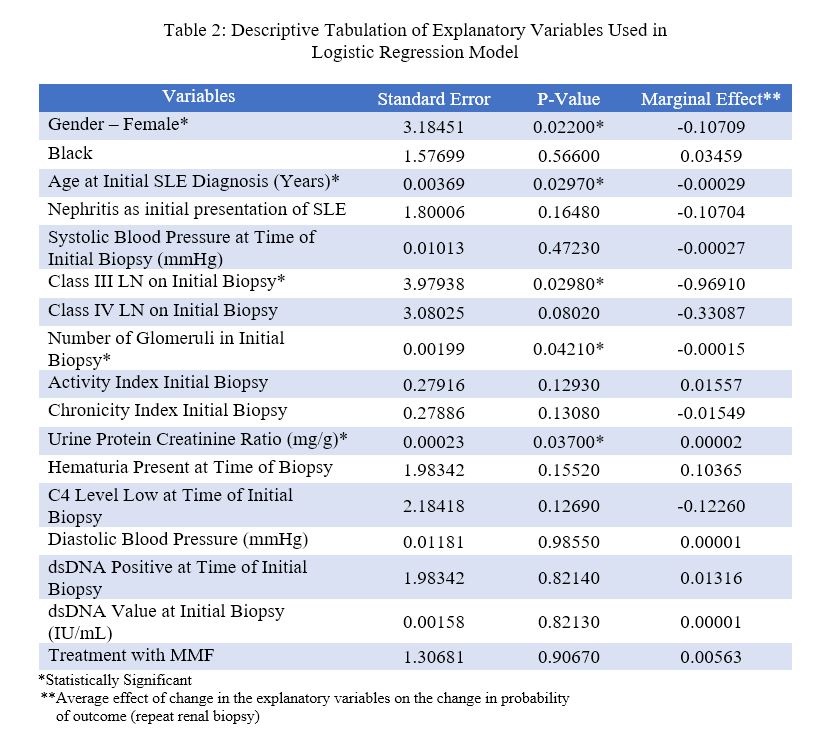 Descriptive Tabulation of Explanatory Variables in Logistic Regression
Descriptive Tabulation of Explanatory Variables in Logistic Regression
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santana-Flores R, Ramu A, Rajevac H, Jim B. Predictors of Future Repeat Renal Biopsies in Patients with Lupus Nephritis and Influence of Repeat Biopsy in Flare Management: A Retrospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-future-repeat-renal-biopsies-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-and-influence-of-repeat-biopsy-in-flare-management-a-retrospective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-future-repeat-renal-biopsies-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-and-influence-of-repeat-biopsy-in-flare-management-a-retrospective-study/
