Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Inflammatory Arthritis – RA, SpA, & Gout (0560–0593)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patient characteristics including serostatus, body mass index (BMI), and smoking are considered to be associated with their response to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARD) treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA); however, previous real-world studies using claims data failed to identify factors strongly related to biologic DMARD treatment patterns. We utilized a linked database of claims and electronic health records (EHR) to explore how additional factors derived from the clinically rich EHR data may play a role in predicting
Methods: We used Optum Market Clarity database which linked pharmacy and medical claims with continuous, longitudinal EHR data from 01/01/2011 to 09/30/2019. We identified adults with RA who initiated a TNFi from prescription or procedure records. The first TNFi prescription date was defined as index date. Patients were required to have at least two RA diagnosis codes without any biologic or targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs during 365-day pre-index baseline period. One-year continuous clinical activity were required before and after the index date. Outcomes were assessed during one-year post-index period. The primary outcome was any treatment change defined as having a different TNFi or switching to non-TNFi biologic or tsDMARDs. The secondary outcomes were the individual components of the primary outcome and non-persistence. Treatment non-persistence was defined as having no subsequent refill of the index TNFi or other biologics/tsDMARDs. Multivariable logistic regression with pre-defined variables and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression model were used as prediction models. C-statistics of each model and odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals of predictors were reported.
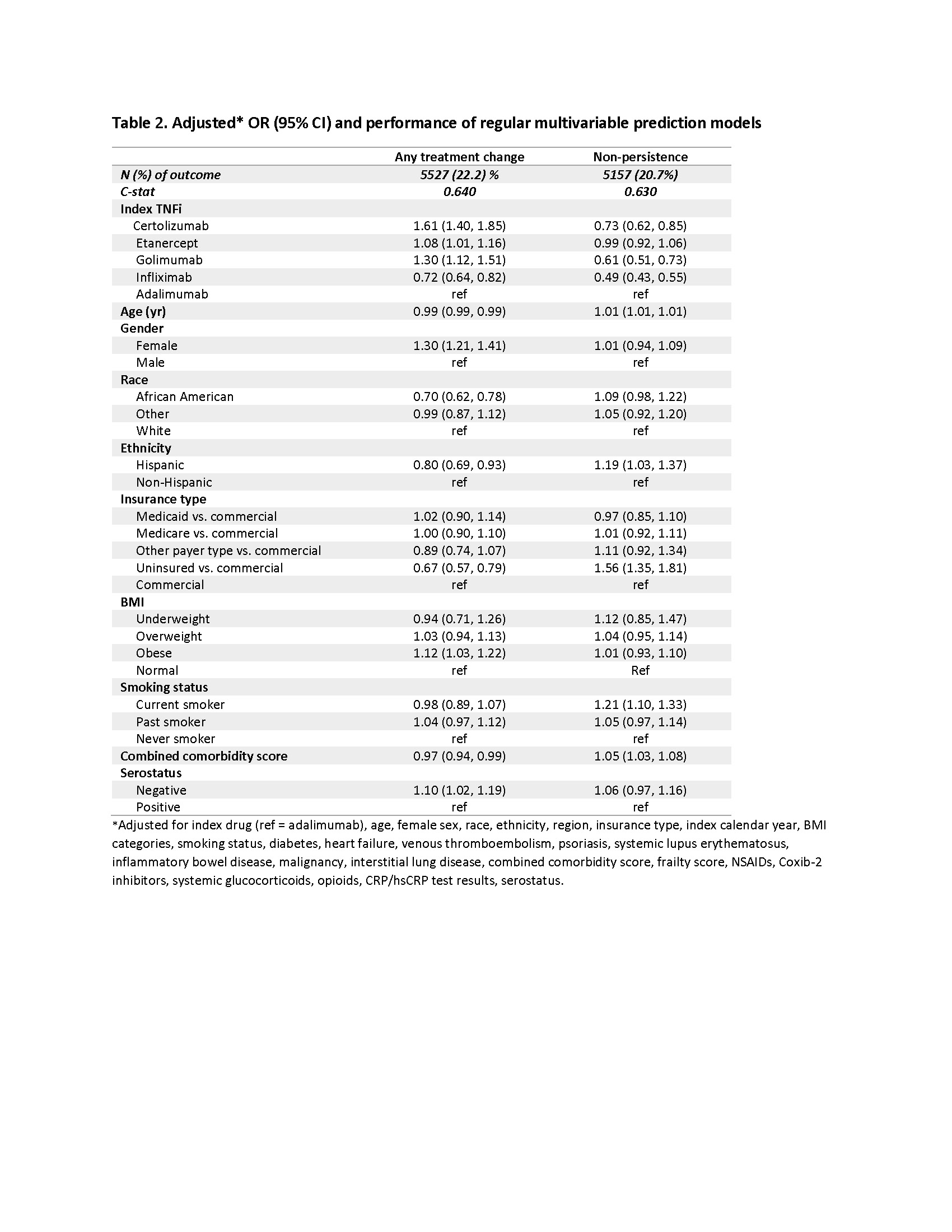
Results: We identified 24,871 RA cohort who initiated TNFi: 10,471 adalimumab, 1,166 certolizumab pegol, 9,391 etanercept, 1,037 golimumab, and 2,806 infliximab initiators. The mean age was 55.5 (±13.7) years and 77.2% were female. 83% were White, and 53.3% were covered by commercial insurances. 30.9% of the study patients were seropositive (Table 1). During the one-year after index TNFi initiation, 5,527 (22.2%) patients had either TNFi cycling or switching to non-TNFi/tsDMARDs. Specifically, 3,870 (15.6%) had TNFi cycling, 1,646 (6.6%) switched to non-TNFi biologics, and 780 (3.1%) switched to tsDMARDs. 5,157 (20.7%) were non-persistent users. In multivariable logistic regression models, index TNFi, gender, race, and insurance types were predictors of the treatment changes (Table 2). Model performance was similar between the regular and LASSO regression models. Adding EHR-specific factors, including BMI, smoking status, and serology tests improved the prediction models to some extent but the model performance was still suboptimal (c-statistics 0.64).
Conclusion: Predicting treatment change in RA patients with both claims and clinically rich EHR data still remains challenging. It could be due to unmeasured factors such as prescriber’s preference or patient’s belief in the medication which may play an important role in the treatment patterns.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jin Y, Landon J, Krueger W, Liede A, Kim S. Predicting Treatment Change in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with TNF Inhibitors as First-Line Biologic Agent [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-treatment-change-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tnf-inhibitors-as-first-line-biologic-agent/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-treatment-change-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tnf-inhibitors-as-first-line-biologic-agent/