Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy IV: Biomarkers
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: The ORBIT study demonstrated that rituximab is non-inferior to a TNFi-first strategy in biologic naive, sero-positive patients with active RA over 12 months (Lancet doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00380-9). However, a significant proportion of patients failed to respond to their first biologic drug and switched to an alternative. The ability to identify and stratify these patients prior to treatment would improve patient care and optimise the use of scarce financial resources. The aim of this study was to identify peripheral blood transcriptional biomarkers in the ORBIT cohort that can predict subsequent response/non-response to biologic therapy.
Methods: RNA was sequenced (Illumina NextSeq 500) from the peripheral blood of 241 patients recruited to the ORBIT study, after depletion of ribosomal and globin RNA. 70% (n=169) of samples were used to develop response prediction models, and 30% (n=72) were reserved for validation. Clinical response was defined as a fall in DAS28-ESR of >1.2 units between baseline and three months. Multiple machine learning techniques were used to train models that predicted 1) general responsiveness to both TNFi and rituximab therapy 2) differential response to TNFi or rituximab therapy. Tenfold cross validation was used to train the models, which were then tested on the validation set.
Results: Three gene sets were identified using support vector machine (SVM) recursive feature elimination. These predicted: general responsiveness to both TNFi and rituximab therapy (8 genes), response to TNFi therapy (23 genes) or rituximab (23 genes) respectively. When tested on the validation set, these models resulted in ROC plots with an AUC of 91.6% for general responsiveness, 89.7% for TNFi response, and 85.7% for rituximab response. 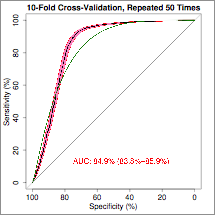
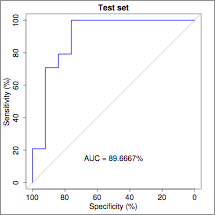 ROC plot showing the performance of the 25-feature SVM RBF classifier predicting specific response of TNFi therapy. When the drug specific models were combined, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV for response prediction at 3 months were 96%, 91%, 96% and 92%, respectively. Patients who were predicted to respond at three months were also more likely to have a DAS28 good response (43% v 23%) or DAS28 remission (23% v 10%) at 12 months.
ROC plot showing the performance of the 25-feature SVM RBF classifier predicting specific response of TNFi therapy. When the drug specific models were combined, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV for response prediction at 3 months were 96%, 91%, 96% and 92%, respectively. Patients who were predicted to respond at three months were also more likely to have a DAS28 good response (43% v 23%) or DAS28 remission (23% v 10%) at 12 months.
Conclusion: At baseline, whole blood transcriptomic profiles of biologic naive patients with sero-positive RA predict future responsiveness to TNFi and rituximab therapy. These signatures needs to be validated but if they prove to be robust they will herald a new stratified approach to treatment selection resulting in improved patient outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Porter D, Goodyear CS, Nijjar JS, Messow M, Siebert S, Mudaliar M, McInnes IB. Predicting the Response to TNF Inhibition or B Cell Depletion Therapy from Peripheral Whole Blood Gene Expression Profiles in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-the-response-to-tnf-inhibition-or-b-cell-depletion-therapy-from-peripheral-whole-blood-gene-expression-profiles-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-the-response-to-tnf-inhibition-or-b-cell-depletion-therapy-from-peripheral-whole-blood-gene-expression-profiles-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/
