Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Mice bearing
mutations affecting Kit (stem cell factor receptor) exhibit multiple
hematologic phenotypes, including mast cell deficiency, and have been used to assess
the role of mast cells in K/BxN arthritis. We observed that arthritis
susceptibility in disease-resistant KitW/Wv mice could be rescued not
only by engraftment of cultured mast cells, but also by marrow from mast
cell-deficient KitWsh/Wsh mice, implicating another lineage in
addition to mast cells in the KitW/Wv phenotype.
Methods: Unirradiated KitW/Wv
were engrafted with bone marrow from mice deficient in key lineages
determinants (GFI-/-, IL-1-/-, NF-E2-/-, and
GPVI-/-). 14 days after transfer, arthritis was initiated with i.p.
injection of 150μl of serum from K/BxN mice on day 0 and day 2. Arthritis
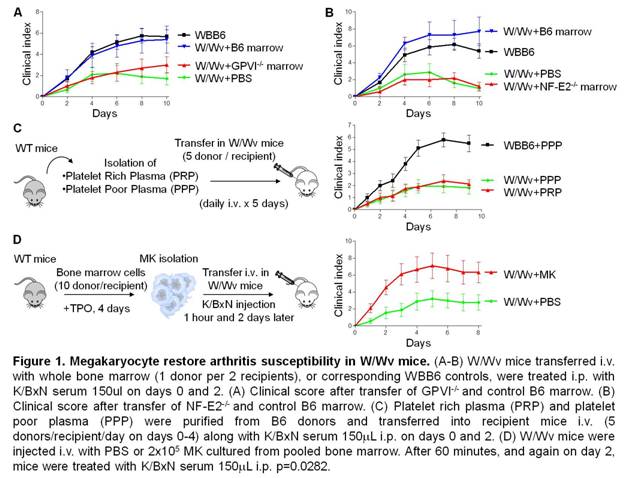
was graded on a 0-12 clinical scale. In other experiments, KitW/Wv were engrafted i.v. with lineages of interest, including bone marrow neutrophils, platelets, and megakaryocytes (MK), prior to arthritis induction. MK were generated by culturing bone marrow cells with medium supplemented with 1% supernatant from the TPO-producing fibroblast cell line GP122.
Results: Neutrophils transfer
failed to restore arthritis in KitW/Wv, yet transfer of marrow from neutrophil-deficient
mice GFI-1-/- restored arthritis as well as WT B6 marrow, confirming
that neutropenia is not a critical basis for arthritis resistance in KitW/Wv.
Instead, overcoming arthritis resistance in KitW/Wv required donor
marrow expressing IL-1 and the platelet/MK lineage determinants GP-VI and NF-E2
(Figure 1A-B), suggesting that platelet is the lineage that restores arthritis
in KitW/Wv. However, KitW/Wv mice are not
thrombocytopenic, and platelet transfer failed to restore arthritis in these
mice (Figure 1C). Because KitW/Wv are megakaryocytopenic, we
considered the possibility that restoration of arthritis might be mediated
directly by MK. Indeed, we found that MK produce IL-1 rich microparticles capable
of stimulating fibroblast-like synoviocytes in manner dependent on IL-1
receptor expression. In confirmation, we found that engraftment of MK
relatively incompetent in platelet production could fully restore arthritis
susceptibility in KitW/Wv (Figure 1D).
Conclusion: This study identifies
megakaryocytes – likely independent of daughter platelets, but potentially
mediated by MK microparticles – as a previously unrecognized participant in
arthritis, and more generally, as a highly novel actor in IL-1-mediated
systemic disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cunin P, Penke L, Thon J, Monach PA, Jones T, Chen M, Iwakura Y, Ware J, Gurish M, Italiano J, Boilard E, Nigrovic PA. Platelet-Independent Role of Megakaryocytes in Antibody-Mediated Murine Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/platelet-independent-role-of-megakaryocytes-in-antibody-mediated-murine-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/platelet-independent-role-of-megakaryocytes-in-antibody-mediated-murine-arthritis/