Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Diagnosis and Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), sarcopenic obesity is associated with significant cardiometabolic disease and mortality. Biomarkers of disease activity in RA and obesity are complicated by inflammation associated with both conditions. The microRNA miR-146a is implicated as a biomarker in both RA pathogenesis and adiposity. However, it is unclear whether systemic miR-146a is impacted primarily by autoimmunity or obesity in RA. Here, we investigated relationships of miR-146a with RA disease activity, body composition and metabolic intermediates associated with obesity.
Methods:
All RA patients in this study satisfied 1987 ACR criteria. Plasma miR-146a-5p expression was measured via PCR as delta cycle threshold (ΔCt) using a reference microRNA sequence in 48 persons with RA and 23 age-, sex- and BMI-matched healthy controls. Plasma acylcarnitine and amino acid measurements were made via flow injection tandem mass spectrometry. Body composition was assessed using CT scan analyses to determine central and muscle adipose and thigh muscle tissue size and tissue density. Disease activity in RA was assessed by DAS-28-ESR. Plasma miR-146a-5p was compared in RA versus control subjects using the Wilcoxon signed rank test. Correlations were evaluated using SpearmanÕs rho. Strengths of associations for the two groups were compared with Fisher r-to-z transformations.
Results:
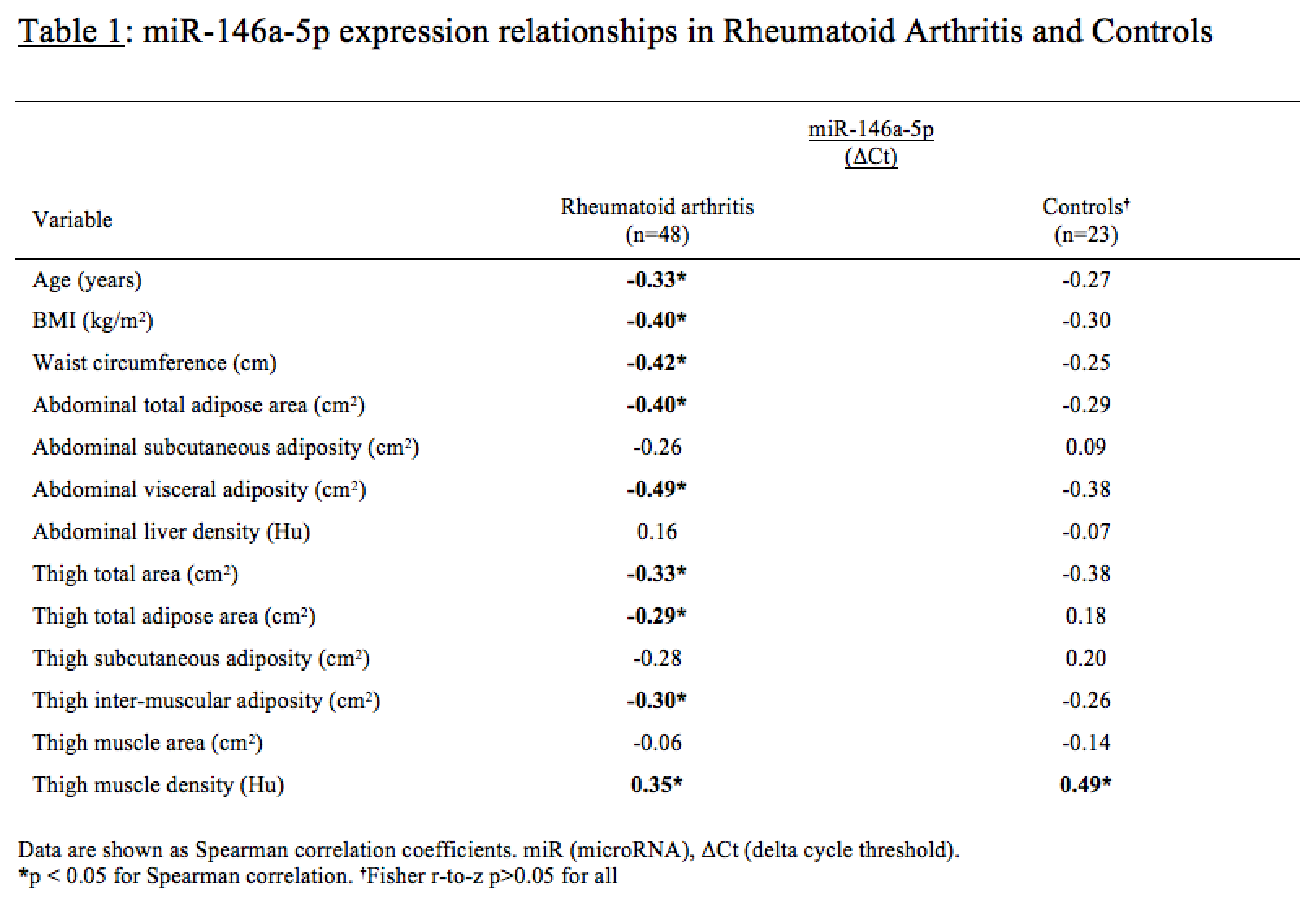
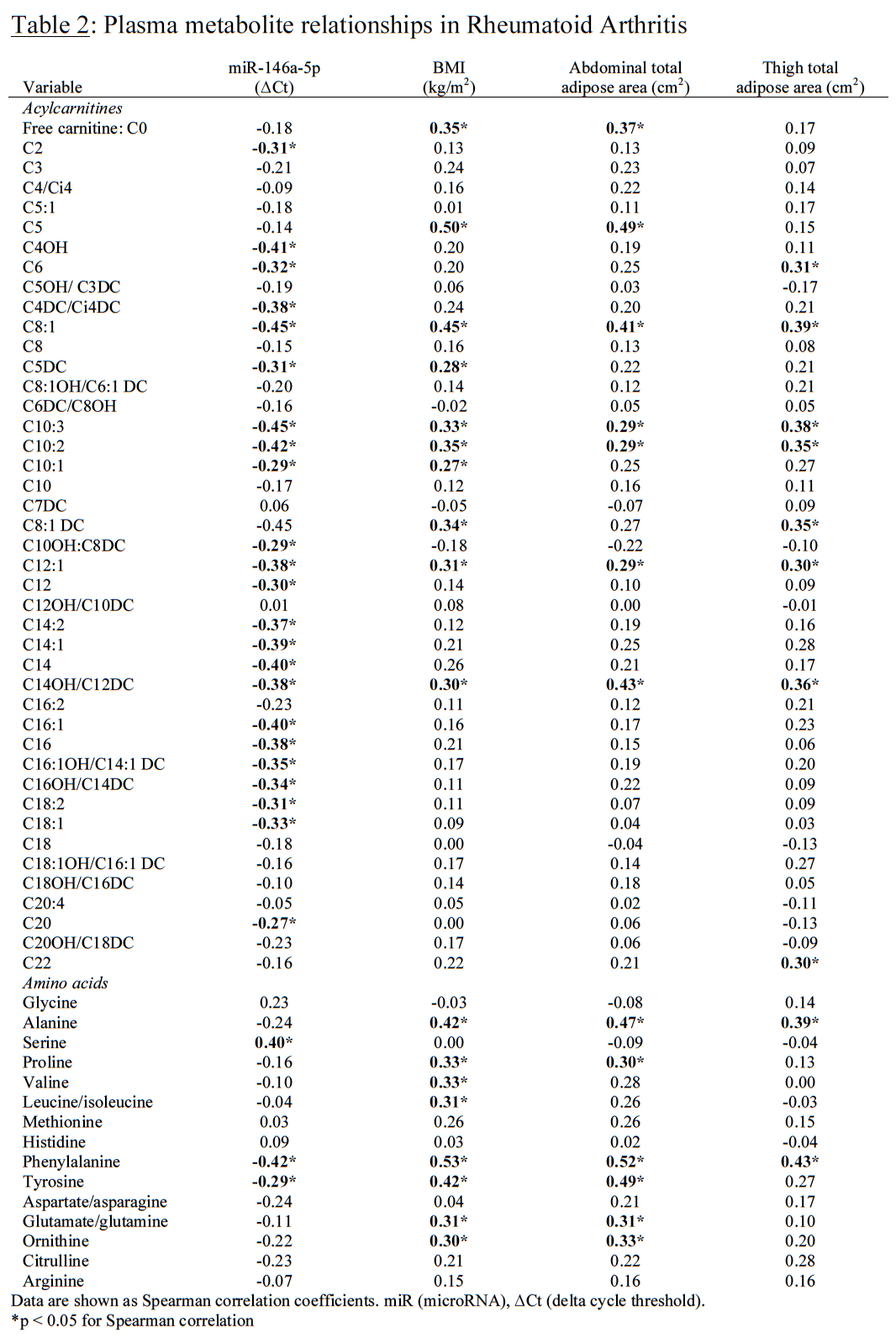
There was no significant difference in plasma miR-146a-5p expression between RA (-0.158±0.98(SD) ΔCt) versus controls (-0.086±1.53 ΔCt; p=0.69). miR-146a-5p was not correlated with RA disease activity (r=-0.03, p=0.84). In RA, greater expression of miR-146a-5p was associated with younger age, lower BMI, smaller waist circumference, less adiposity, and greater thigh muscle density (Table 1). Body composition correlations were not significantly different between groups (Fisher r-to-z p>0.05 for all). In RA, greater miR-146a-5p was also associated with lower concentrations of adiposity-related (Newgard et al. Cell Metabolism (2009); 9: 311–326) metabolic intermediates, acylcarnitines and branched chain amino acids (Table 2).
Conclusion:
Greater plasma miR-146a-5p was associated with multiple indicators of reduced adiposity: smaller central and thigh fat areas, less intra-muscular adiposity, and less circulating adiposity-related metabolic intermediates. Plasma miR-146a-5p expression in RA was similar to controls and not associated with DAS-28 scores. These findings suggest that rather than disease activity, in established RA, plasma miR-146a-5p inversely reflects adiposity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Andonian BJ, Chou CH, Kraus VB, Kraus WE, Huffman KM. Plasma Mir-146a-5p Associates with Beneficial Body Composition and Plasma Metabolic Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/plasma-mir-146a-5p-associates-with-beneficial-body-composition-and-plasma-metabolic-profiles-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/plasma-mir-146a-5p-associates-with-beneficial-body-composition-and-plasma-metabolic-profiles-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/