Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Shared decision making, a cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) management1, allows physicians and their patients to make informed decisions about their treatment goals and choice of care. As new treatments become available, it is important to understand rheumatologists’ reasons for choosing Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi), rheumatologist and patient satisfaction and alignment with this choice in patients with RA.
Methods: The Adelphi RA Disease Specific Programme™2 is a large, multinational, point-in-time survey conducted amongst rheumatologists and their consulting patients with RA in Europe (Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK) between January and October 2020.
Physicians completed record forms for up to 10 consecutive RA patients, collecting demographic, clinical and treatment data, and reasons for current treatment choice. Patients were invited to complete a patient questionnaire to assess their satisfaction with ongoing treatment (5-point scale), and perceptions of shared decision making for the current treatment.
Results: 316 rheumatologists provided data for 3121 patients, of whom 1130 (36.2%) completed patient reported questionnaires. Overall, 67% were female, mean age was 53 years (SD 14), 23% had moderate-high disease activity score (DAS28: >3.2). 68% of patients were currently receiving either a biologic or targeted synthetic DMARD (defined here as advanced therapy, AT), 72% were on first line AT.
Overall, physicians and their patients were aligned that a conversation took place about a treatment decision (n=855, 79% net alignment), and this was a shared treatment decision (n=814, 75% net alignment).
15% of patients not taking an AT were reported to have a clinical condition warranting one; reasons for not taking AT included patients’ concerns about infection (24%), csDMARDs were tolerable and safe in the patient (18%), and patient dislike of infusions/injections (17%).
Of 2143 patients receiving AT, 19% were prescribed JAKi; 57% as monotherapy, 43% as combination therapy. For physician stated reasons for choice of JAKi, factors were driven by both perceptions of clinical efficacy and onset of action, as well as factors relating to patient acceptability such as method of delivery and ease of use (Figure 1).
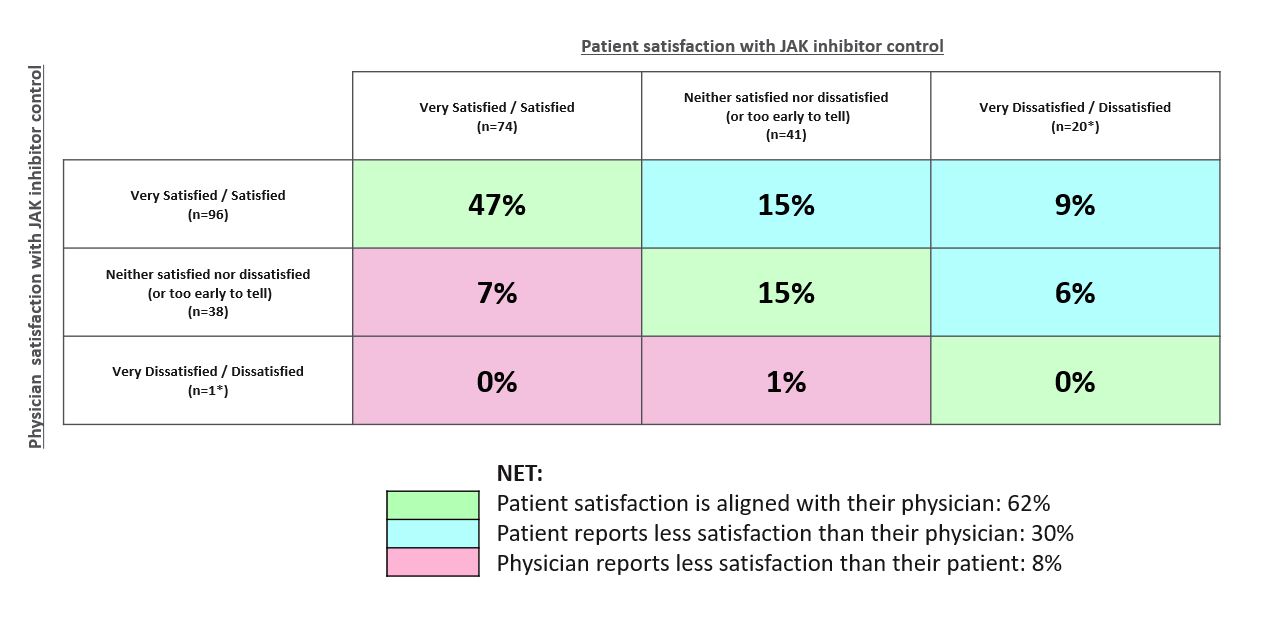
With respect to JAKi treatment (n=135 patient-physician pairs), 62% of physicians and their patients were aligned on satisfaction, however 30% of patients reported less satisfaction than their consulting physician (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Communicating the choice of pharmacological therapy to patients with RA has become increasingly complex for physicians with expansion of approved treatments. In this subgroup of patients on JAKi, the drug attributes considered as reasons for prescribing were driven by clinical factors as well as by patient centric attributes. Although communications between patients and physicians were largely aligned, better understanding of patient expectations might serve to improve messaging about treatment options and resulting satisfaction.
References:
1. Smolen JS, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76.
2. Anderson P, et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24(11):3063-3072.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Fautrel B, Piette Y, Romero-Yuste S, Broen J, Welcker M, Holdsworth E, Zignani M, Van Beneden K, Caporali R, Alten R. Physicians’ Reasons for Prescribing Janus Kinase Inhibitors (JAKi) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Associated Alignment Between Physicians and Patients in a Real-world Clinical Setting [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physicians-reasons-for-prescribing-janus-kinase-inhibitors-jaki-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-associated-alignment-between-physicians-and-patients-in-a-real-world-clinical-sett/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physicians-reasons-for-prescribing-janus-kinase-inhibitors-jaki-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-associated-alignment-between-physicians-and-patients-in-a-real-world-clinical-sett/