Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies - Poster I: Clinical Practice
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Verinurad (RDEA3170) is a novel selective uric acid reabsorption inhibitor in clinical development for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. This Phase 1, single-blind, multiple dose, drug-drug interaction study evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of verinurad in combination with allopurinol (ALLO) in adult male subjects with gout.
Methods: Adult males with gout, aged 18-75 years, with serum uric acid (sUA) ≥8 and ≤10 mg/dL were randomized to receive once-daily oral doses of ALLO 300 mg or verinurad 10 mg alone for 7 days, ALLO 300 mg + verinurad 10 mg on Days 8−14, and the alternative single agent (verinurad 10 mg or ALLO 300 mg) on Days 15−21. Colchicine 0.6 mg was taken once daily from day −14. Serial plasma/serum and urine samples were drawn at predetermined time points on Days 7, 14 and 21 and assayed for verinurad, ALLO, oxypurinol (OXY), colchicine, and uric acid. Baseline samples were drawn on Day –1. Safety was assessed by adverse event (AE) reports, laboratory tests, vital signs, and electrocardiograms (ECGs).
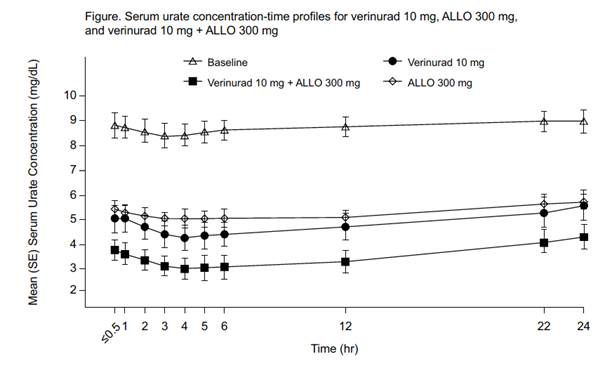
Results: Subjects (N=12) were mostly white (58.3%) with mean (SD) age of 51 (10) years. Following multiple doses, ALLO had no effect on Cmax and AUC of verinurad. ALLO Cmax was increased 33% but AUC was unaltered by verinurad. The Cmax and AUC for OXY, the active metabolite of ALLO, were reduced 32% and 38%, respectively, by verinurad. Colchicine plasma exposures were unaltered by verinurad. ALLO had no effect on urinary excretion of verinurad, whereas urinary excretion of OXY was increased 19% by verinurad. The mean maximal decrease in sUA was 65% with verinurad + ALLO compared with verinurad (51%) or ALLO (43%) alone (Figure). Consistent with the mechanism of action (MOA) of verinurad, 24-h fractional excretion of uric acid (FEUA) and clearance of uric acid (CLUR) were increased in the absence (9.2% and 11.5 mL/min, respectively) or presence of ALLO (7.9% and 11.8 mL/min) vs baseline (4.5% and 5.7 mL/min) or ALLO alone (3.7% and 5.0 mL/min). Consistent with its MOA, ALLO decreased the amount of uric acid excreted in 24-h urine (363 mg) compared with baseline (683 mg), verinurad alone (739 mg) or verinurad + ALLO (522 mg) but had no effect on FEUA or CLUR. No serious AEs, discontinuations due to AEs, or clinically significant laboratory or ECG abnormalities were noted.
Conclusion: Although a modest drug–drug interaction was found between verinurad and ALLO, the combination was safe and well tolerated at the studied doses and resulted in greater reduction of sUA than either alone. These results support the evaluation of verinurad + ALLO as an alternative once-daily treatment option for hyperuricemia and gout.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hall J, Gillen M, Yang X, Liu S, Walker S, Clauson V, Kankam M. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Tolerability of Concomitant Multiple Dose Administration of Verinurad (RDEA3170) and Allopurinol in Adult Male Subjects with Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics-and-tolerability-of-concomitant-multiple-dose-administration-of-verinurad-rdea3170-and-allopurinol-in-adult-male-subjects-with-gout/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics-and-tolerability-of-concomitant-multiple-dose-administration-of-verinurad-rdea3170-and-allopurinol-in-adult-male-subjects-with-gout/