Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a severe manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus, marked by kidney inflammation and damage. Obinutuzumab, a glycoengineered, type II CD20 antibody demonstrated effective B-cell depletion, reduced serum anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies and increased complement C3 and C4 levels in patients (pts) with LN in the Phase II NOBILITY (NCT02550652) trial. The Phase III REGENCY trial (NCT04221477) of obinutuzumab plus standard therapy in pts with active LN demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in Week 76 complete renal response and an acceptable safety profile.Exploratory analyses of peripheral B-cell populations and serological markers were performed to confirm the pharmacodynamic effects of obinutuzumab in pts enrolled in the REGENCY trial.
Methods: Adults with active LN received placebo or obinutuzumab plus standard therapy (mycophenolate mofetil plus glucocorticoids). All pts met ACR SLE classification criteria and had biopsy-proven proliferative LN. Peripheral B cells and B-cell subsets were assessed using validated high-sensitivity flow cytometry (HSFC) assays minimal residual B-cell panel (MRB)1.1 and BCP2.2, respectively. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of CD19+ B cells by MRB1.1 is 0.441 cells/μL. Complement and anti-dsDNA antibody levels were measured by nephelometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. Peripheral B-cell and serum biomarker assessments were performed on samples from Weeks 0, 4, 12, 24, 50 and 76.
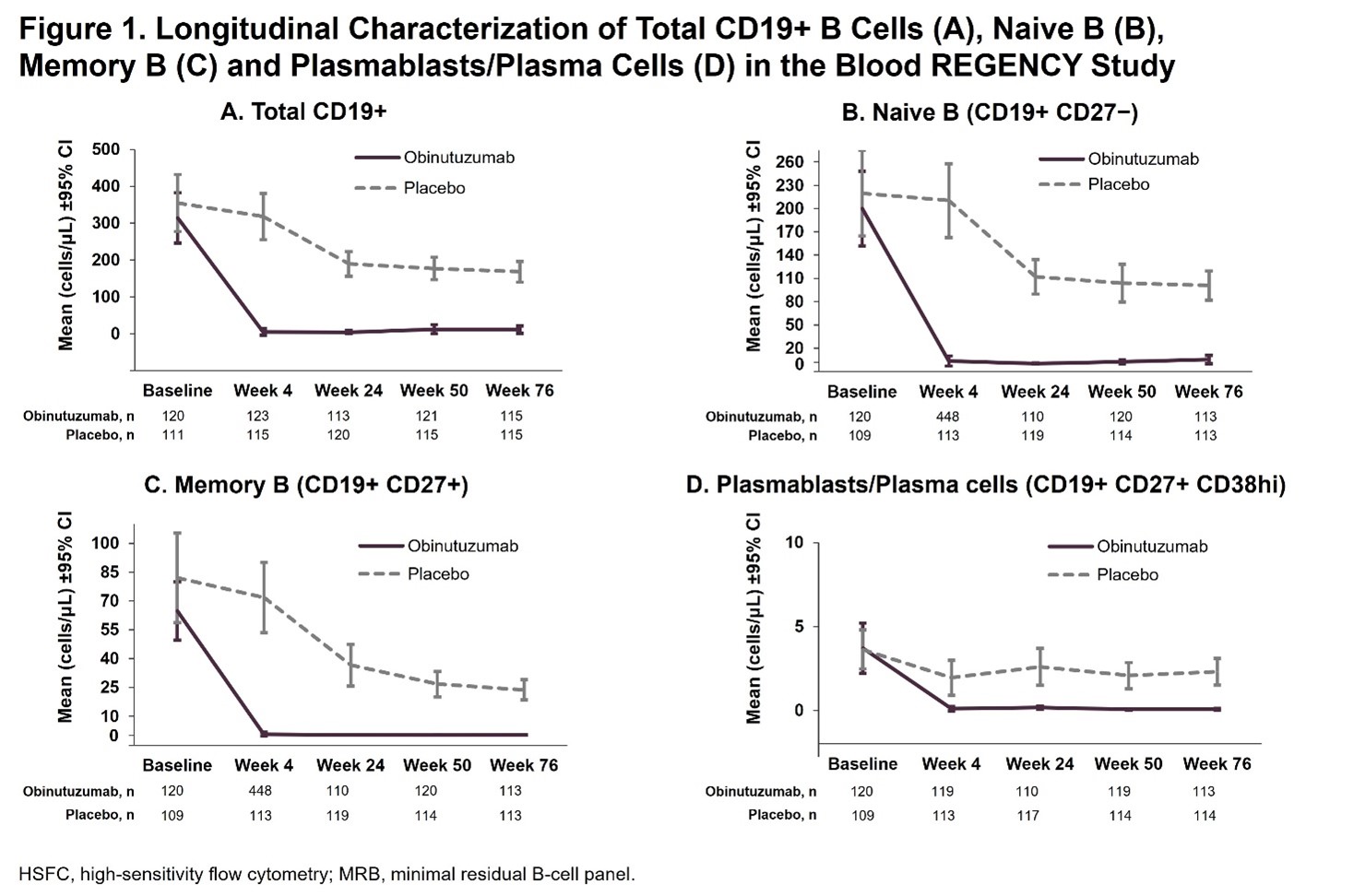
Results: Baseline biomarker levels were comparable between arms and no pt had B-cell levels below the LLOQ. At Week 4, mean total CD19+ B-cell levels were greatly reduced with obinutuzumab (mean cells/μL [SD]: 4.7 [45.6], −99.8 median % change from baseline) vs placebo (mean cells/μL [SD]: 317.8 [338.5], −4.2 median % change) and remained low relative to placebo at every timepoint tested through Week 76 (Figure 1A). Similar decreases in B-cell subsets were observed with obinutuzumab relative to placebo from Week 4-76 (Figures 1B-D). Obinutuzumab treatment also resulted in greater reductions in anti-dsDNA antibody levels and increases in complement C3 and C4 vs placebo. In pts with abnormal baseline serologies, higher normalization rates for C3 (43% vs 14%), C4 (70% vs 39%) and anti-dsDNA antibody levels (45% vs 11%) were observed at Week 12 for obinutuzumab vs placebo; these normalization rates were sustained or further improved through Week 76, with normalization rates of 62% vs 29% for C3, 88% vs 55% for C4 and 56% vs 16% for anti-dsDNA antibody levels at Week 76 (Table 1).
Conclusion: Obinutuzumab plus standard therapy induced rapid and sustained depletion of total peripheral CD19+ B cells and B-cell subsets in pts with active LN. Obinutuzumab treatment demonstrated improvements in serological markers of disease activity, increases in serum C3 and C4 levels, and reductions in anti-dsDNA antibody levels over placebo in all pts. Among pts with abnormal baseline marker values, obinutuzumab led to earlier and greater normalization rates vs placebo. These data support the hypothesis that deep B-cell depletion with obinutuzumab contributes to the improved clinical responses observed in pts with LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Parodis I, Jones R, Lightstone L, Hwang O, Au-Yeung A, Hassan I, Mao H, Pendergraft W, Garg J, Raghu H, Rovin B. Pharmacodynamic Effects of Obinutuzumab on B cells and Serological Markers in Patients With Active Lupus Nephritis: Results From a Phase III Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacodynamic-effects-of-obinutuzumab-on-b-cells-and-serological-markers-in-patients-with-active-lupus-nephritis-results-from-a-phase-iii-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacodynamic-effects-of-obinutuzumab-on-b-cells-and-serological-markers-in-patients-with-active-lupus-nephritis-results-from-a-phase-iii-trial/

.jpg)