Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Durable vaccine-mediated immunity relies on the generation of long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells (MBCs), differentiating upon germinal center (GC) reactions. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induces a strong GC response in healthy volunteers (HC), but limited data is available in patients with medically induced B cell impairment upon rituximab treatment.
Methods: We evaluated humoral as well as B and T cellular responses upon 3rd vaccination in seven patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who initially mounted anti-spike SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies after primary 2x vaccination and got re-exposed to RTX 1-2 months after the second vaccination. Ten patients with RA on other therapies and ten HC represented the control groups. As control for known long-lived induced immunity, we analyzed humoral and cellular tetanus toxoid (TT) immune responses in steady-state. To assess subpopulations of circulating antigen-specific, receptor-binding domain (RBD+) B cells before and after 3rd vaccination (and as control TT+ B cells at steady state), we implemented a high-dimensional flow cytometry analysis using Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP). Antigen-specific T cells were assessed after 2nd and 3rd vaccination.
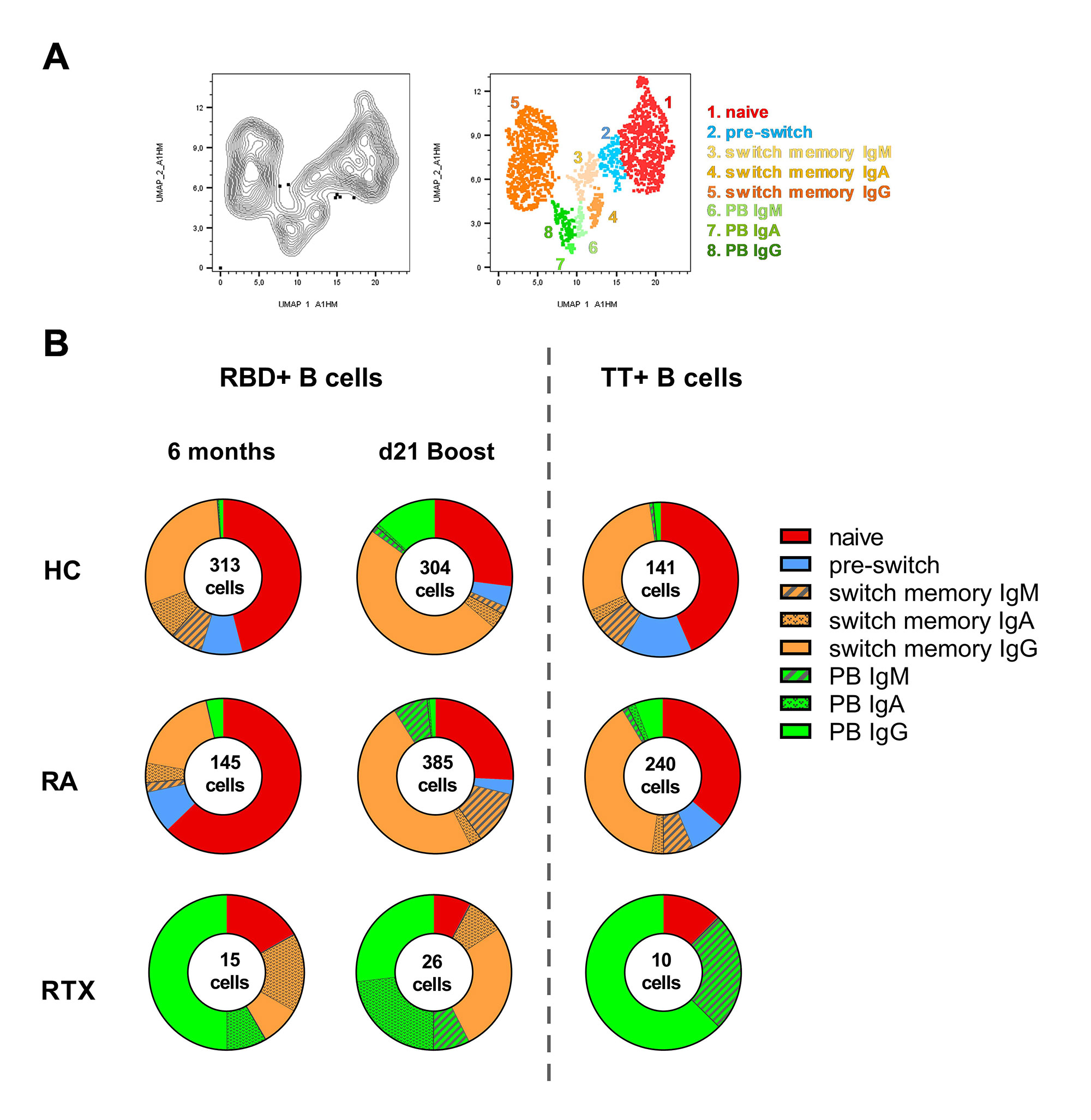
Results: After 3rd vaccination, 5/7 RTX patients were IgG seroconverted, revealing lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG titers but similar neutralizing capacity compared with HC. The fine-tuning of high-affinity antibodies as a direct result of somatic hypermutation seems functional also in RTX treated patients. Antibody levels after 2nd vaccination correlated with titers after 3rd vaccination, suggesting that upon RTX re-exposure, induction strength of the immune response within recall vaccination, is largely related to pre-existing memory formation. Despite significant reduction of circulating total and antigen-specific B cells in RTX re-exposed patients, we observed the induction of IgG+ MBCs upon 3rd vaccination (Fig.1 A, B). Notably, only RTX treated patients revealed a high amount of IgA+ memory B cells before 3rd vaccination with induction of IgA+ plasmablasts (PB) upon boost, suggesting a persistent but disturbed germinal center activity. In contrast, IgA+ B cells were not part of the steady state TT+ B cell pool. With respect to antigen-specific T cells, TNF-secretion and generation of effector memory CD4 spike-specific T cells were significantly boosted upon 3rd vaccination.
Conclusion: Herein, we describe for the first time humoral and cellular responses upon 3rd SARS-CoV-2 injection in patients re-exposed to RTX after initially seroconversion upon primary vaccination. While functional aspects of spike-specific CD4 T cells are boosted upon 3rd vaccination, we report a persistent but disturbed germinal center activity, possibly supported by (semi-primary and /or) additional extrafollicular responses in patients re-exposed to RTX as potential compensatory mechanisms employed in such medically induced B cell impairment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stefanski A, Rincon-Arevalo H, Schrezenmeier E, Szelinski F, Ritter J, Chen Y, Meisel C, Schrezenmeier H, Lino A, Dörner T. Persistent but Disturbed Germinal Center Reaction Among 3rd SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination After Rituximab Exposure [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/persistent-but-disturbed-germinal-center-reaction-among-3rd-sars-cov-2-vaccination-after-rituximab-exposure/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/persistent-but-disturbed-germinal-center-reaction-among-3rd-sars-cov-2-vaccination-after-rituximab-exposure/