Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) is a promising imaging modality for assessing volumetric bone mineral density (BMD) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and has shown potential for use as an alternative to X-ray for detecting erosions in patients with RA. However, knowledge about the association between erosions and peripheral volumetric BMD is lacking. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the association between erosions and volumetric BMD in patients with RA.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 301 patients with established RA (disease duration > 5 years) according to the ACR/EULAR (2010) classification criteria were included. In total, 184 patients were imaged at the distal radius and 117 patients were imaged at the ultra-distal radius by HR-pQCT. All patients underwent radiographic examinations of the hands, wrists, and feet and were scored using the Sharp/Van der Heijde (SvH) method. Furthermore, the patients with RA imaged at the distal radius was matched by sex and age with a cohort of healthy controls (HC) with HR-pQCT of the distal radius (n =169).
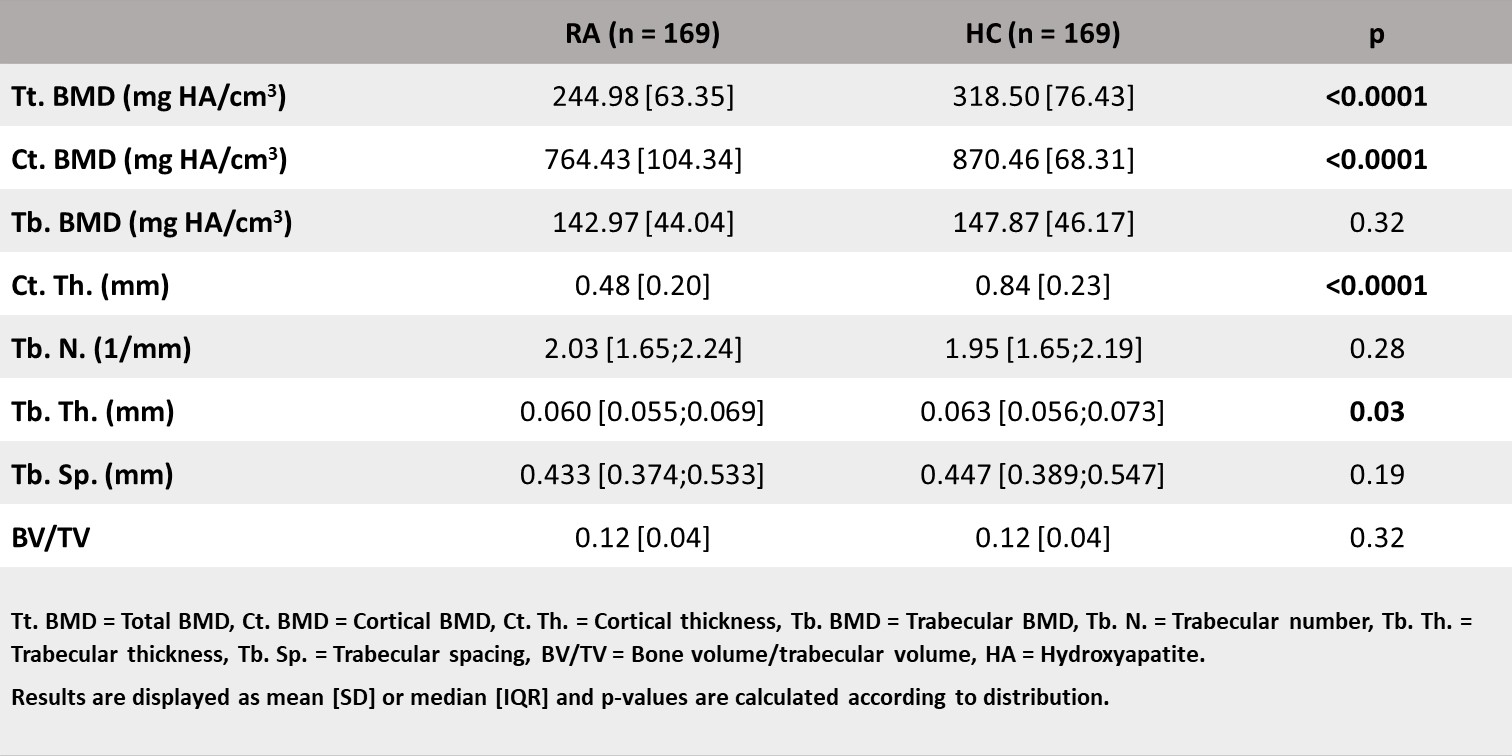
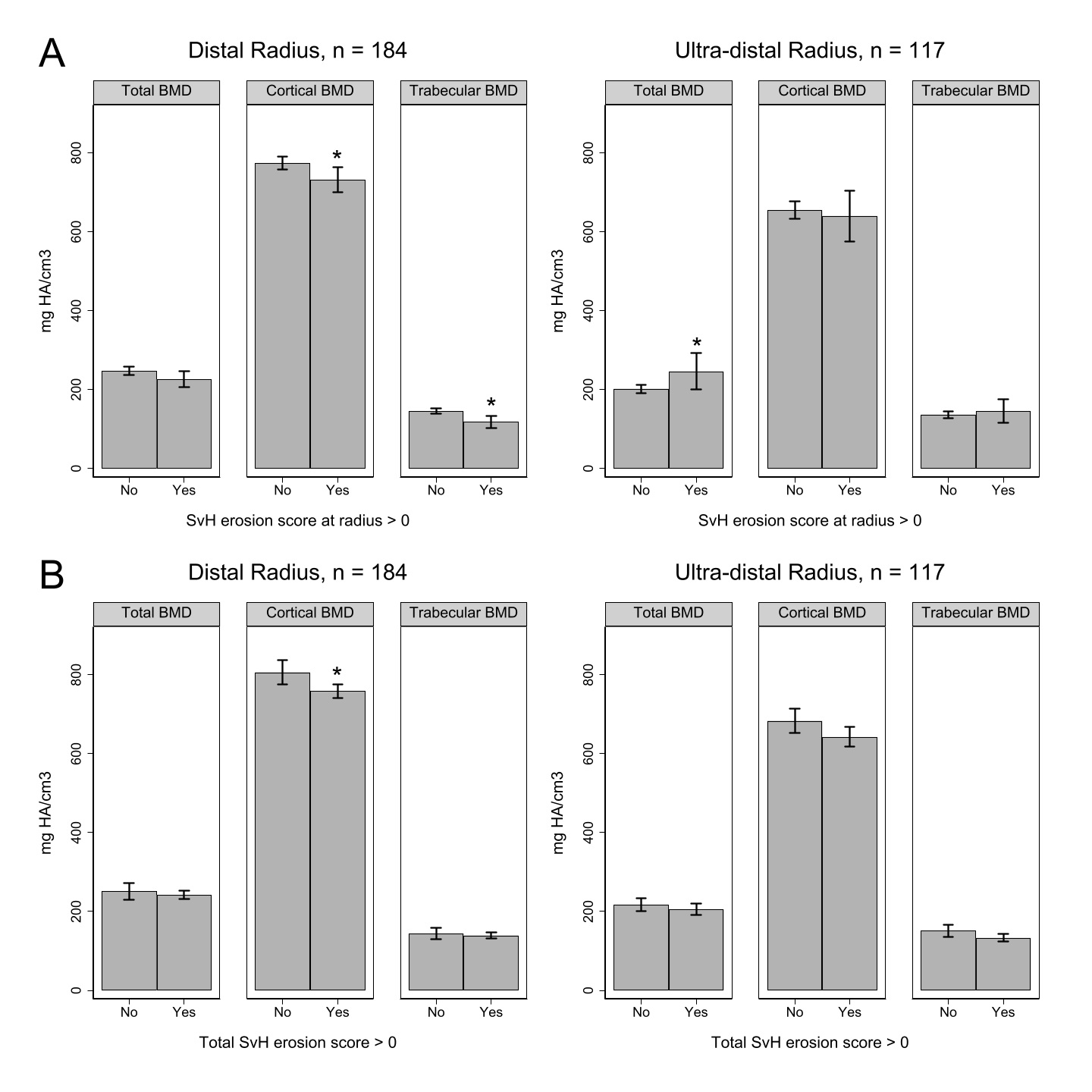
Results: 301 patients with RA (median age 63.7 [55.1;70.8] years, 71 % women) were included in the study. The median disease duration was 14 [8;21] years. Compared with healthy controls, patients with RA had significantly lower total and cortical BMD at the distal radius (26.1%, p < 0.0001 & 13.0%, p < 0.0001), with no statistically significant difference in trabecular BMD. Furthermore, cortical and trabecular thickness was significantly lower in patients with RA compared to healthy controls (54.5%, p < 0.0001 & 4.9%, p = 0.03) (Table 1). Local erosions were associated with significantly decreased cortical and trabecular BMD at the distal radius (p = 0.03 & p = 0.0008), while at the ultra-distal radius, local erosions were associated with significantly higher total BMD (p = 0.005). Erosive disease in general was associated with significantly decreased cortical BMD at the distal radius (p = 0.02) with no statistically significant difference between the groups at the ultra-distal radius (Figure 1). At the distal radius, multivariate linear regression analyses showed a significant negative association between total SvH erosion score and trabecular BMD (coefficient = -0.28, p = 0.001) with no statistically significant associations between total and cortical BMD after adjusting for disease activity, sex, age, height, weight and tobacco pack years. At the ultra-distal radius, multivariate linear regression analyses showed a significant positive association between total SvH erosion score and total BMD (coefficient = 0.49, p = 0.001) with no statistically significant associations between total SvH erosion score and cortical and trabecular BMD.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that erosive disease in RA causes systemic bone changes resulting in decreased BMD at the cortical and/or trabecular bone compartment. This indicates that evaluation of erosive disease likely adds value to the assessment of systemic bone changes in patients with RA. Furthermore, it underlines the need for longitudinal studies investigating the changes in erosive status and BMD over time.
(A): Stratified by Sharp/Van der Heijde erosion score at the radius. (B): Stratified by total Sharp/Van der Heijde erosion score.
* = p < 0.05.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hänel M, Klose-Jensen R, Therkildsen J, Garm Blavnsfeldt A, Langdahl B, Gadegaard Hansen S, Keller K, Hauge E. Peripheral Volumetric Bone Mineral Density and Erosive Disease in Patients with Established Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study Using High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-volumetric-bone-mineral-density-and-erosive-disease-in-patients-with-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cross-sectional-study-using-high-resolution-peripheral-quantitative-computed-tomogra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-volumetric-bone-mineral-density-and-erosive-disease-in-patients-with-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cross-sectional-study-using-high-resolution-peripheral-quantitative-computed-tomogra/