Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III (1836–1861)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Response to immunosuppression is variable in systemic sclerosis (SSc) related interstitial lung disease (ILD). Contrary to pulmonary tissue, peripheral blood cell (PBC) RNA can be obtained during routine clinical care and can be used as easily accessible source for biomarker development. This study aims to examine the PBC gene expression changes ensuing from mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or cyclophosphamide (CYC) treatment and to determine the predictive significance of baseline PBC transcript scores for response to immunosuppressive treatment in SSc-ILD.
Methods: All patients with an available baseline PBC RNA sample (stored in PAXgene tubes) enrolled in the Scleroderma Lung Study II (SLS II) were included. Baseline and 12-month samples corresponding to the active treatment period in both MMF and CYC arms were investigated by global RNA sequencing. A paired-end 150 bp sequencing strategy was used to generate an average of 99 million reads per sample. A modular analysis using 62 curated whole blood modules was pursued as previously described (Chaussabel et al. Nat Rev Immunol 2014). Each treatment arm was analyzed separately. First, a paired analysis comparing the 12-month to baseline samples was performed. Next, the predictive significance of baseline composite modular scores for the course of forced vital capacity (FVC) % predicted measurements from 3 to 12 months was investigated using a joint model (combines a mixed effects model for the longitudinally obtained FVC%s with a survival model to handle non-ignorable missing data). All analyses were corrected for multiple comparison by FDR method.
Results: A total of 134 patients with SSc-ILD (CYC=69 and MMF=65) enrolled in SLS II were investigated. The pairwise comparison of 12 month to baseline samples showed an upregulation of erythropoiesis, inflammation, and myeloid lineage related modules and a down-regulation of lymphoid lineage related modules in the CYC arm (Table 1). The modular changes resulting from MMF treatment were more modest. Plasma cell and cell cycle modules were downregulated after MMF treatment (Table 2).
In the longitudinal joint model, none of the baseline composite transcript module scores significantly predicted the course of FVC% in the CYC arm. In contrast, composite scores of certain transcript modules showed differential predictive significance in the MMF arm (Figure 1). Specifically, higher baseline Lymphoid Lineage (including T-cells and Cytotoxic/NK cells), and Mitochondrial Modules predicted better subsequent FVC% course, while higher baseline Myeloid Lineage (including Neutrophils / Granulocytes) and Inflammation modules predicted worse subsequent FVC% course in the MMF arm.
Conclusion: Oral CYC has a profound impact on the PBC gene expression profile in patients with SSc-ILD. MMF treatment leads to more modest gene expression changes including a decline in plasma cell modules. The predictive significance of immune related modules for response to MMF treatment varies as follows: Consistent with the primary mechanism of action of MMF on lymphocytes, patients with higher baseline lymphoid modules have a better response to MMF, while those with a higher myeloid cell lineage activation score have a poorer response.
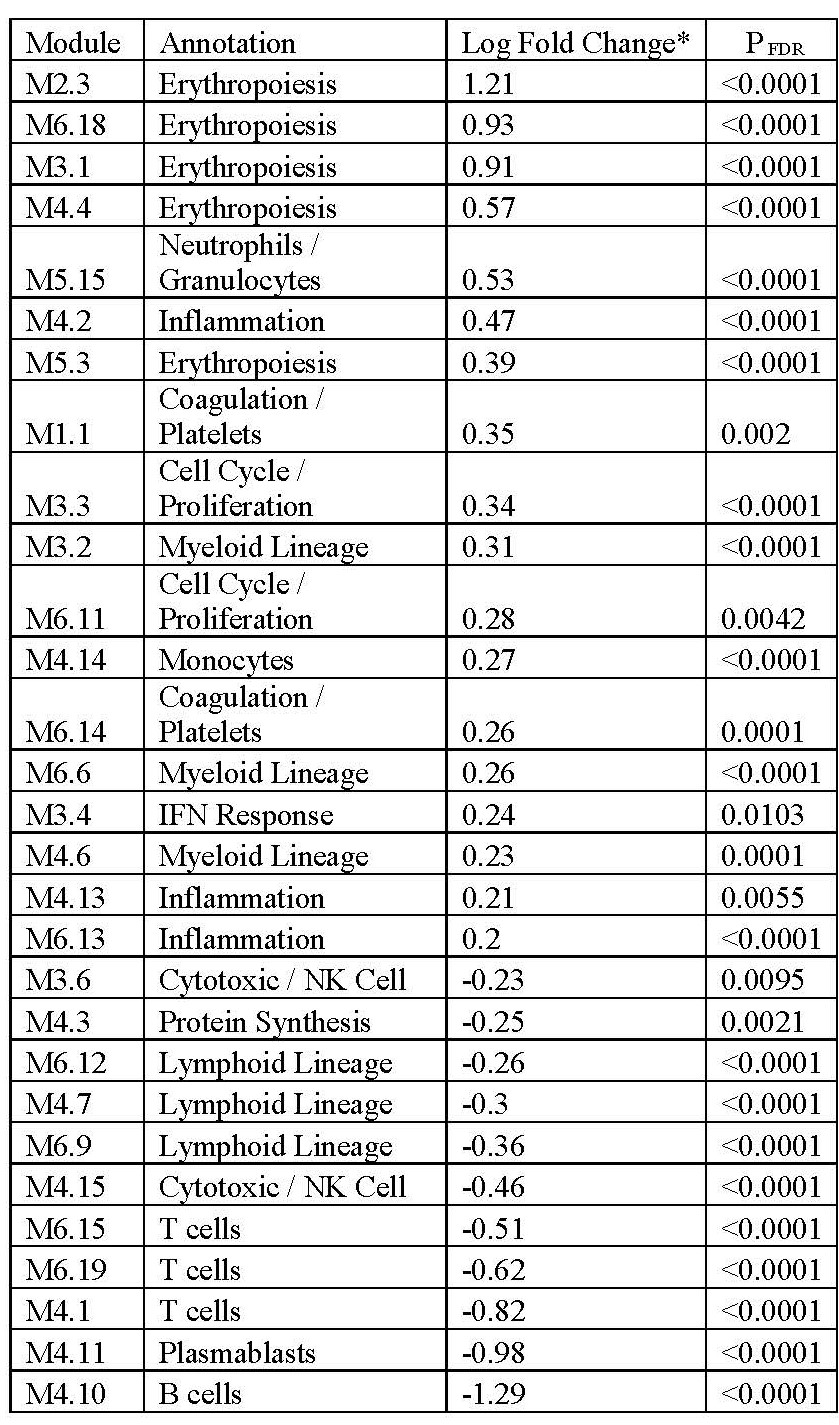 Table 1: Significantly changed transcript modules in pairwise comparison of 12-month to baseline samples in the CYC arm
Table 1: Significantly changed transcript modules in pairwise comparison of 12-month to baseline samples in the CYC arm
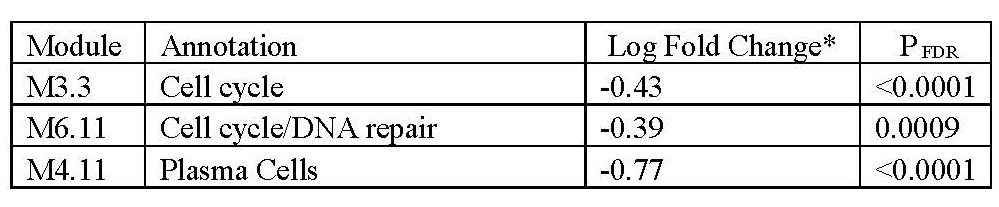 Table 2: Significantly changed transcript modules in pairwise comparison of 12-month to baseline samples in the MMF arm
Table 2: Significantly changed transcript modules in pairwise comparison of 12-month to baseline samples in the MMF arm
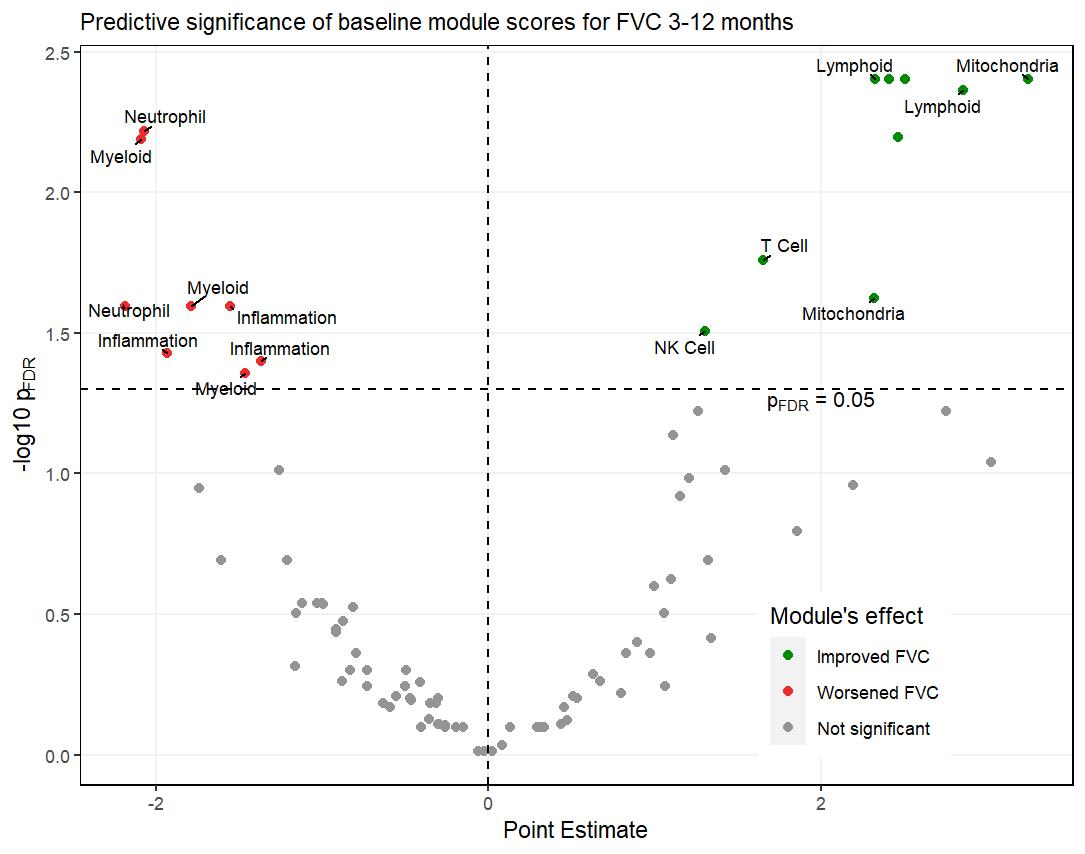 Volcano Plot_FVC_3_12M_2021-05-03.jpeg”Figure 1: Predictive significance of baseline modular scores for FVC% during 3_12 month visits in the MMF arm. Higher T- and B-lymphocyte module scores predicted better ILD course while higher neutrophil/myeloid lineage module scores predicted worse ILD course. Of note, the modular analysis method can assign the same biological function to multiple modules.
Volcano Plot_FVC_3_12M_2021-05-03.jpeg”Figure 1: Predictive significance of baseline modular scores for FVC% during 3_12 month visits in the MMF arm. Higher T- and B-lymphocyte module scores predicted better ILD course while higher neutrophil/myeloid lineage module scores predicted worse ILD course. Of note, the modular analysis method can assign the same biological function to multiple modules.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Assassi S, Zheng W, Volkmann E, Wang X, Wilhalme H, Lyons M, Roth M, Tashkin D. Peripheral Blood Cell Gene Expression Profiling Predicts Response to Mycophenolate in Systemic Sclerosis Related Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-cell-gene-expression-profiling-predicts-response-to-mycophenolate-in-systemic-sclerosis-related-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-cell-gene-expression-profiling-predicts-response-to-mycophenolate-in-systemic-sclerosis-related-interstitial-lung-disease/
