Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis (SpA) including axial SpA (axSpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) differs from fibromyalgia (FM). However, symptoms partially overlap and both patient groups suffer from pain and stiffness. In addition, SpA patients may also develop a secondary form of FM. Classification criteria for SpA and diagnostic criteria for FM are used to differentiate between these subsets. Patient reported outcomes (PRO) often generated by questionnaires are used to assess severity and other disease features. We aim to study whether PROs developed for axSpA, PsA, and related physician-based information behave in a similar way in patients diagnosed with FM without an additional chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease (CIRD) as in patients with a primary diagnosis of SpA without or with secondary FM.
Methods: Patients were consecutively recruited. The main inclusion criterion was a clinical diagnosis of FM (without CIRD), axSpA or PsA (without or with secondary FM) and the indication for a treatment adaptation (escalation or change within the same class) for any reason, based on the judgement of experienced rheumatologists. Standardized assessment tools and lab parameters (BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP, DAPSA, patient´s and global assessment (NRS), CRP, BASFI, Fibromyalgia Impact questionnaire (FIQ), Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI), Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis (MASES) and SpA Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) Enthesitis Score were assessed and compared between subgroups.
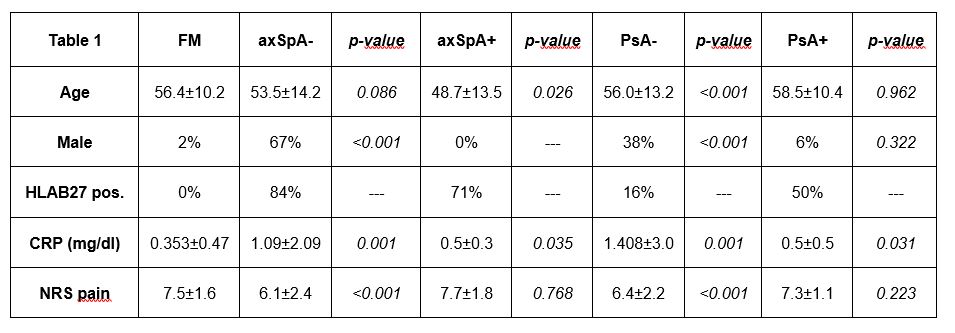
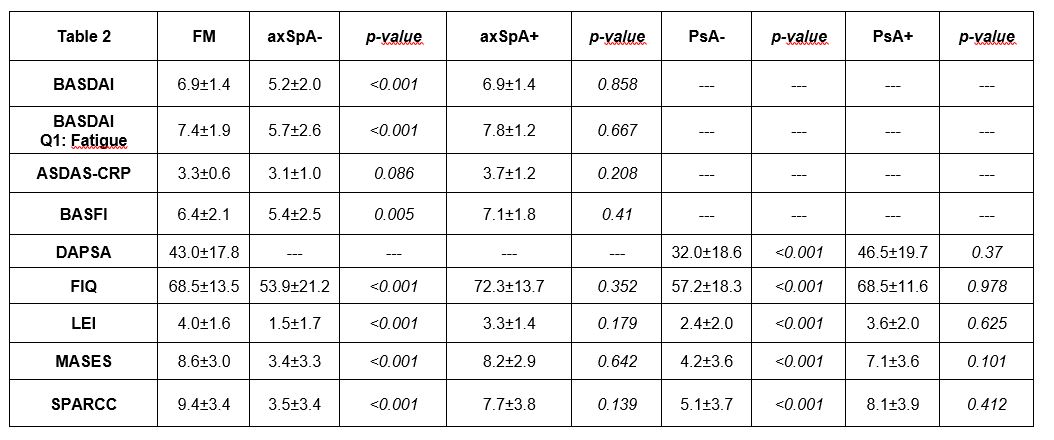
Results: The baseline demographics of 300 recruited patients (100 FM. 100 axSpA and 100 PsA) are shown in Table 1. All patients with FM (primary or secondary to SpA) showed the highest scores in almost all assessments, and this was independent of the main diagnosis (Table 2). In comparison, patients with axSpA or PsA without secondary FM showed significantly lower scores in all PROs as compared to those with primary and secondary FM, with exception of (i) scores of ASDAS-CRP and (ii) duration of morning stiffness (Question 6 of BASDAI), which were not affected by the presence of secondary FM (Table 2).
Conclusion: Secondary FM is leading to significantly higher levels of SpA-specific scores. ASDAS-CRP was the only score that was not influenced by the presence of secondary FM in patients with axSpA even though it was also increased in patients with primary FM, while similar results were found for the duration but not the level of morning stiffness. On the other hand, FM-specific questionnaires also showed high scores in patients with axSpA and PsA with concomitant FM but not in those without.
‘+’ : diagnosis with concomitant FM, ‘-‘: diagnosis without concomitant FM
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Tsiami S, Gkelaki M, Dukatz P, Kiltz U, Braun J. Performance of Standardized Scores for Disease Assessment and Pain in Patients Withspondyloarthritis and Fibromyalgia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-standardized-scores-for-disease-assessment-and-pain-in-patients-withspondyloarthritis-and-fibromyalgia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-standardized-scores-for-disease-assessment-and-pain-in-patients-withspondyloarthritis-and-fibromyalgia/