Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) assesses axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) with good internal consistency and discriminative capacity. However, a scientific calculator or electronic application is required for its calculation. SASDAS (simplified ASDAS) is the sum of the ASDAS´s components, which includes C-reactive protein (CRP), and is easy to perform in daily practice. The objective of this analysis was to compare the SASDAS index against the standard ASDAS index (CRP version) at baseline and post-baseline in a randomized controlled trial (EMBARK).
Methods: EMBARK assessed etanercept (ETN) 50 mg/week in early active NSAID-refractory non-radiographic axSpA patients receiving background NSAID. Subjects received ETN or placebo (PBO) for 12 weeks (double-blind) followed by ETN only (open-label). Continuous ASDAS and SASDAS were evaluated by Spearman’s Correlations, and agreement in ASDAS vs SASDAS disease categories (minimal, low, high, very high disease activity) by Cohen’s weighted kappa for individual and pooled treatments. The capacity to discriminate between treatments was evaluated by treatment effect size (ES) for ETN vs PBO at Week 12, and the sensitivity to change from baseline at Weeks 12 and 24 by ES for change.
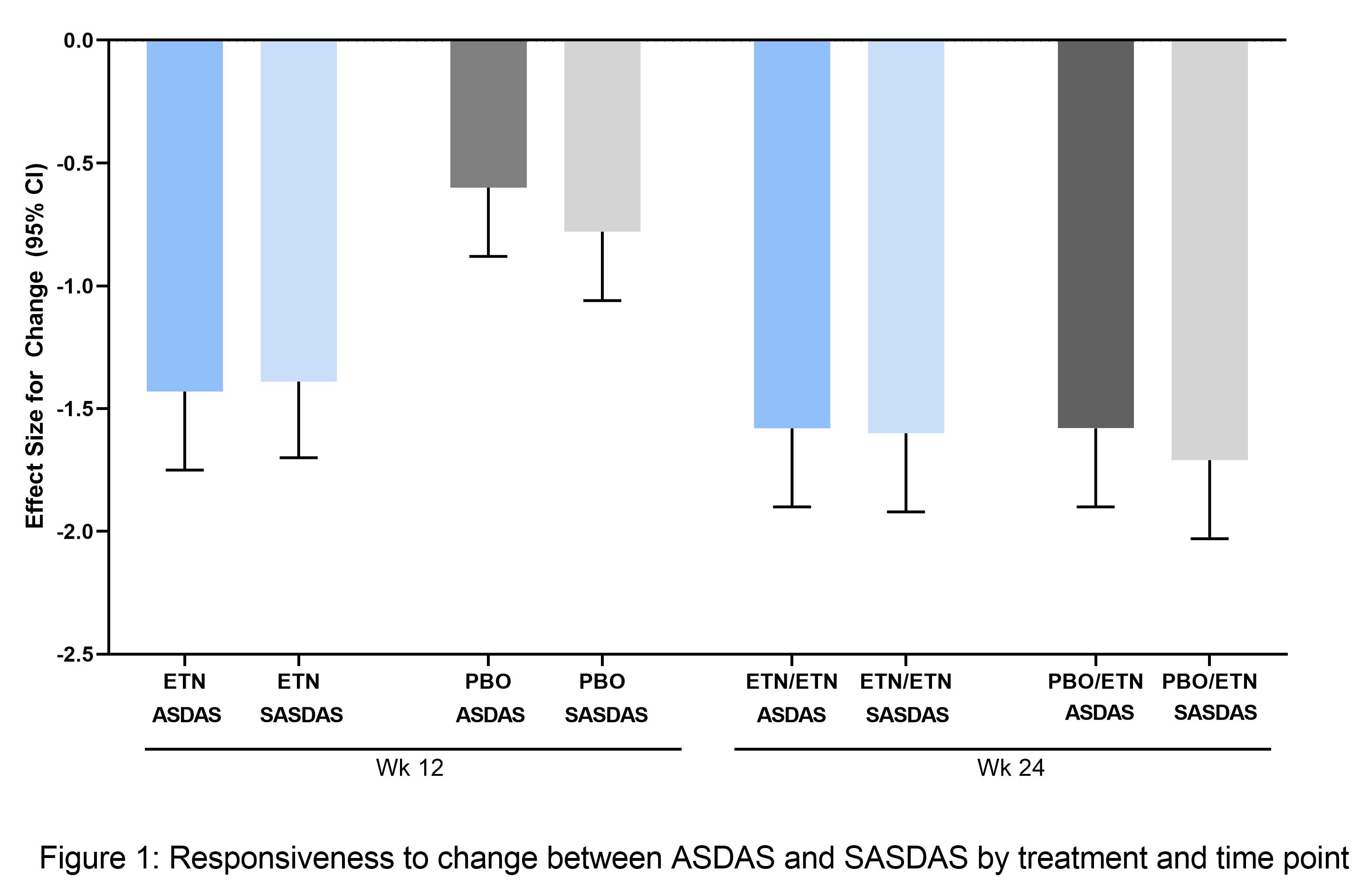
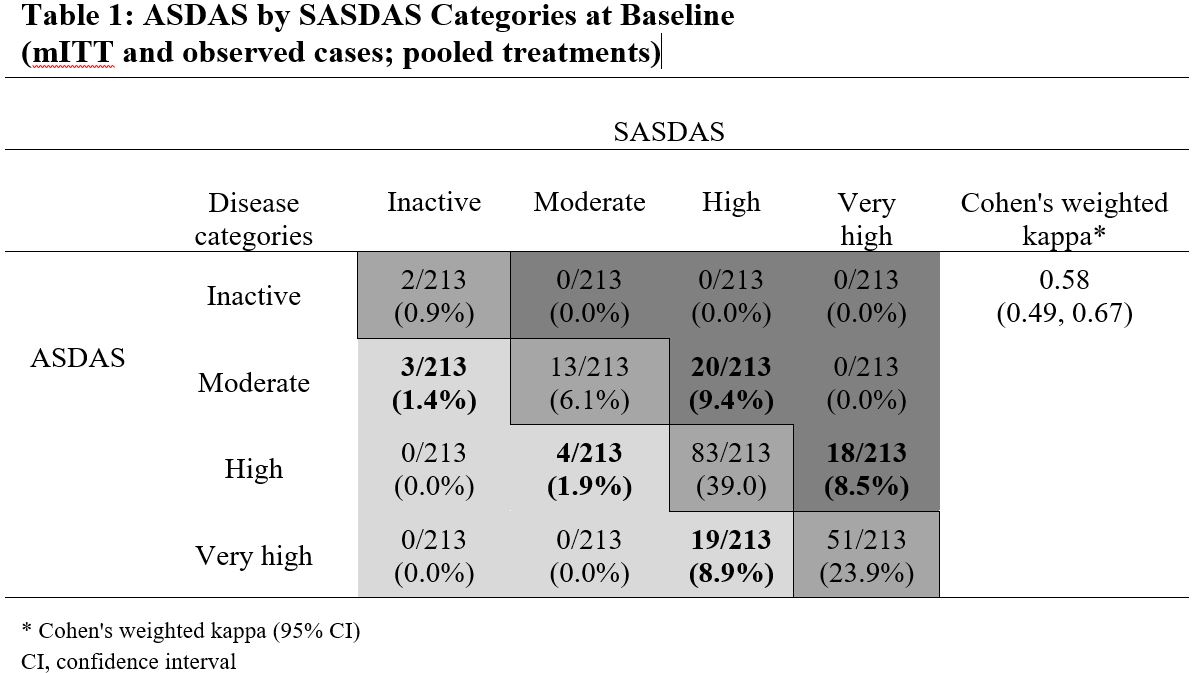
Results: Of 215 patients in the modified intention-to-treat (mITT) population (ETN, n=106; PBO, n=109), 208 entered the open-label phase (ETN/ETN, n=102; PBO/ETN, n=106). The mean age was 32 years, 64% (ETN) and 58% (PBO) were male, and average disease duration was 2.4 (ETN) and 2.5 years (PBO). There was a strong correlation between continuous ASDAS and SASDAS. At baseline, Spearman’s correlation was 0.82 (ETN) and 0.87 (PBO); at Weeks 12 and 24 it was 0.89 (ETN), 0.90 (PBO), and 0.88 (both treatments), respectively. The evaluation of categorical SASDAS placed more patients in high or very high disease activity compared with categorical ASDAS; for example, at baseline, in the whole population, 38/213 patients (17.8%) with moderate and high disease activity by ASDAS were categorized with higher disease activity by SASDAS (20/213 moderate, 18/213 high), and 26/213 patients (12.2%) categorized with lower disease activity (3/213 moderate, 4/213 high, 19/213 very high) (Table 1). A similar pattern was seen post-baseline. Cohen’s weighted kappa statistics range from 0.54 ─ 0.73 for all individual/pooled treatments and time points, reflecting moderate-to-substantial agreement. The discriminant capacity evaluated by the treatment ES was higher with ASDAS compared with SASDAS (ES [95% CI], ASDAS: -0.74 [-1.03,-0.46]; SASDAS: -0.51 (-0.79, -0.23), but the sensitivity to change was similar (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Despite the simplicity of SASDAS, these data suggest a moderate-to-substantial agreement with ASDAS for classifying patients with active disease and a lower treatment discriminant capacity. Further evaluation of this composite index is required before implementation in daily practice and/or clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schneeberger E, Citera G, Ponce de Leon D, Szumski A, Kwok K, Cutri M, Dougados M. Performance of SASDAS (Simplified Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score) versus ASDAS in a Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-sasdas-simplified-axial-spondyloarthritis-disease-activity-score-versus-asdas-in-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-randomized-controlled-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-sasdas-simplified-axial-spondyloarthritis-disease-activity-score-versus-asdas-in-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-randomized-controlled-clinical-trial/