Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Only 37% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receive screening for cardiovascular disease (CVD) despite their high risk. To improve CVD prevention, we designed the CArdiovascular Risk assEssment for patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (CARE RA) intervention. It consists of patient education alongside the assistance of a peer coach. A peer coach is a person with RA that has been trained to coach another person with RA to request a CVD risk assessment from their rheumatologist. The goal of this abstract is to present the preliminary results for this intervention.
Methods: This is a randomized controlled trial for patients with RA. We included patients with RA between 40-75 years of age, no history of CVD, and no cholesterol test or CVD risk assessment in the past 2 years. We excluded people with diabetes or already on lipid lowering therapy (LLT). Participants were randomized to either CARE RA or a control group. CARE RA participants completed 4 weekly calls with a peer coach right before their rheumatologist appointment, to coach their client on requesting CVD risk from their rheumatologist, and one call the week after their appointment to discuss steps to follow once the intervention was completed. The calls followed a curriculum on RA and CVD, that included strategies to lower the risk for CVD and the importance of a CVD risk assessment. The control arm completed the same curriculum but without the assistance of a peer coach. The primary outcome was the number of participants who received a CVD risk assessment defined as, having a cholesterol test, discussing the results of a cholesterol test with their rheumatologist, or initiating LLT if indicated. Data was collected at baseline (5 weeks prior to the rheumatologist appointment), 1-week, and 3-months after the appointment. Differences between arms were determined at 1-week and 3-months after the rheumatologist appointment.
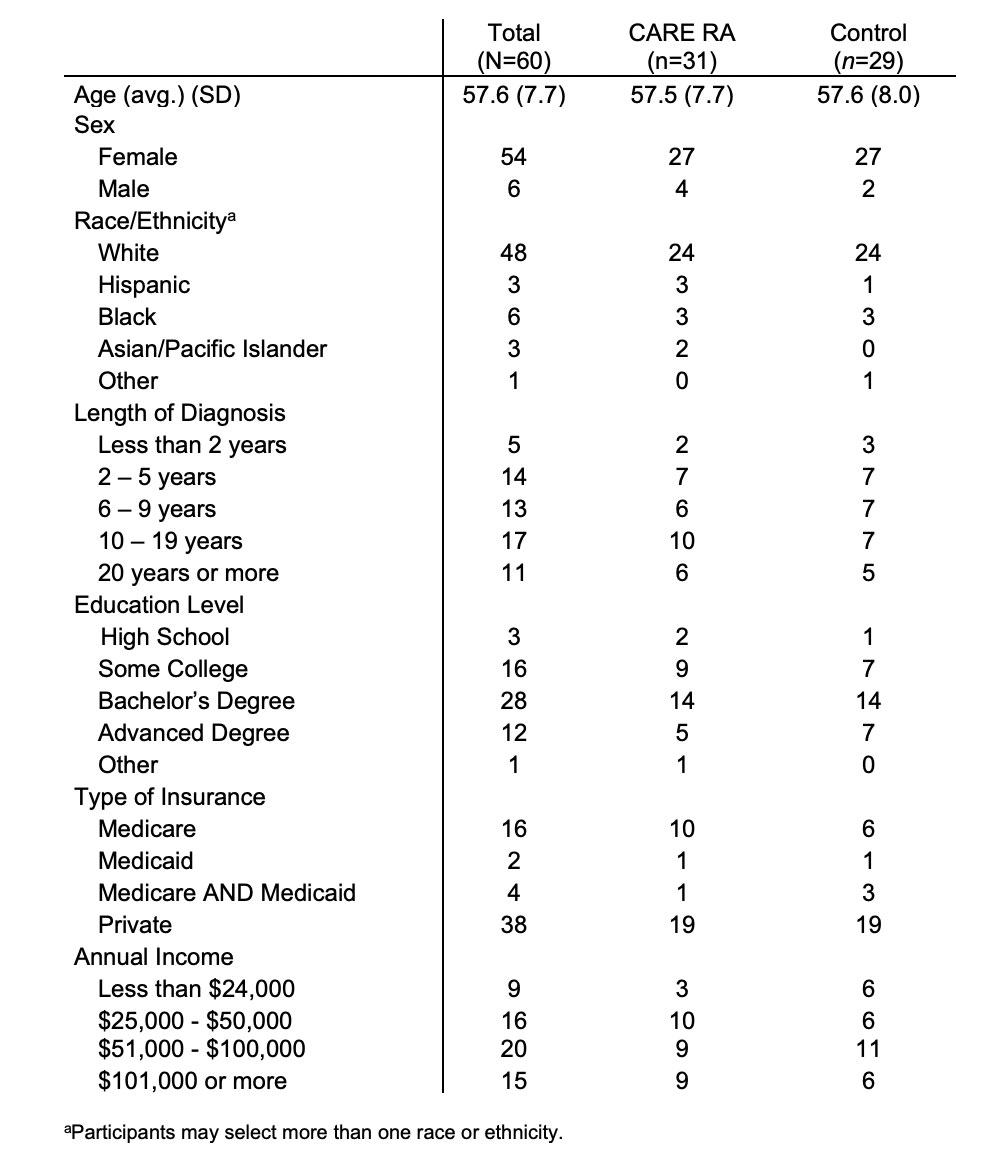
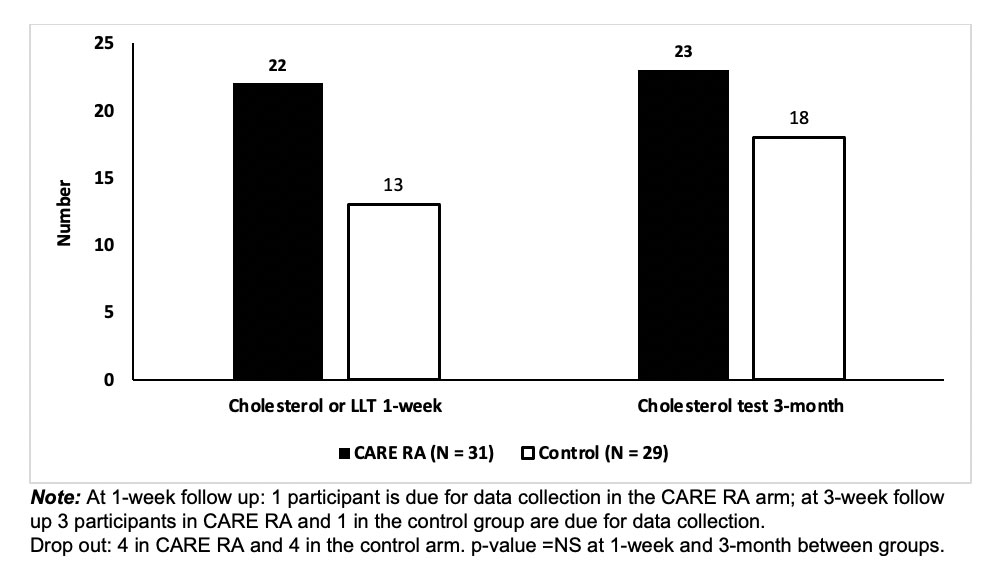
Results: There were 60 participants (Figure 1); 4 dropped out from CARE RA and 4 from the control arm; mean age was 57, 90% females, 80% white (Table 1). At 1-week, 22 participants in CARE RA versus 18 in the control arm received a CVD risk assessment. At 3-month, all participants that completed CARE RA had a CVD risk assessment (Figure 2; p=0.62) and 5 initiated LLT. No participant in the control arm initiated LLT.
Conclusion: The CARE RA intervention seems feasible by means of participants completing the intervention with the peer coaches. Preliminarily, CARE RA seems promote CVD risk assessment, but a larger sample is needed to obtain definitive results about its effectiveness.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Navarro-Millan I, Brown M, Domínguez Páez Y, Lui G, Weiner J, fritz S, Sydnor-Campbell T, Allen A, Jabri A, Venkatachalam S, Gavigan K, Nowell W, Curtis J, Fraenkel L, Safford M. Peer Coach Intervention to Improve Primary Cardiovascular Disease Screening for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peer-coach-intervention-to-improve-primary-cardiovascular-disease-screening-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peer-coach-intervention-to-improve-primary-cardiovascular-disease-screening-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/