Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: PD-1hiCXCR5–CD4+T peripheral helper cells (Tph) are newly identified pathogenic CD4+T helper cells and participate in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis. However, the clinical significance of Tph cells has not yet been elucidated in RA. Our aim is to evaluate the usefulness of Tph cells as biomarkers in RA patients and determine their value in predicting the clinical response to anti-TNF treatment.
Methods: Fifty-two RA patients who visited our rheumatology department from July 2022 to June 2024 were enrolled. Among them, 21 patients with an incomplete response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) were changed to anti-TNF treatment, and their Tph cells were studied at baseline and 3 months. Patients who didn’t achieve ACR20 improvement at the third month after enrollment were defined as non-responders (n=8) and others were defined as responders (n=13). The proportion of Tph cells among CD4+T cells was accessed by flow cytometry. Age- and sex- matched osteoarthritis (OA) patients (n=10) and healthy controls (HCs) (n=15) were included as a control. The relationships between the proportion of Tph cells and the clinical features, laboratory parameters, 28-Joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) and other 24 immune cell subsets were analyzed in RA.
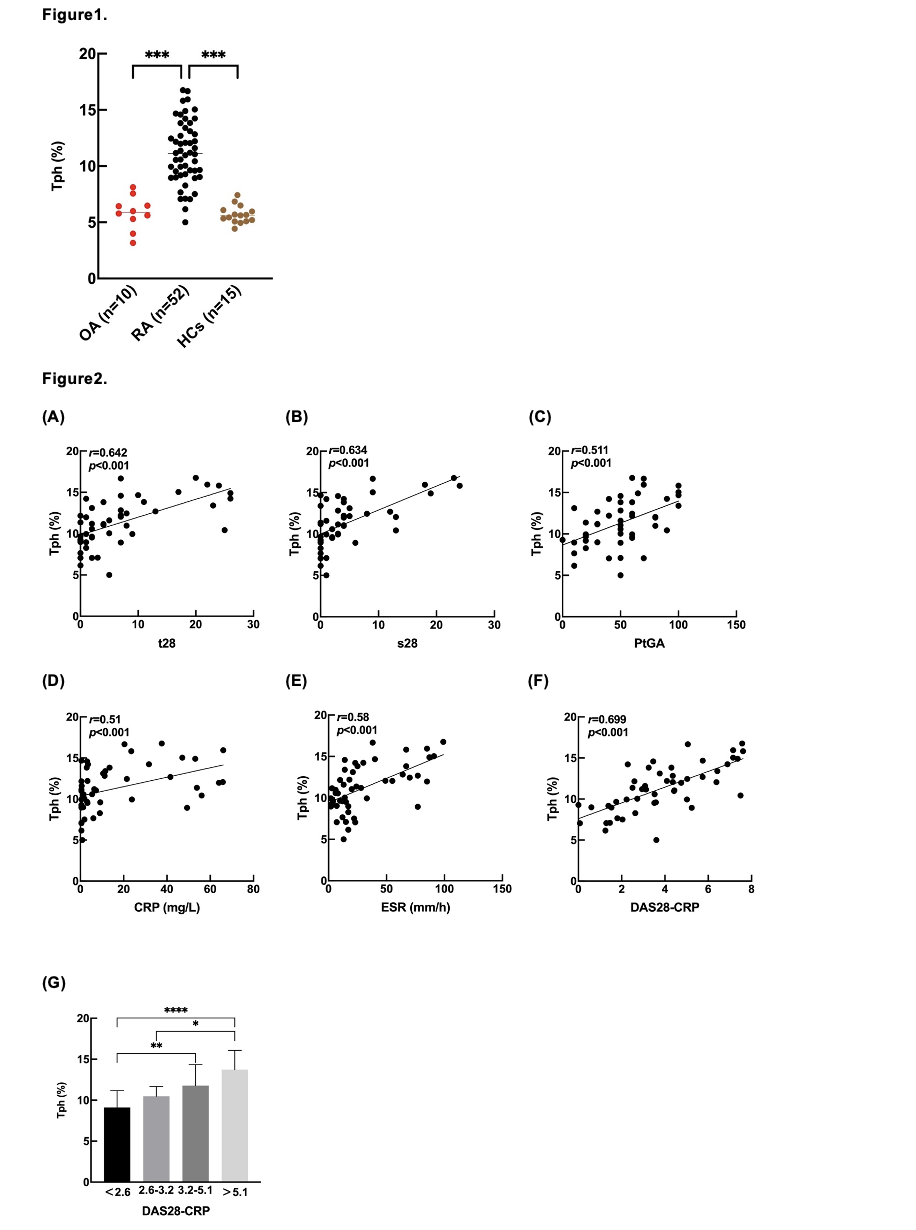
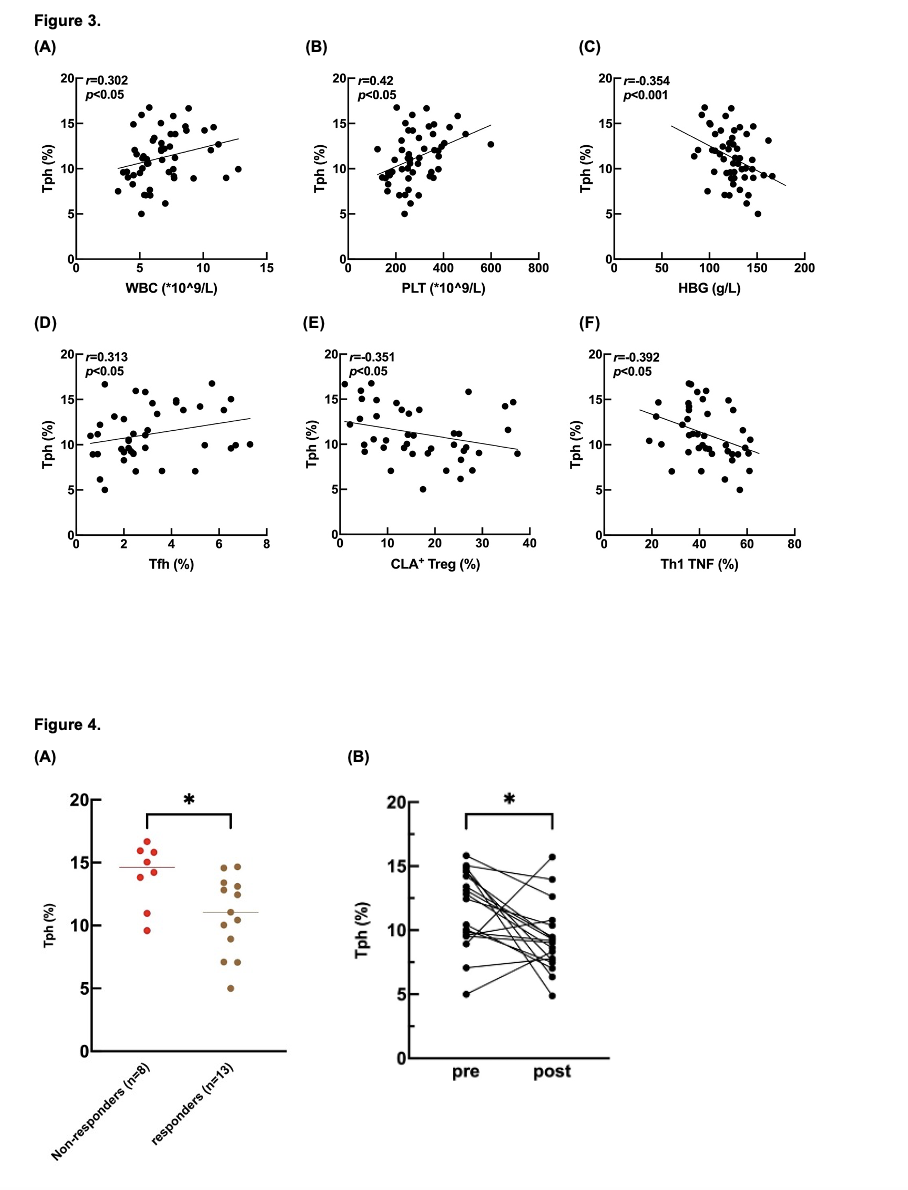
Results: The demographic data and clinical characteristics of the RA patients and controls were described in Table 1. The proportion of Tph cells was significantly (p< 0.001) increased in RA patients (11.21±2.8%) in comparison to those in OA (5.84±1.49%) patients and HCs (5.69±0.78%). (Figure 1) The proportion of Tph cells was positively correlated with the number of tender joints (r=0.642, p< 0.001), swollen joints (r=0.634, p< 0.001), scores of patients’ global assessment (PtGA) (r=0.511, p< 0.001), level of C-reactive protein (CRP) (r=0.51, p< 0.001) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (r=0.58, p< 0.001) and DAS28-CRP score (r=0.699, p< 0.001). With the increase of DAS28-CRP score, the proportion of Tph cells showed an increasing trend. (Figure 2) The counts of white blood cells (WBC) (r=0.302, p< 0.05) and platelets (r=0.42, p< 0.05) also demonstrated positive correlations with the proportion of Tph cells, but the level of hemoglobin (HBG) showed a negative correlation (r=-0.354, p< 0.001). Furthermore, the proportion of Tph cells was positively correlated with the proportion of PD-1hiCXCR5+CD4+T cells (Tfh) (r=0.313, p< 0.05) but negatively correlated with the proportion of CLA+ regular T cells (CLA+ Tregs) (r=-0.351, p< 0.05) and type1 T helper cells (Th1) (r=-0.392, p< 0.05). (Figure 3) Among the 21 patients treated with anti-TNF treatment, non-responders (n=8) showed higher proportion of Tph cells at baseline than those in responders (n=13) (14.01±2.50% vs. 10.82±3.08%, p< 0.05). After 3 months of anti-TNF treatment, the proportion of Tph cells significantly decreased in 18 followed-up RA patients. (pre-treatment: 9.32±2.66% vs. post-treatment: 11.75±3.06%, p< 0.05). (Figure 4)
Conclusion: Our study showed that Tph cells were correlated with disease activity of RA, and patients with higher Tph subset may have poor response to anti-TNF treatment.
Figure 2. Tph cells were significantly associated with RA disease activity
Figure 4. (A) Non-responders and responders Tph cells at the baseline (B) Tph cells at pre-treatment and post-treatment
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ho W, Zhu H, Ye H, Fu D, Xu X. PD-1hiCXCR5-CD4+T Peripheral Helper Cells Enrich in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Predict Clinical Response to Anti-TNF Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pd-1hicxcr5-cd4t-peripheral-helper-cells-enrich-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-predict-clinical-response-to-anti-tnf-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pd-1hicxcr5-cd4t-peripheral-helper-cells-enrich-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-predict-clinical-response-to-anti-tnf-treatment/