Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: PsA is characterized by joint and skin inflammation, and associated with debilitating symptoms of pain and fatigue.1 Previous research has shown that pain and fatigue in patients (pts) with PsA may be driven by inflammatory symptoms.2,3 Consequently, understanding the association between clinically-assessed inflammatory features and pt‑reported symptoms is of interest. We investigated the association between achieving stringent control of swollen joint count (SJC) and reductions in pt‑reported pain and fatigue severity in pts with PsA up to 2 years, using data from two phase 3 studies.
Methods: We analyzed the association between SJC (0 [complete resolution], 1–3, ≥4) and improvements in pt-reported pain and fatigue, assessed using the arthritis Pain Visual Analog Scale (Pain VAS) and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)‑Fatigue (observed case). Pts with SJC 1–3 were pooled due to low pt numbers in these groups.
Pts with PsA from two clinical studies evaluating subcutaneous bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W), BE OPTIMAL (NCT03895203; biologic DMARD [bDMARD]-naïve) and BE COMPLETE (NCT03896581; TNF inhibitor inadequate response/intolerance [TNFi‑IR]), were included. Both had a 16-week (wk) double-blind, placebo-controlled period; BE OPTIMAL included a reference arm (adalimumab 40 mg Q2W). Pts completing Wk 52 of BE OPTIMAL or Wk 16 of BE COMPLETE were eligible for BE VITAL (NCT04009499; open-label extension), in which all pts received BKZ.
Data are reported here for all pts, pooled regardless of treatment arm. Associations are reported at Wks 16, 52, and 104 for BE OPTIMAL; Wks 16, 52/40, and 100/88 for BE COMPLETE (FACIT-Fatigue collected at Wks 40 and 88).
Results: Overall, 710/852 (83.3%) bDMARD-naïve and 322/400 (80.5%) TNFi-IR pts completed Wk 104/100. At baseline, bDMARD-naïve pts had slightly lower SJC and pain and fatigue scores compared with TNFi-IR pts: bDMARD-naïve/TNFi-IR mean (standard deviation) SJC 9.2 (6.7)/9.9 (7.7), Pain VAS 55.2 (23.9)/59.5 (24.3), FACIT-Fatigue 37.0 (9.7)/35.6 (10.3).
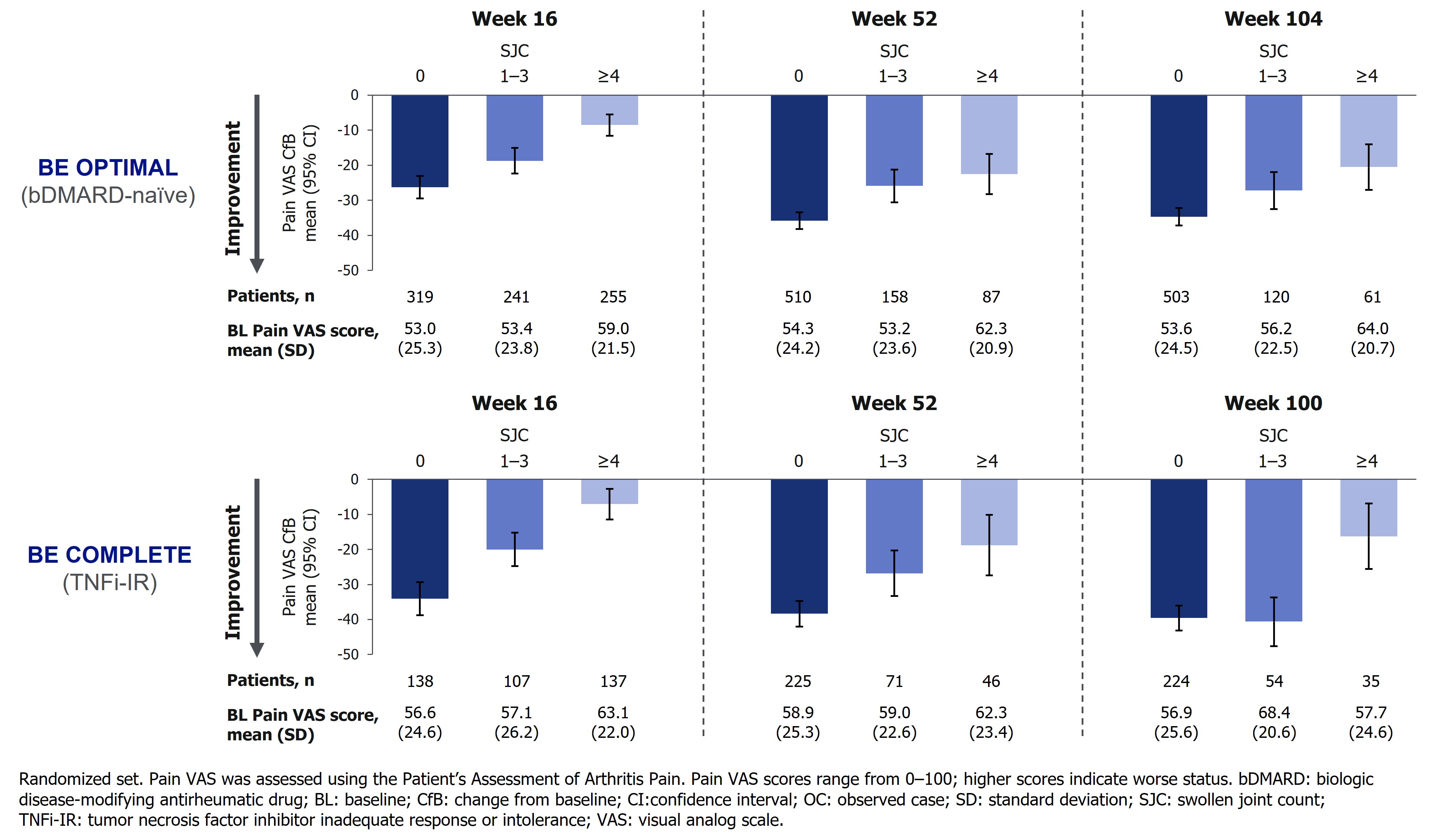
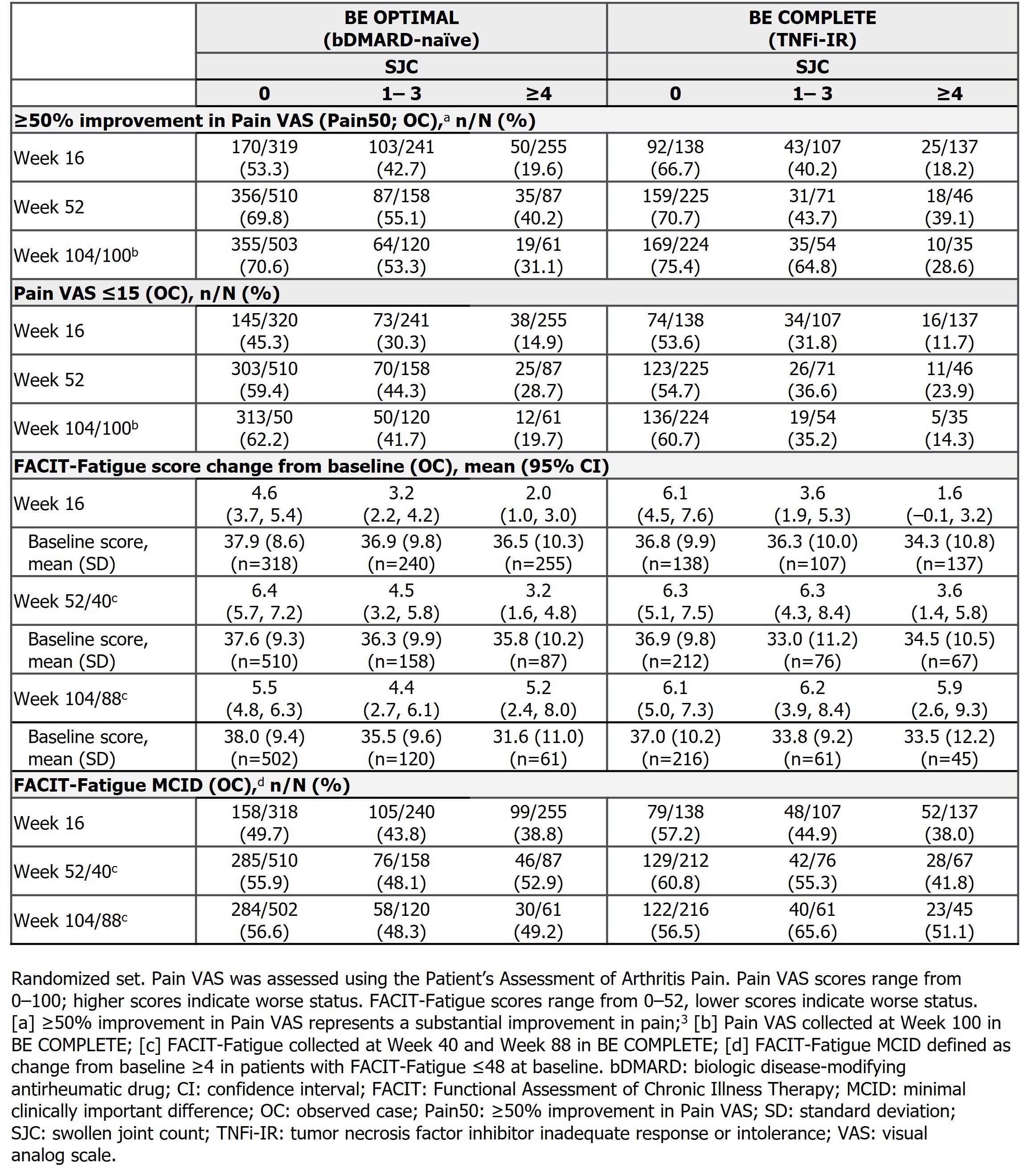
Pts achieving lower SJC demonstrated greater improvements in Pain VAS from baseline at Wk 16; these trends persisted through Wk 52/40 and Wk 104/100 (Figure). Similarly, greater proportions of pts with lower SJC achieved ≥50% improvement in Pain VAS (substantial improvement in pain)4 or Pain VAS score ≤15 at Wks 16 and 52; both were sustained to Wk 104/100 (Table). A similar trend emerged for FACIT‑Fatigue improvements, though these results were less pronounced than Pain VAS, possibly due to the multifaceted nature of fatigue in PsA (Table).5
Conclusion: Attaining stringent control of SJC was associated with greater improvements in pt‑reported pain and fatigue, sustained up to 2 years in pts with PsA. Notably, the most substantial improvements were observed with SJC=0, underscoring the pivotal role of complete resolution as a treatment target.
References: 1. Gudu T. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2018;14:405–17; 2. Mease PJ. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2024;36:282–8; 3. Skougaard M. J Rheumatol 2020;47:548–52; 4. Dworkin RH. J Pain 2008;9:105–21; 5. Krajewska-Włodarczyk M. Reumatologia 2017;55:125–30.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Husni M, Mease P, Gladman D, Ink B, Lambert J, Healy P, Gossec L. Patient-Reported Symptoms Improved with Stringent Control of Swollen Joints in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies of Bimekizumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-symptoms-improved-with-stringent-control-of-swollen-joints-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies-of-bimekizumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-symptoms-improved-with-stringent-control-of-swollen-joints-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies-of-bimekizumab/