Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Early biologic use can improve long-term control of RA, and early use of abatacept (ABA) + MTX has demonstrated sustained improvements in selected patient-reported outcomes (PROs).1,2 AVERT-2 (NCT02504268) is an ongoing, large, Phase IIIb, randomized, double-blinded study evaluating efficacy and safety of SC ABA + MTX vs ABA placebo (PBO) + MTX in ACPA positive (+) patients (pts) with early RA (disease duration ≤6 months) for 56 weeks, followed by a 48-week de-escalation.3 Results of a post hoc analysis of PROs at 24 and 52 weeks in the AVERT-2 study are presented.
Methods: For the induction period, pts were randomized to SC ABA (125 mg weekly) + MTX or ABA PBO + MTX for 56 weeks. Key inclusion criteria: age ≥18 years; RA diagnosis ≤6 months (ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria); ACPA+; CRP >3 mg/L (upper limit of normal/ESR ≥28 mm/h); TJC ≥3 and SJC ≥3; DMARD naïve. PROs included pain (visual analog scale [VAS], 0–10 cm), pt assessment of disease activity (PtDA; VAS, 0–10 cm), physical function (HAQ-DI; 0–3), fatigue (Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue), Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire and pt overall quality of life (Short-Form 36 [SF-36] physical component summary [PCS]/mental component summary version 2.0). Adjusted mean change from baseline (adMCFB) and the proportion of pts attaining a minimal clinically important difference (MCID; values defined in Table 2)4 at 24 and 52 weeks were calculated for each PRO in the intention-to-treat population. AdMCFB was estimated using a mixed effect model with repeated measures.
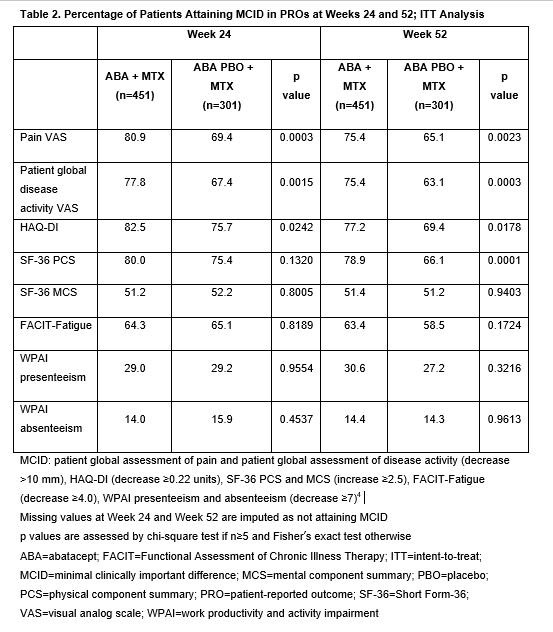
Results: Of the 752 randomized pts, 451 were treated with ABA + MTX and 301 with ABA PBO + MTX. Baseline characteristics were similar across treatment arms.3 The adMCFB showed improvements in all PROs at both timepoints for both treatment arms (Table 1), with ABA + MTX vs ABA PBO + MTX showing greater magnitude of improvement in pain PtDA, HAQ-DI and SF-36 PCS at both Weeks 24 and 52 (p≤0.0001). For all PROs except WPAI, more than half of pts achieved the MCID (Table 2). Compared with ABA PBO + MTX, a significantly greater proportion of ABA + MTX–treated pts attained the MCID in pain, PtDA and HAQ-DI at Weeks 24 and 52 (p< 0.05). Although there was no difference at Week 24, by Week 52 a greater proportion of pts attained the MCID in SF-36 PCS with ABA + MTX than with PBO + MTX.
Conclusion: In pts with early RA, treatment with abatacept + MTX and abatacept PBO + MTX were both associated with substantial improvements in PROs and quality of life by 24 weeks that were sustained over 1 year. Compared with abatacept PBO + MTX, a significantly greater proportion of abatacept + MTX–treated pts reported clinically meaningful improvements in pain, PtDA and function (HAQ-DI) by 24 weeks; this difference was sustained at 52 weeks. Further long-term follow-up analysis including impact of de-escalation of therapy is warranted.
References:
- Emery P, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:19–26.
- Emery P, et al. RMD Open 2019;5:e000840.
- Emery P, et al. ACR Annual Meeting 2018; San Diego, CA, USA: Poster 563.
- Reilly MC, et al. Gut2007;56(Suppl 3):159.
Professional medical writing: Claire Line, PhD, funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Emery P, Tanaka Y, Bykerk V, Bingham C, Huizinga T, Citera G, Zhuo J, Huang K, Wong R, Connolly S, Elbez Y, Fleischmann R. Patient-Reported Outcomes of Abatacept in Combination with MTX in Early, MTX-Naïve, ACPA Positive Patients with RA: 1-Year Results from a Phase IIIb Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-of-abatacept-in-combination-with-mtx-in-early-mtx-naive-acpa-positive-patients-with-ra-1-year-results-from-a-phase-iiib-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-of-abatacept-in-combination-with-mtx-in-early-mtx-naive-acpa-positive-patients-with-ra-1-year-results-from-a-phase-iiib-study/