Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2019–2038) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a severe and common (50%) organ-threatening manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus and is associated with a high risk of progression to chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.1 LN treatment goals include normalization of kidney function, low disease activity and, increasingly, improvements in health-related quality of life (HRQOL). Assessment of content validity for the Short Form-36 (SF-36) and FACIT-Fatigue scales have identified fatigue, pain, vitality and physical well-being as particularly impactful in patients with LN compared with healthy controls.2,3 Limited data exist on the relationship between renal function and HRQOL in patients with LN.
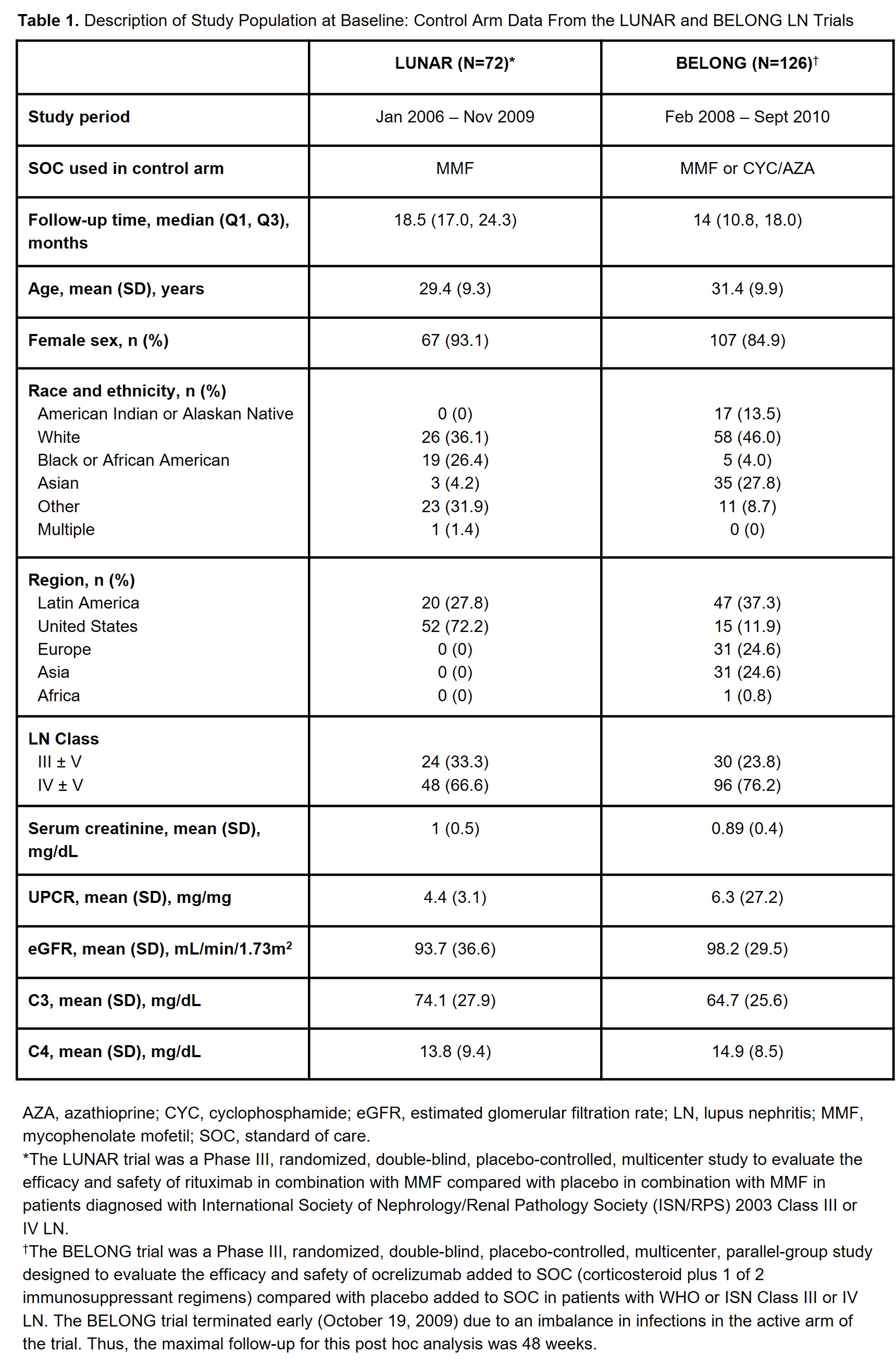
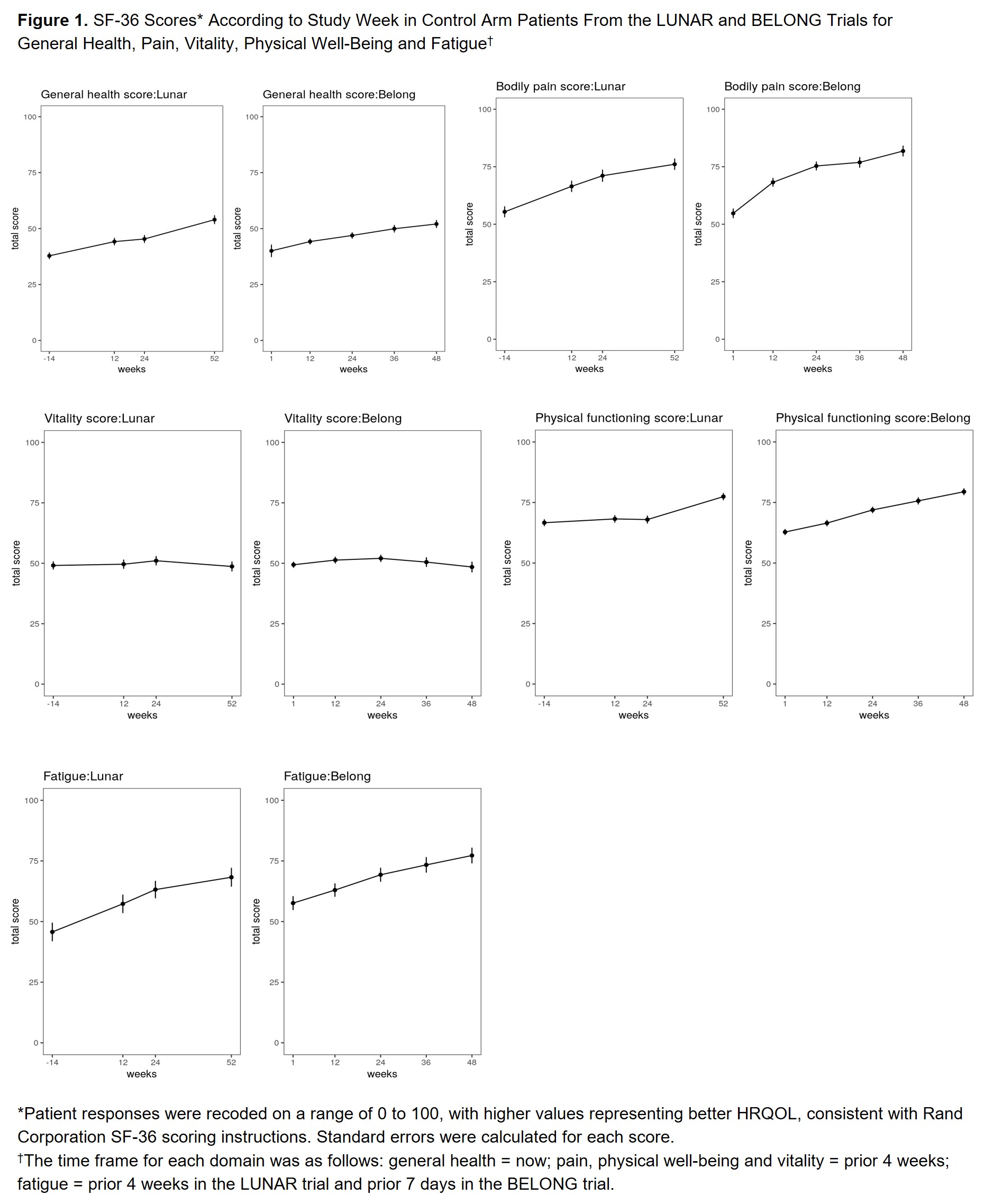
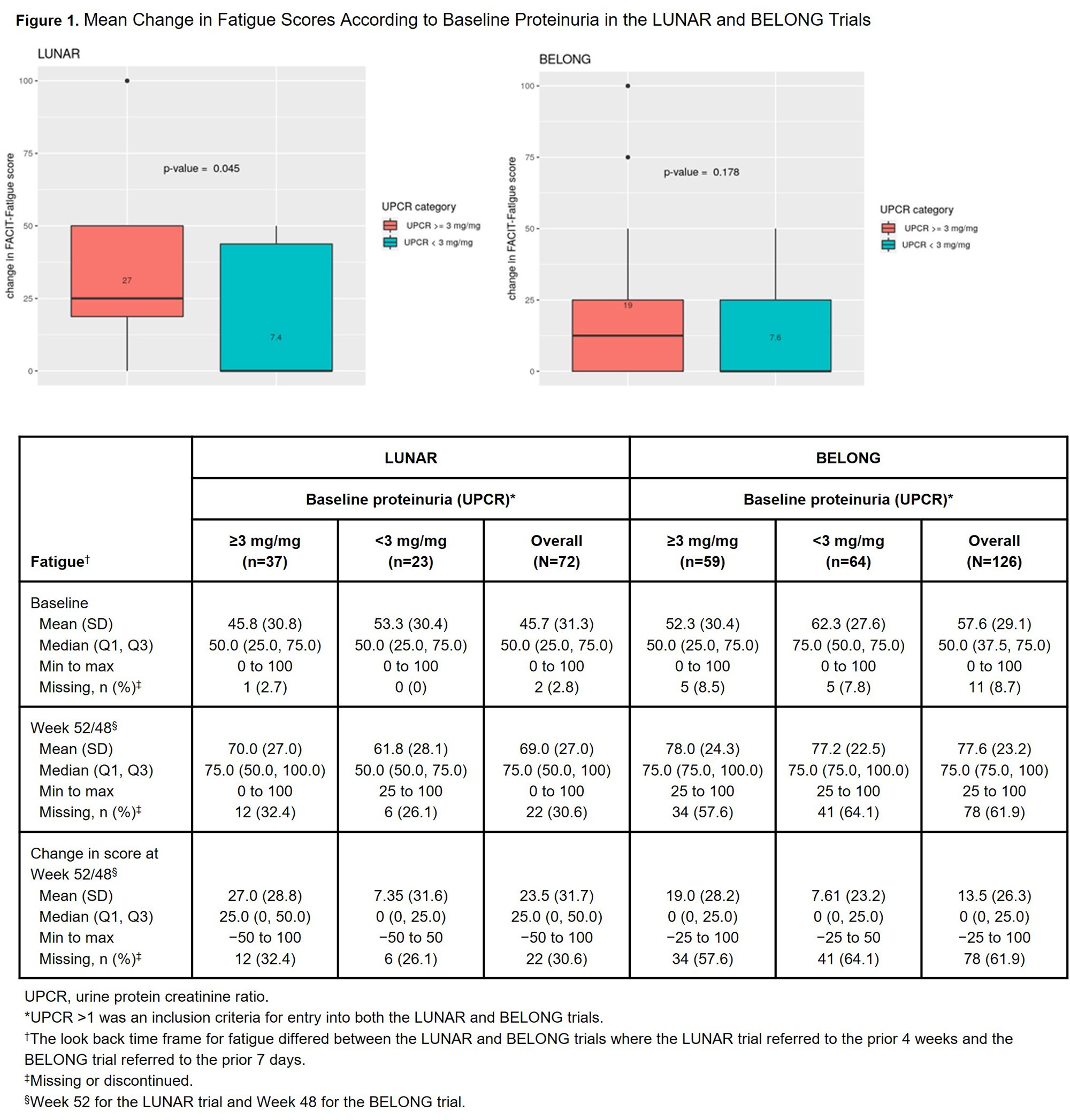
Methods: We conducted a post hoc descriptive analysis of data collected from the control arms of 2 global Phase III LN RCTs: LUNAR (NCT00282347)4 and BELONG (NCT00626197).5 We excluded active-arm patients to focus on patients receiving standard of care (SOC) therapy. These studies included adult ANA+ patients with biopsy-confirmed class III/IV LN and proteinuria. We described patients according to baseline factors and characterized HRQOL scores over study week. The LUNAR trial included the Expanded Health Survey (EHS) (Weeks 0, 12, 24 and 52), and BELONG included the SF-36, FACIT-Fatigue and modified Brief Pain Inventory (Weeks 0, 12, 24, 36 and 48). The SF-36 and EHS include information on general health, social/physical functioning, role limitations due to physical/emotional problems, vitality, emotional well-being and pain. We analyzed these tools based on recoding responses to a range of 0 to 100, with higher values representing better HRQOL. We assessed the relationship between (1) baseline proteinuria (urine protein creatinine ratio [UPCR]) and (2) complete renal response (CRR) and mean change in fatigue and general health scores using stratified analyses and Mann-Whitney test for differences.
Results: Table 1 describes baseline study-specific patient characteristics. The lowest baseline scores were identified for general health and vitality in the SF-36 and for fatigue, tiredness and energy in the FACIT-Fatigue. Figure 1 provides SF-36 scores for general health, pain, vitality, physical functioning and fatigue by study week. HRQOL trajectories suggest consistent patterns across trials with improvements in domains such as fatigue and pain. Patients with baseline UPCR ≥3 had greater change in fatigue score at Week 52/48 than those with UPCR < 3 (Figure 2). We did not identify significant changes in fatigue score by CRR status, nor change in general health score at Week 52/48 according to baseline UPCR or CRR.
Conclusion: Initial post hoc analysis of patients in the control arms of the LUNAR and BELONG trials suggest greater improvements in fatigue among patients with baseline UPCR ≥3. Additional multivariate analyses will provide enhanced understanding of the relationship between renal function and HRQOL over time. References:
- Parikh SV, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76:265-281.
- Williams-Hall R, et al. Lupus Sci Med. 2022;9:e000712.
- Kharawala S, et al. Lupus. 2022;31:1029-1044.
- Rovin BH, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:1215-1226.
- Mysler EF, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2368-2379.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tchakoute C, Mao H, Wallenstein G, Ross Terres J, Yoshida S, Lindsay L. Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Lupus Nephritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of Control Arm Data from Two Completed Phase III Randomized Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-control-arm-data-from-two-completed-phase-iii-randomized-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-control-arm-data-from-two-completed-phase-iii-randomized-clinical-trials/