Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have long been considered the gold standard for clinical research, but can be complemented with real-world data (RWD) to further inform clinical decision-making. We evaluated patient (pt) characteristics, efficacy, and treatment patterns for tofacitinib monotherapy in pts with RA using RCT data and available RWD.
Methods: Three cohorts of pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID monotherapy were defined for post hoc analyses of RCT data: Cohort (C)1, pts with an inadequate response to DMARDs from Phase (P)3 and P3b/4 RCTs (NCT00814307/NCT02187055); C2, MTX-naïve pts from a P3 RCT (NCT01039688); and C3, pts who completed an index study and continued in any long-term extension study (NCT00413699/NCT00661661). Outcomes included Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) low disease activity (LDA; scores ≤ 10) rates, and rates of/time to study discontinuation due to lack of efficacy or adverse events (AEs; per Kaplan–Meier plots). Across outcomes, available RWD are presented for contextualization, identified by non-systematic literature searches of PubMed, Embase, and ACR/EULAR abstracts, from 2013–2021.
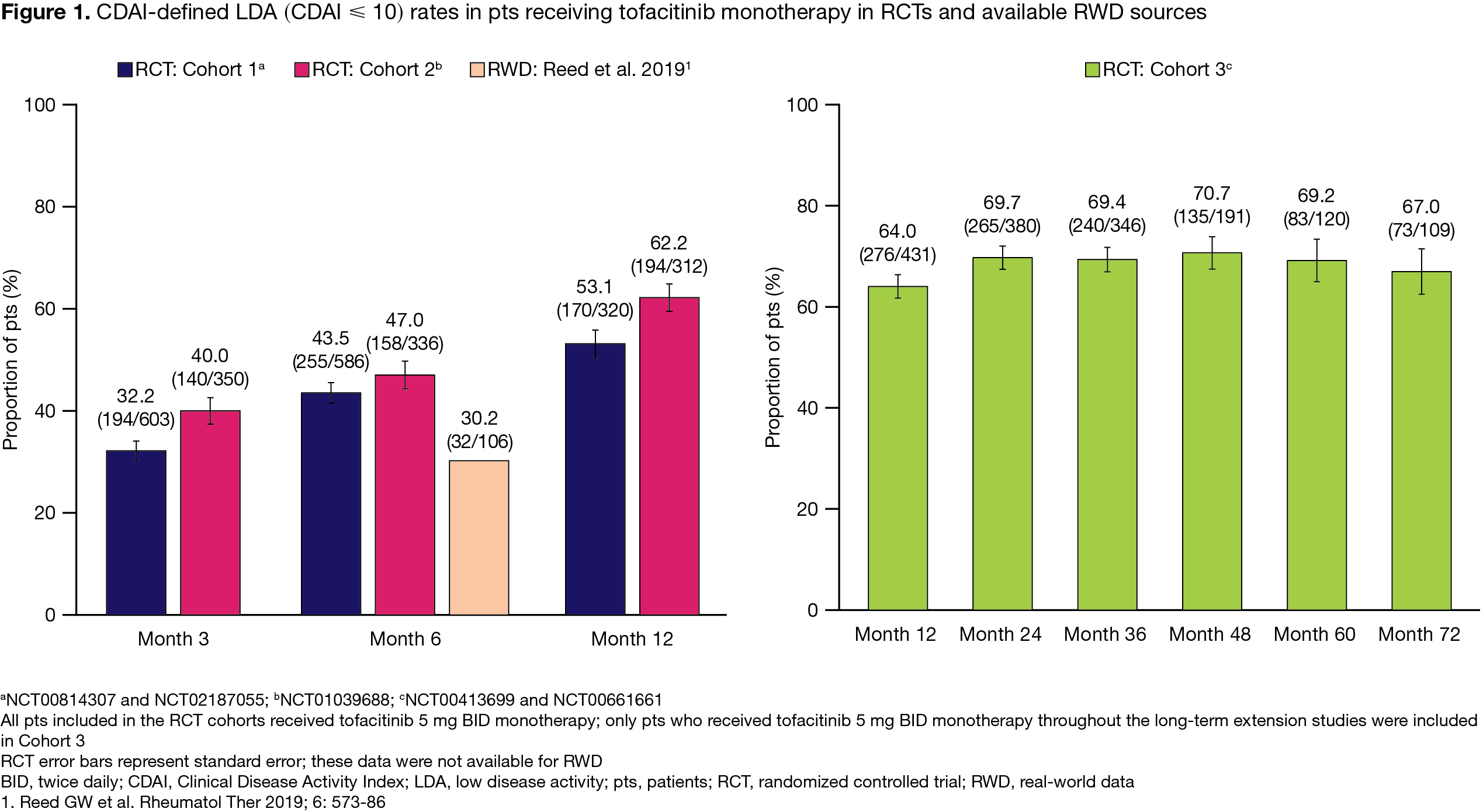
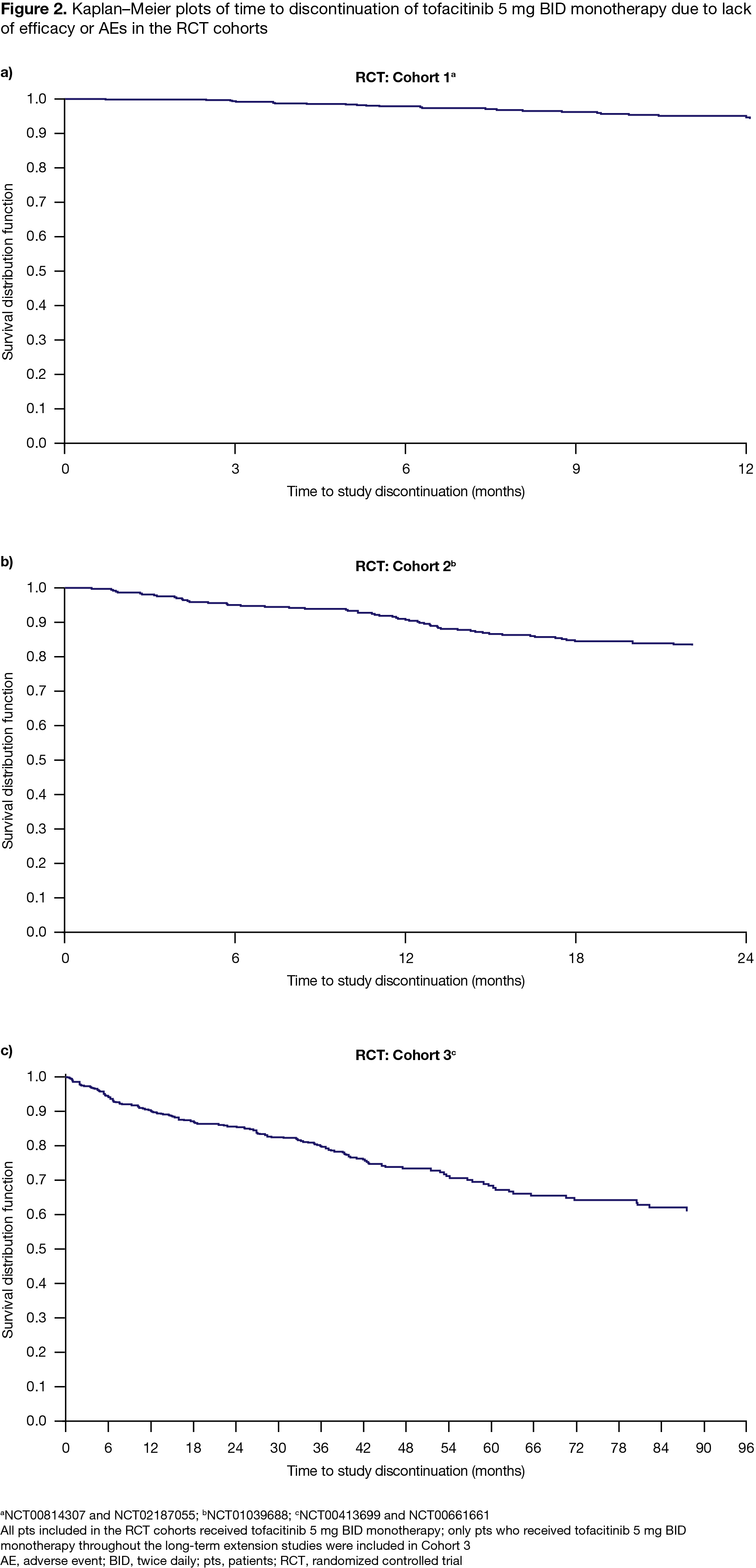
Results: 1,498 pts treated with tofacitinib 5 mg BID monotherapy were included in the RCT analysis (C1, n=627; C2, n=373; C3, n=498); generally, baseline (BL) disease activity was high, most pts received concomitant glucocorticoids (GC) and were biologic (b)DMARD‑naïve (Table). C1 and C2 CDAI LDA rates were ≥ 32.2% by Month (M)3 and sustained through M12 (Figure 1); C3 LDA rates ranged from 64.0–70.7% through M72 (Figure 1). In C1, C2, and C3, respectively, 4.0%, 15.6%, and 27.7% of pts discontinued due to lack of efficacy or AEs; Kaplan–Meier plots of time to discontinuation are presented in Figure 2. We identified 6 RWD publications that included tofacitinib monotherapy data; across publications, 16.6–59.2% of tofacitinib-treated pts received tofacitinib monotherapy.1-6 Only 1 paper reported BL characteristics with tofacitinib monotherapy: median disease activity was moderate, pts had low GC use, and most were bDMARD-experienced1 (Table 1). In the same paper, M6 CDAI LDA rates were 30.2% (Figure 1). Another paper estimated the 1‑year retention rate for tofacitinib monotherapy as 59.7%.6 While no RWD on treatment discontinuation specific to tofacitinib monotherapy were identified, 1 paper reported no significant differences in retention with tofacitinib monotherapy vs tofacitinib + conventional synthetic DMARDs (HR 1.11 [95% CI 0.91, 1.35]).4
Conclusion: Tofacitinib 5 mg BID monotherapy demonstrated good efficacy and persistence in post hoc analyses of RCT data. Variable monotherapy rates were seen in RWD; based on available data, tofacitinib monotherapy demonstrated good efficacy, and retention comparable with combination therapy.
1. Reed GW et al. Rheumatol Ther 2019; 6: 573-86
2. Babaeva A et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79: 635.
3. Bird P et al. Clin Rheumatol 2020; 39: 2545-51.
4. Finckh A et al. RMD Open 2020; 6: e001174.
5. Mueller RB et al. J Clin Med 2019; 8: 1548.
6. Bilgin E et al. Turk J Med Sci 2021; 51: 297-308.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by K Woollcott, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pope J, Finckh A, Silva-Fernández L, Mandl P, Fan H, Rivas J, Valderrama M, Montoro M. Patient Characteristics, Efficacy, and Treatment Patterns of Tofacitinib Monotherapy in Patients with RA: Contextualization of Randomized Controlled Trial Results with Real-world Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-characteristics-efficacy-and-treatment-patterns-of-tofacitinib-monotherapy-in-patients-with-ra-contextualization-of-randomized-controlled-trial-results-with-real-world-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-characteristics-efficacy-and-treatment-patterns-of-tofacitinib-monotherapy-in-patients-with-ra-contextualization-of-randomized-controlled-trial-results-with-real-world-data/