Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biosimilars have been approved for the treatment of inflammatory arthritis and evidence from randomised controlled trials have demonstrated equivalent efficacy to biologics. Etanercept biosimilar, SB4, is licensed for use to treat inflammatory arthritis. While some patients may selectively switch from reference etanercept (ETN) to SB4 by a rheumatologist or rheumatology nurse specialist, others may be automatically switched, by pharmacy. Currently, it is the policy of one Health Board area in Wales to use SB4 in place of ETN and to automatically switch ETN patients to SB4. While in a neighboring Health Board area, patients are not automatically switched but can selectively switch or commence SB4 treatment.
Methods: Using electronic health records we will investigate the safety and efficacy of switching of ETN to SB4 in one health region (Automatic SB4 area), compared with selective use and switching in a neighboring health region (Selective SB4 area). Data from the Secure Anonymised Information Linkage (SAIL) databank in Wales, United Kingdom was used to create a retrospective cohort study using linked, general practitioner, hospital and rheumatology clinic records. Patients aged 18 years or over with diagnosis codes for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) or Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and treated with SB4 were included. Data was included from 2014 to 2019 to coincide with the introduction of biosimilar therapies in UK clinical practice.
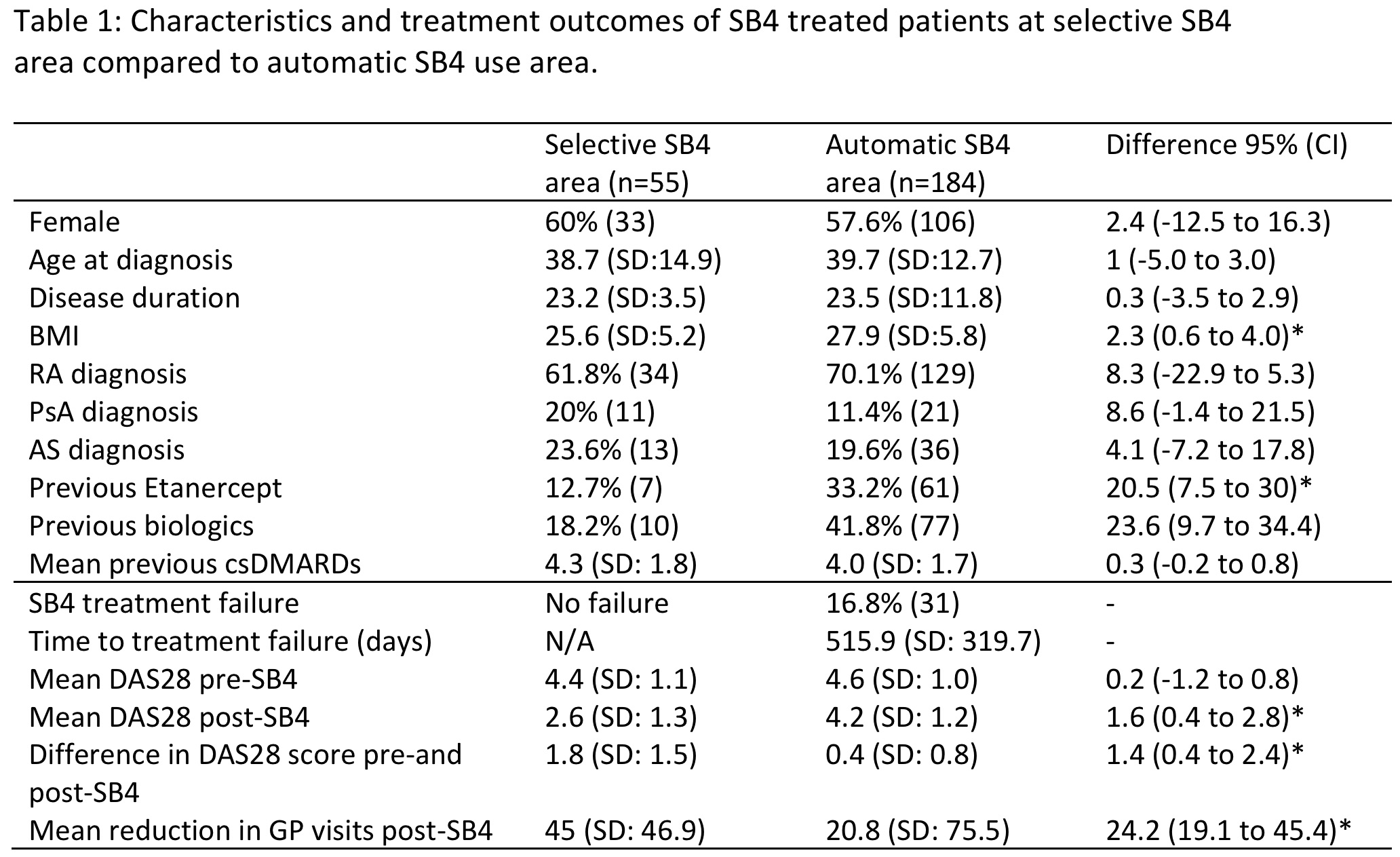
Results: There were 239 patients with inflammatory arthritis treated with SB4 included in the study (Table 1). The majority of the patients had RA. In the automatic switching area, 184 patients were treated with SB4, compared to 55 in selective use area, where most patients were biologic naïve (45/55). Here, 7 of these patients (12.7%) were selectively switched from ETN to SB4 (Table 1). In the automatic switching area, 61 out of 181 (33.2%) were automatically switched; the remaining patients would have automatically commenced SB4 in place of reference ETN. Following treatment with SB4, the DAS28 reduced by 1.8 + 1.5 in the selective SB4 area compared to a reduction of 0.4 + 0.8 in the automatic SB4 area. This confirmed patients were switched from stable disease. The GP visits were reduced in both selective (45 + 46.9) and the automatic SB4 area (20.8 + 75.5). The GP visit reduction was significantly larger in patients from the selective area compared to automatic area (difference 24.2 visits, 95% CI: 3.0 to 45.4).
Sensitivity analyses compared changes in DAS28 scores pre- and post-SB4 treatment between biologic naïve and biologic experienced SB4 patients. No significant difference was found in the change in DAS28 scores between biologic naïve and biologic experienced SB4 patients (difference 0.1, 95% CI: -1.2 to 1.4).
Conclusion: SB4 was effective in etanercept naïve patients. Automatically switching did not lead to disease worsening significant. Furthermore, treatment with SB4 reduced healthcare utilisation of patients, as measured by GP visits, whether automatically or selectively treated with the drug.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cooksey R, Brophy S, Azizur M, Kennedy J, Choy E. Outcomes and Efficacy of Selective versus Automatic Switching from Etanercept to a Biosimilar in Inflammatory Arthritis Using Electronic Health Records from UK [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-and-efficacy-of-selective-versus-automatic-switching-from-etanercept-to-a-biosimilar-in-inflammatory-arthritis-using-electronic-health-records-from-uk/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-and-efficacy-of-selective-versus-automatic-switching-from-etanercept-to-a-biosimilar-in-inflammatory-arthritis-using-electronic-health-records-from-uk/