Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: It has been demonstrated that pretreatment with intravenous glucocorticoids can prevent infusion-related reactions (IRR) that may occur in RA patients receiving rituximab infusions [1]. However, glucocorticoids can also be administered orally. This has advantages, including decreased total medication administration time and cost reduction [2]. Therefore, intravenous prednisolone was switched to oral prednisolone as premedication of rituximab infusions in January 2022 in our rheumatology clinic. Since oral prednisolone is rapidly and completely absorbed, oral administration is expected to be as effective in preventing IRR as intravenous administration, however, solid data are lacking. Therefore, we aim to compare the occurrence of IRR between pretreatment with oral prednisolone and intravenous prednisolone.
Methods: A single-center, explorative, retrospective, observational, cohort study was performed. All rituximab infusions administered between January 31st 2020 and January 30th 2024 in adult RA patients at the rheumatology department of a clinic in The Netherlands were included. The primary outcome was the crude cumulative incidence of IRR during the period of intravenous prednisolone administration (January 31st 2020 – January 30th 2022) compared to oral administration (January 31st 2022 – January 30th 2024) using Chi-squared test. IRR were defined as all reported reactions during and after infusion of rituximab.
Secondary outcomes were severity of IRR (based on the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) [3]), reaction type (type I versus other reactions), actions taken after IRR and clinical signs and symptoms. Analyses were adjusted for confounders (first infusion and concomitant conventional synthetic DMARD) using multivariate logistic regression.
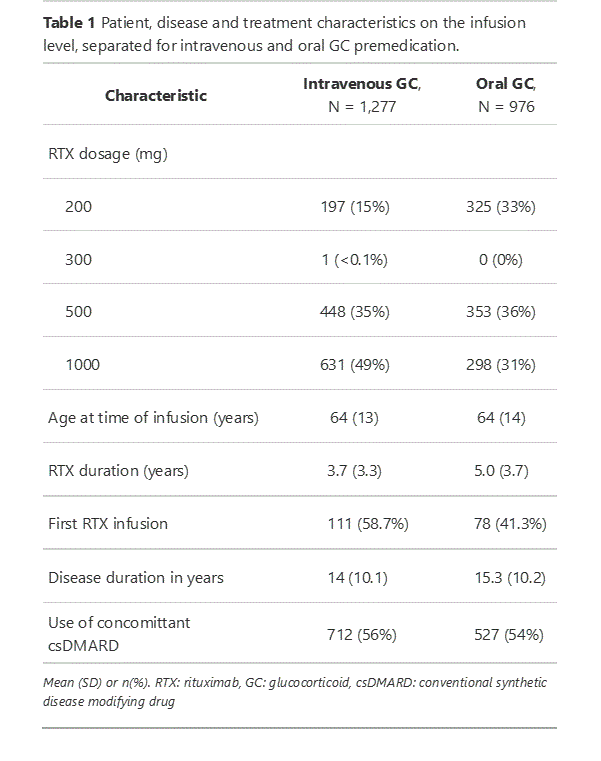
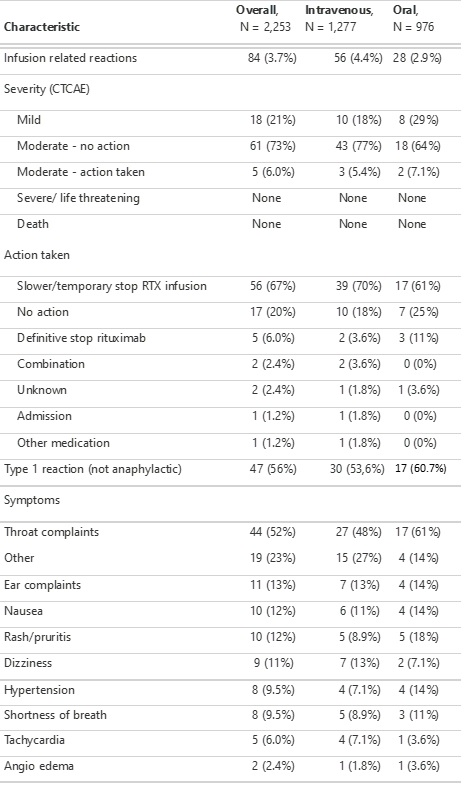
Results: In total, 2,253 infusions were analysed, of which 189 (8.4%) were first rituximab infusions. Mean age of patients at the time of infusion was 65 years of age (SD = 13), and 70% was female (Table 1). The overall incidence of IRR was 84 (3.7%) of which 16 (8.5%) occurred after first infusion of rituximab. The crude cumulative incidence of IRR was similar in the oral premedication group (2.9%) compared to the intravenous premedication group (4.4%) (p=0.077) (Table 2). The adjusted analysis confirmed this non significant difference in favor of oral premedication (odds ratio = 0.54; 95% confidence interval: 0.28-1.02). Secondary outcomes were also similar between treatment groups (Table 2).
Conclusion: Oral prednisolone was at least equally effective compared to intravenous prednisolone in preventing IRRs of rituximab. Switch to oral prednisolone in the premedication of rituximab could be considered in all facilities administering rituximab to RA patients.
References
[1] Emery Pet al. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(5):1390–1400.
[2] Carter, J.Det al. Clin Rheumatol 31, 1605–1610 (2012).
[3] Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 5.0, published 17 November 2017 https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_8.5×11.pdf
IRR: infusion-related reactions, RTX: rituximab, GC: glucocorticoid, CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bovens P, Van Esveld L, Wientjes M, van Herwaarden N, Ten Cate D, Melis E, Lesuis N, van den Bemt B, den Broeder A. Oral Glucocorticoid Premedication Is at Least as Effective as Intravenous Glucocorticoid Premedication for Prevention of Infusion-related Reactions to Rituximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oral-glucocorticoid-premedication-is-at-least-as-effective-as-intravenous-glucocorticoid-premedication-for-prevention-of-infusion-related-reactions-to-rituximab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oral-glucocorticoid-premedication-is-at-least-as-effective-as-intravenous-glucocorticoid-premedication-for-prevention-of-infusion-related-reactions-to-rituximab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/