Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The EULAR recommendations for the treatment of RA state, by expert opinion, that if a treatment target is not achieved with the first csDMARD strategy, addition of a bDMARD or a tsDMARD should be considered if at least 1 poor prognostic factor (PPF) is present. PPF are defined as: moderate to high disease activity after csDMARDs, high acute phase reactant levels, high swollen joint counts presence of RF and/or ACPA (especially in high levels), combinations of aforementioned PPFs and presence of early erosions. We investigated the presence of PPF in early RA patients, aiming to compare the clinical response on either csDMARD combination or bDMARD therapy in relation to presence or absence of PPF, in the IMPROVED trial.
Methods: In the IMPROVED trial, 479 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (2010-criteria) started treatment with MTX and a 4-month tapered high dose of prednisone bridging scheme. Patients not in early remission (DAS ≥1.6) after 4 months of the initial treatment were randomized to either 4 months MTX + HCQ + SSZ + continued low dose prednisone (arm 1) or to 4 months MTX + adalimumab (arm 2). A maximum of 5 PPFs could be present in any patient. High acute phase reactants were defined as CRP ≥0.8 mg/dl or ESR levels >20 mm/hour in women and >15 mm/hour in men. For swollen joint counts (SJC), we defined a high SJC as >10 in our main analysis and performed a sensitivity analysis with a definition of high SJC when the SJC was >4.
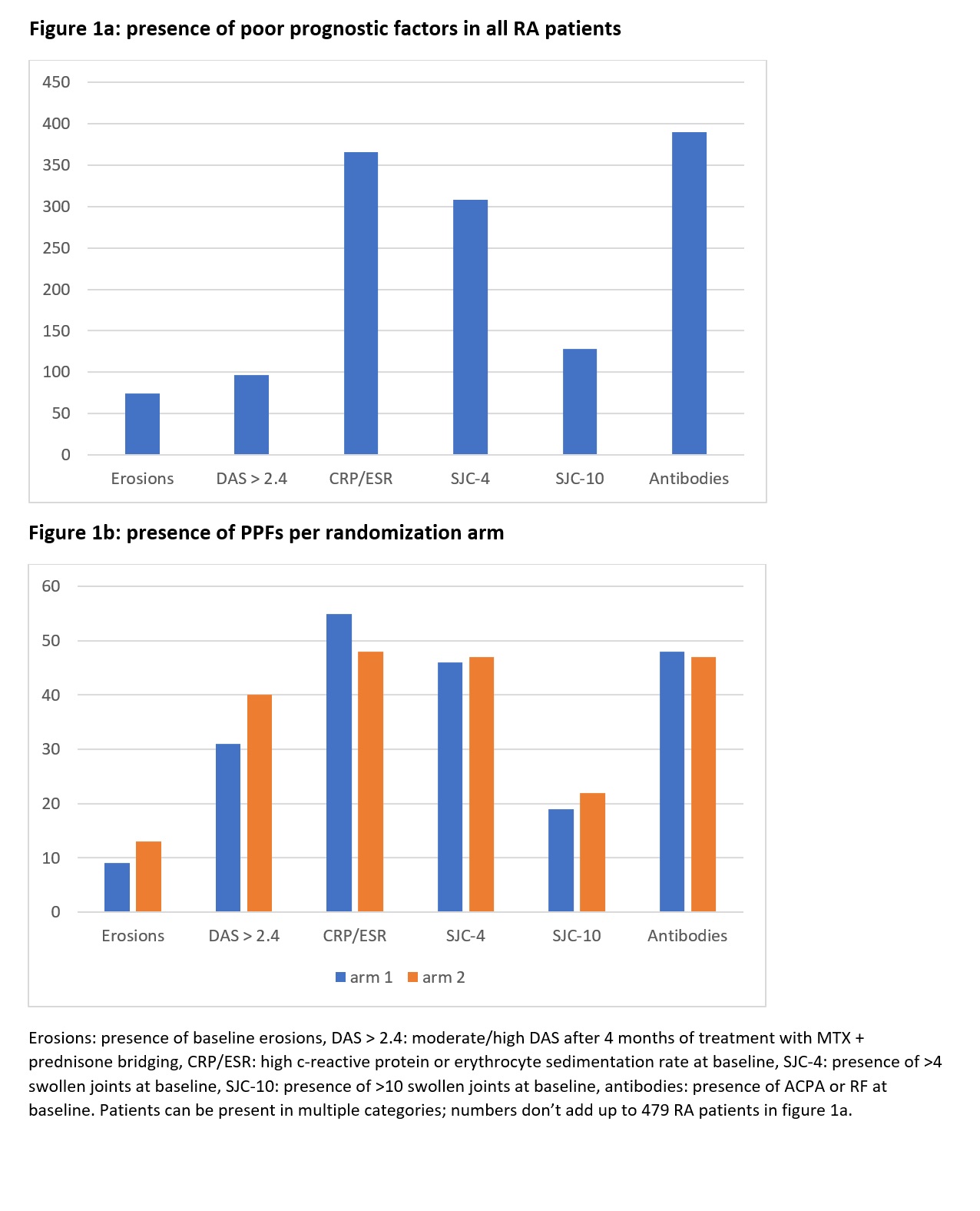
Results: Almost all RA patients had at least one PPF as mentioned in the EULAR recommendations. Presence of each PPF is displayed in figure 1. High inflammatory parameters and presence of antibodies at baseline were the most frequent PPFs (present in 366 and 390 patients, respectively). Presence of PPFs was evenly distributed between the randomization arms (figure 1b). Only 5 patients (1%) had no PPFs in the main analysis and only 10 (2%) in the sensitivity analysis. Of these, 2/5 and 2/10 patients did not achieve early remission and were randomized to the two treatment arms. Due to these small numbers, no further comparison in treatment response was done. In total, 65 patients with PPFs were evenly randomized to each study arm. Mean (SD) DAS change in arm 1 was -0.47 (-0.79) and in arm 2 -0.57 (-0.74), p = 0.48. Changes in HAQ were similar, median (IQR) HAQ change was -0.13 (-0.13 ; 0.13) in arm 1 and -0.13 (-0.25 ; 0.25) in arm 2, p=0.13. In the 5 and 6 patients that showed progression of radiographic damage, median (IQR) progression was 1 (0.5 ; 2) in arm 1 and 0.5 (0.5 ; 1) in arm 2, p =0.48.
Conclusion: Empirically identified PPFs were present in up to 99% of patients with early RA. High prevalence of PPFs is probably due to a large overlap between these PPFs and the 2010 RA classification criteria. According to current EULAR recommendations, it is recommended to start a b/tsDMARD in patients with PPF after failing first therapy with MTX and GC bridging. After failure to achieve the treatment target on this first treatment, we found no significantly better response in these patients on bDMARDs compared to csDMARDs. No comparison could be made with non-PPF patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van der Pol J, Bergstra S, Huizinga T, Allaart C. Omnipresent Poor Prognostic Factors in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis in the IMPROVED Trial; Is Earlier bDMARD Treatment Escalation for All Necessary? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/omnipresent-poor-prognostic-factors-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-improved-trial-is-earlier-bdmard-treatment-escalation-for-all-necessary/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/omnipresent-poor-prognostic-factors-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-improved-trial-is-earlier-bdmard-treatment-escalation-for-all-necessary/