Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Olokizumab (OKZ) is an interleukin-6-inhibitor for treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). In these analyses, we present patient reported outcomes (PROs) reported by MTX-IR patients with moderate to severely active RA treated with OKZ vs adalimumab (ADA) or placebo in a phase 3 randomized controlled trial (RCT) CREDO2 (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02760407).1
To assess the effect of OKZ treatment compared with placebo and ADA in patient global assessment of disease activity (PtGA), pain, physical function (HAQ-DI), fatigue (FACIT-F) and health related quality of life (SF-36 physical (PCS) and mental (MCS) component summary and domain scores) and work participation (WPS-RA) at week 12.
Methods: 1648 patients receiving MTX were randomized to receive SQ injections: 1) OKZ 64 mg every 2 weeks (q2w, n=464), 2) OKZ 64 mg q4w (n=479), 3) ADA 40 mg q2w (n=462) and 4) placebo q2w (n=243). At week 14, non-responders: subjects without ≥ 20% improvements in both swollen and tender joint counts, added rescue medication (sulfasalazine and/or hydroxychloroquine) to study treatment. Between groups differences in least-squares mean (LSM) changes from baseline were analyzed
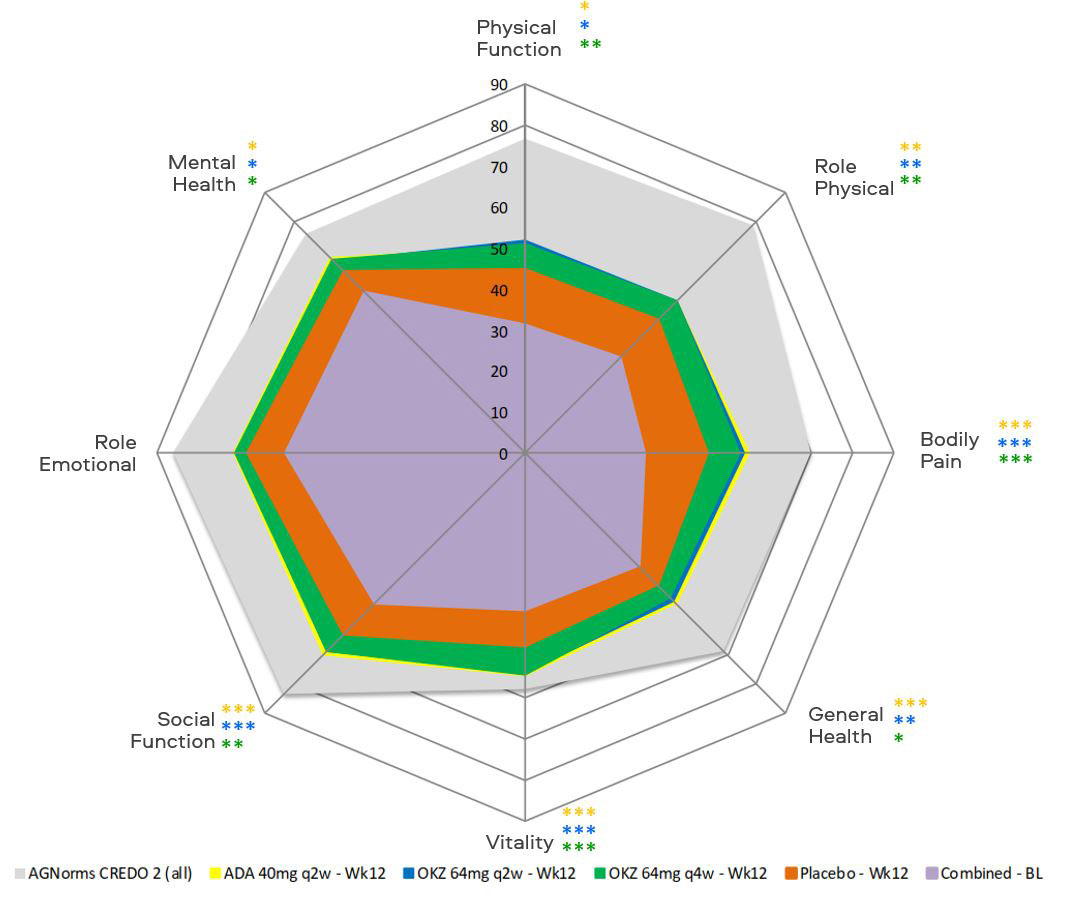
Results: At week 12, treatment with both OKZ doses and ADA resulted in statistically greater LSM changes from baseline than placebo across all PROs, including 7 of 8 domains of SF-36 with exception of role emotional. (Table and Figure). Reported work and household work impairments, days productivities were reduced by half and missed household work days because of arthritis were all improved (p< 0.01) with OKZ and ADA treatment. PROs further improved to week 24 in the active treatment arms. Post hoc analyses demonstrated that a higher proportion of patients receiving both doses of OKZ as well as ADA reported improvements ≥ minimum clinically important differences vs placebo (p< 0.01) across all PROs, indicating clinically meaningful benefits on an individual patient basis. Estimates of numbers needed to treat indicated that between 5 and 10 patients would need to be treated to achieve these benefits. More patients in both OKZ groups reported scores ≥ normative values in PtGA, HAQ-DI and SF-36 PCS scores; with ADA in PtGA and HAQ-DI.
Conclusion: Treatment with both doses of OKZ resulted in similar, statistically significant improvements across PROs vs placebo in MTX-IR patients with moderate to severely active RA, comparable to ADA, that were clinically meaningful.
Footnotes: LSM difference (SE) 97.5% CI by ANCOVA. NRS imputation.
*, secondary endpoint; †p≤0.05, ⱡ p<0.01, #p<0.001 vs placebo; VAS (mm).
Footnotes:
*p≤0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 ADA vs placebo (orange);
*p≤0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 OKZ q2w vs placebo (blue);
*p≤0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 OKZ q4w vs placebo (green).
AGNorms, age- and gender-matched; BL, baseline.
Reference: 1. V. Strand, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022; 81:43_44.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Nasonov E, Lisitsyna T, Lila A, Kuzkina S, Samsonov M, Feist E. Olokizumab Improves Patient Reported Outcomes in Moderate to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Inadequately Controlled by Methotrexate (MTX-IR): Results from the Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/olokizumab-improves-patient-reported-outcomes-in-moderate-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-inadequately-controlled-by-methotrexate-mtx-ir-results-from-the-phase-iii-randomized-contr/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/olokizumab-improves-patient-reported-outcomes-in-moderate-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-inadequately-controlled-by-methotrexate-mtx-ir-results-from-the-phase-iii-randomized-contr/