Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate efficacy and safety of olokizumab (interleukin-6 inhibitor) in RA patients with special attention to chronic pain and a signs of central sensitization.
Methods: An open-label observational non-interventional study of the effectiveness of olokizumab in RA was conducted. A total of 183 patients with RA were enrolled in the study, with data available for 160 patients in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population and 144 patients in the per-protocol population. The mean age of the patients was 50.6±13.6 years, 82.7% women, mean DAS28-CRP 5.1±0.9. 87.8% of patients were positive for rheumatoid factor and 74.3% for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies. The patients reported moderate to severe pain, mean score 6.0±2.0 (numerical rating scale, NRS 0-10).
All patients received olokizumab 64 mg subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks with methotrexate. We assessed DAS28-CRP, patient’s global assessment of disease activity (PGA), FACIT-Fatigue, pain (NRS), functional impairment (NRS), signs of central sensitization (CSI) and symptoms of neuropathic pain (PainDETECT) for ITT and per protocol populations.
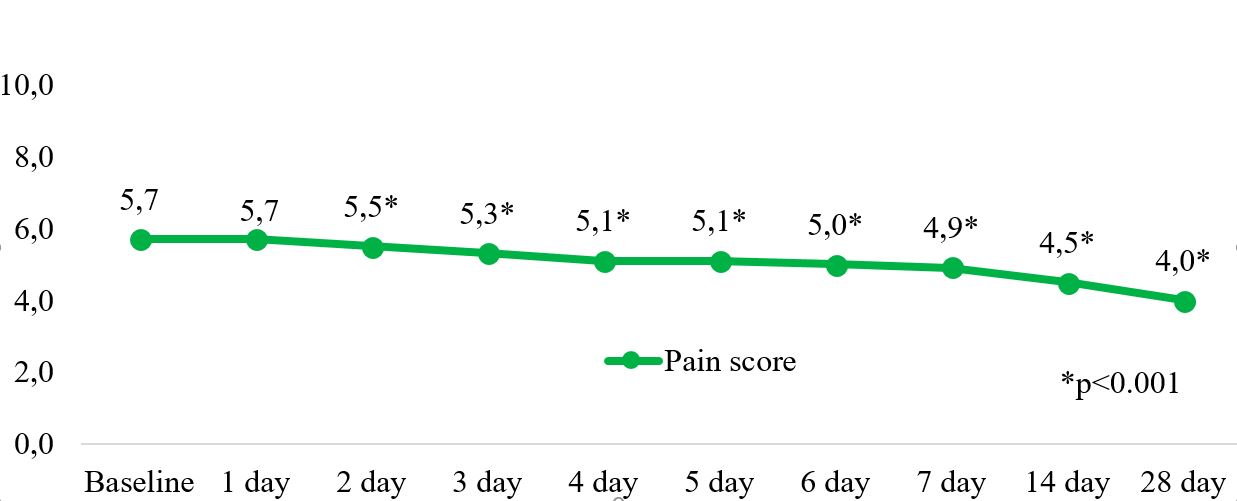
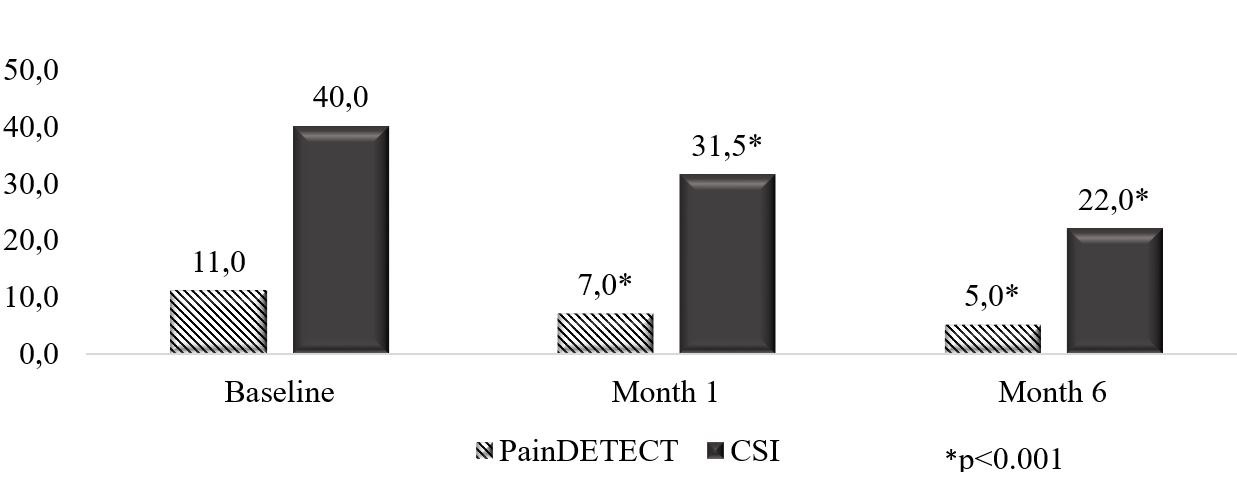
Results: After 6 months, DAS28-CRP decreased to 3.3±0.9 (p< 0.001) and 37.6% of patients achieved low disease activity or remission. There was a significant reduction in pain intensity (Figure 1). Notably, there was a significant decrease in pain intensity as early as day 2 after the first administration of OKZ (p< 0.05). The number of patients with signs of central sensitization (CSI ≥40) and with symptoms of neuropathic pain (PainDETECT >18) significant decreased after 24 weeks (Figure 2). The use of NSAIDs decreased from 70.8% to 33.8% (p< 0.001), and the use of glucocorticoids decreased from 54.2% to 32.6% (p< 0.001).
Adverse events were noted in 20 (14.7%) of patients, with 3 serious AEs: dysfunctional uterine bleeding -1 (0.5%), shoulder phlegmon -1 (0.5%), and perforated duodenal ulcer -1 (0,5%). The result of the vast majority of AEs, including serious ones, was recovery or their resolution.
Conclusion: Olokizumab significantly reduces RA activity and chronic pain intensity. The analgesic effect of olokizumab may be associated not only with an anti-inflammatory effect, but also with a positive effect on the nociceptive system dysfunction.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karateev A, Kuzkina S, Togizbayev G, Polishuk E, Filatova E, Amirdzhanova V, Khlaboshchina V, Lapkina N, Baranov A, Lila A. Olokizumab Effect on Chronic Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results of the Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/olokizumab-effect-on-chronic-pain-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-of-the-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/olokizumab-effect-on-chronic-pain-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-of-the-observational-study/