Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster III: Treatment and Classification Criteria
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Novel Classification Of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Based On Distinctive Features And Autoantibodies: Analysis Of 67 Korean Patients
Background/Purpose: Since Bohan and Peter first described their diagnostic criteria for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) in 1975, new discoveries such as myositis-specific and myositis-associated autoantibodies (Abs) have been made.
To investigate correlations between specific myositis Abs and their frequencies and clinical associations across different IIM groups, collectively demonstrating the utility of the new clinicoserologic classification in Korean adult patients with IIM.
Methods: We conducted a multicenter cohort study including 67 adult patients (age¡Ã18 years) who have been diagnosed as IIM by ENMC criteria. Immunoblot assay with Euroline strip (EUROIMMUN, Germany) was performed using the sera of definite deramatomyositis (DM, n=36), definite polymyositis (PM, n=25), amyopathic DM (n=4), DM sine dermatitis (n=1), and immune mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM, n=1). Patients were classified based on three classifications: 1) novel clinicoserologic classification suggested by Troyanov et al. in 2017. 2) 2017 EULAR/ACR classification criteria. 3) 2004 European neuromuscular center (ENMC) criteria. Associations of myositis Abs and clinical subsets of IIM were investigated.
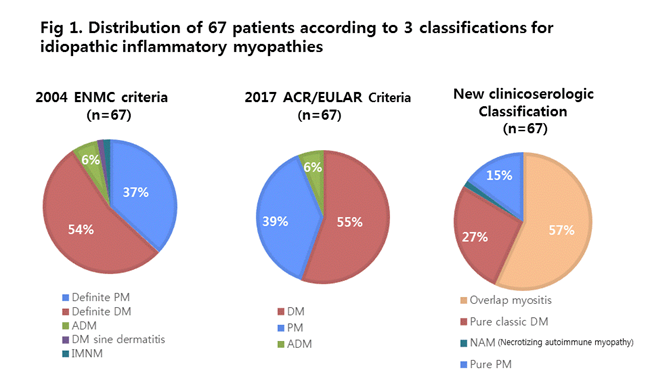
Results: The distribution of the various IIM differed strikingly from those using the 3 classifications (Fig 1). According to the 2004 ENMC classification and 2017 EULAR/ACR classification criteria, DM and PM was the most and the second frequent entities (DM: 55.2%, 56.7 %; PM: 35.8%, 37.3%). But, using the new clinicoserologic classification, overlap myositis (OM) is the major type of IIM and the frequency of PM is significantly decreased. Anti-ARS Abs specificity included anti-Jo-1(16.4%), -OJ(4.6%), -EJ(6.2%) -PL-7(3.1%), and -PL-12(4.6%). Interstitial lung disease was closely associated with anti-MDA5, and anti-ARS Abs, while DM-specific skin lesion was frequently observed in patients with anti-TIF1¥ã and anti-ARS Abs. Seven patients with cancer-associated DM were identified. They were positive for anti-TIF¥ã (5/7) and anti-SRP (3/7) (table 1).
Conclusion: Novel classification based on distinctive features and new myositis Abs reflects the clinical phenotype of IIM better. Establishment of a system routinely available to screen myositis Abs is needed. This will be beneficial to provide more precise diagnosis and proper management for patients with IIM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chung SW, Yoo SJ, Kang SW, Yoo IS, Shim SC, Kwon M, Joung CI, Kim J, Hong SJ, Lee YA. Novel Classification of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Based on Distinctive Features and Autoantibodies: Analysis of 67 Korean Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-classification-of-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-based-on-distinctive-features-and-autoantibodies-analysis-of-67-korean-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-classification-of-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-based-on-distinctive-features-and-autoantibodies-analysis-of-67-korean-patients/